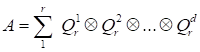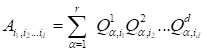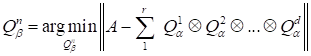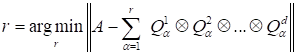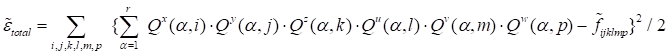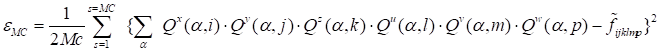The
approximation of the multidimensional functions is of interest in a lot of
applications such as quantum mechanics, solving kinetic equations of the
Boltzmann type, parametric solving of the aerogasdynamic problems.
Consider
function
f(x,y,z,u,v,w)
determined in the domain
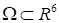 and corresponding the Boltzmann probability
density as the example. It is necessary to store
and corresponding the Boltzmann probability
density as the example. It is necessary to store
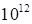 numbers for the grid containing 100
nodes along each coordinate. For the 64-bit number this statement requires the
operative memory 64 TB that corresponds to parameters of the most powerful
modern supercomputers. This circumstance hinders the practical applications of
the Boltzmann equation both from the viewpoint cost and the time of
computations.
numbers for the grid containing 100
nodes along each coordinate. For the 64-bit number this statement requires the
operative memory 64 TB that corresponds to parameters of the most powerful
modern supercomputers. This circumstance hinders the practical applications of
the Boltzmann equation both from the viewpoint cost and the time of
computations.
We
consider the set of numerical solutions for parameter CFD problems as another
example. It is a set of functions
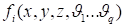 , where
, where
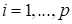 corresponds to the flow
variables (density, velocity components, energy), and
corresponds to the flow
variables (density, velocity components, energy), and
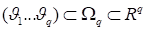 corresponds to the flow
parameters (Mach, Reynolds numbers, angles of attack, etc.). These functions
are defined in five-seven-dimensional spaces for the widespread practical
applications that implies the use of the computational resources similar to above
mentioned ones.
corresponds to the flow
parameters (Mach, Reynolds numbers, angles of attack, etc.). These functions
are defined in five-seven-dimensional spaces for the widespread practical
applications that implies the use of the computational resources similar to above
mentioned ones.
From the
viewpoint of the practical applications, it is desirable to solve these
problems with the computational costs close to resources of the standard
personal computer.
The approximation
of functions in the multidimensional space is very computationally difficult
problem due to exponential growths of required operational memory at increase
of dimensionality (“curse of the dimensionality”). The application of the tensor
forms of the multidimensional problems and their approximation by the tensor
decompositions [1,2,3] is one of the ways to overcome these difficulties. The
present paper id addressed to this problem.
Canonical
decomposition
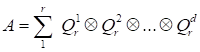 [1,2]
is the most fundamental tensor decomposition
since it determines the rank of the tensor. Herein
[1,2]
is the most fundamental tensor decomposition
since it determines the rank of the tensor. Herein
 is the outer
(tensor) product of vectors having the index form
is the outer
(tensor) product of vectors having the index form
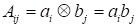 . The canonical decomposition
in the index form is written as
. The canonical decomposition
in the index form is written as
|
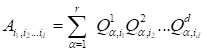
|
(1)
|
This
expression is unique with account the permutation and scaling [4,5].
The memory required in order to
store this approximation of the tensor is about
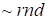 (where
(where
 is the dimension of the space,
is the dimension of the space,
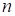 is the number of nodes over one of directions,
is the number of nodes over one of directions,
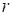 is the tensor rank) (instead the total memory necessary to store the
tensor
is the tensor rank) (instead the total memory necessary to store the
tensor
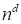 ). The time for the single node calculation
). The time for the single node calculation
 . The canonical decomposition provides the tremendous
compression of the data
(number of grid nodes
used for function approximation in
. The canonical decomposition provides the tremendous
compression of the data
(number of grid nodes
used for function approximation in
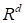 ), that is to say
), that is to say
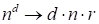 .
.
The
problem for the determination of cores
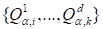 in the variational form has the appearance
in the variational form has the appearance
|
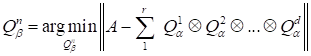 . .
|
(2)
|
The tensor rank
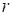 is the key value at application of the canonical
decomposition. In accordance with [1,4] this value is not computable due to the
ill-posedness of the following statement
is the key value at application of the canonical
decomposition. In accordance with [1,4] this value is not computable due to the
ill-posedness of the following statement
|
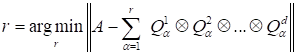 . .
|
(3)
|
The applications of the
canonical decomposition suffers from instabilities and requires a
regularization [1, 4].
Methods for the calculation of the tensor decompositions
may be with certain tolerance subdivided by two subclasses: linear algebra
based methods, for example [3] and variational methods [5] (which are
subdivided by the direct and iterative ones).
The linear algebra based methods significantly depend on
the matrization of the tensors, singular decomposition and contain a lot of
interesting and original algorithms enabling to perform operations directly
over cores without using the approximated functions.
Variational statements usually are based on alternating
least squares (ALS) [6,7], and, as a rule, also apply the matrization of
tensors. Commonly, ALS is realized for the canonical decompositions via the
Khatri Rao
product
(⊙)
[6,7].
Unfortunately, the matrization of the tensor does not
provide its compression and does not relieve the curse of dimensionality.
However, within the frames of the variational approach, one
may construct algorithms that do not apply the matrization of tensors. Herein,
we consider an optimization method including some elements of the alternating
least squares and the stochastic gradient descent. The application of the
special set (“umbrella”), which is used in the optimization, is the specific
feature of the method. This set enables to decompose the goal functional in the
sum of the practically independent functionals. Another feature is the
application of the Tikhonov regularization of the zero order at the estimation
of cores in the gliding over range option. At such approach to the
regularization, the components of cores are affected by the damping that is
proportional to the index of core layer rank.
Formally, the
quality of the approximation of a function by the canonical decomposition at
every step of the global iteration may be estimated using the following
discrepancy (written for 6D).
|
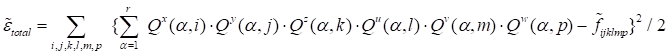 . .
|
(4)
|
Herein,
all nodes of the tensor are used similarly to ALS with the application of the
Khatri-Rao
product.
Unfortunately, for the considered
dimensions, this functional can not be computed (at least, at usual personal
computers) due to tremendous needs for computation time. We numerically
estimated its value using Monte-Carlo method in the form
|
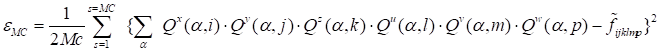 , ,
|
(5)
|
where at every step of
summation
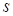 every index from
every index from
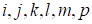 was chosen as the random uniformly
distributed number. In the result, we compute the averaged over the ensemble
sum of the squares of approximation error. The number of tries in the ensemble
is in the range
was chosen as the random uniformly
distributed number. In the result, we compute the averaged over the ensemble
sum of the squares of approximation error. The number of tries in the ensemble
is in the range
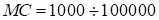 , where the result
relatively weakly changes at the variation of the number of tries.
, where the result
relatively weakly changes at the variation of the number of tries.
Some
alternative is necessary since the functional (4) is practically noncomputable and
functional (5) may be applied to the calculation of cores only in the frame of
the Monte-Carlo method. As such alternative, herein, we apply the special form
of the goal functional, which does not require the great computational efforts and
enables to obtain expressions for the gradient of the goal functional over
cores, which are suitable for the gradient based optimization. In the contrast
to the standard approach based on the
Khatri Rao product, the considered
algorithm is not restricted by the dimensionality (does not applies tensor
matrization or the total set of the tensor nodes) and is significantly simpler
algorithmically.
The special
choice of the ensemble of points used in the optimization is the basic feature
of this algorithm. These points are randomly selected on the hyperplane that is
orthogonal to the coordinate corresponding to the core (on “umbrella”, Fig. 1).
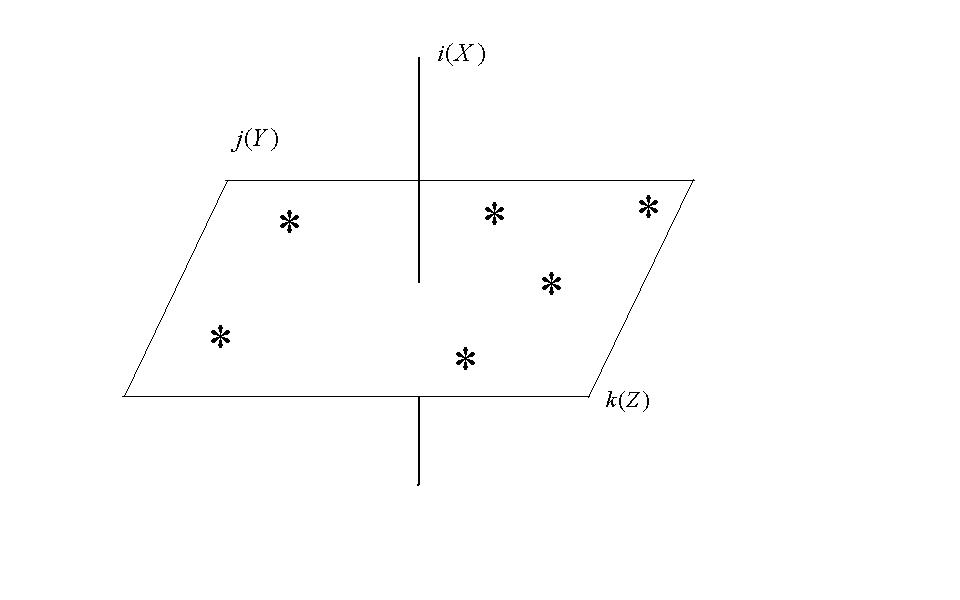
Fig. 1.
The ensemble of points used in the optimization (“umbrella”)
The cores
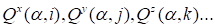 are obtained by the consequent run.
are obtained by the consequent run.
Let’s consider the
algorithm on the example on the core over
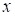 at point
at point
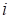 :
:
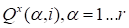 and
corresponding discrepancy
and
corresponding discrepancy
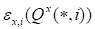 , (other
components of the core
, (other
components of the core
 are
calculated consequently over
are
calculated consequently over
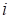 )
)
|
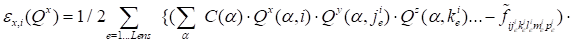
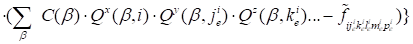 . .
|
(6)
|
The
points of ensemble
 are numbered by the index
are numbered by the index
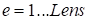 (
(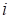 corresponds to the node where the “umbrella” opens.
They are
located on the hyperplane, which is orthogonal to
corresponds to the node where the “umbrella” opens.
They are
located on the hyperplane, which is orthogonal to
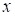 (at point
(at point
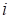 )
and
are selected randomly.
)
and
are selected randomly.
Herein
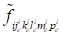 is the exact value of the function at point
is the exact value of the function at point
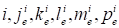 .
.
At
computations, the dimension of the ensemble is much greater the preliminary
estimate of the tensor rank
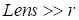 .
The enhancement of the
ensemble dimension increases the computational costs for the discrepancy and
its gradient estimation.
.
The enhancement of the
ensemble dimension increases the computational costs for the discrepancy and
its gradient estimation.
Let’s disturb this core by
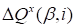 .
Corresponding variation of discrepancy has the
appearance:
.
Corresponding variation of discrepancy has the
appearance:
|
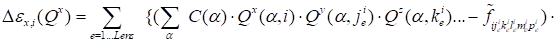
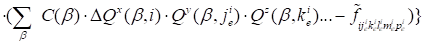 . .
|
(7)
|
Accordingly, the gradient of the discrepancy has the form:
|
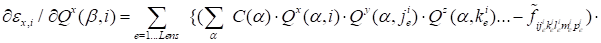
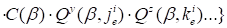 . .
|
(8)
|
For the cross derivatives (over other cores, herein, for example,
over
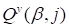 )
in ensemble points
)
in ensemble points
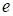 ,
the corresponding expression has the
appearance:
,
the corresponding expression has the
appearance:
|
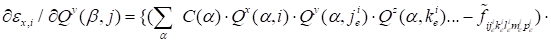
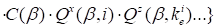 . .
|
(9)
|
at
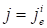 (otherwise- 0). It is important
that the summation over the ensemble disappears. By this reason, such terms are
approximately by
(otherwise- 0). It is important
that the summation over the ensemble disappears. By this reason, such terms are
approximately by
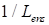 less the main one (8).
Due to this circumstance we neglect these terms that enables to perform the optimization
only over
less the main one (8).
Due to this circumstance we neglect these terms that enables to perform the optimization
only over
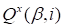 .
.
Thus, instead
single global discrepancy (used in computations for check)
|
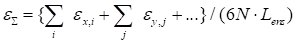
|
(10)
|
we optimize
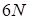 separate
discrepancies (for simplicity, we assume that there is
separate
discrepancies (for simplicity, we assume that there is
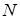 nodes along each coordinate)
nodes along each coordinate)
|
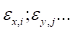 .
.
|
(11)
|
The components of the cores are determined using consequent
optimization of discrepancies over the number of the core and the number of the
node on the core
|
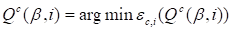
|
(12)
|
The gradient based steepest descent is used for the optimization, for
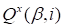 it has the appearance:
it has the appearance:
|
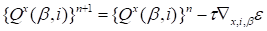 . .
|
(13)
|
The general structure of
the algorithm has the form (circle over cores and their nodes):
|
Algorithm 1.
The search for the cores of the canonical decomposition using steepest
descent
|
|
Input
Initialize
for
 (X,Y,Z,U,V,W)
do ! circle over coordinates
(X,Y,Z,U,V,W)
do ! circle over coordinates
for
i=
 do ! circle over nodes
along core
do ! circle over nodes
along core
The search
of the minimum is realized by the method of the steepest descent
for
 do ! circle over index of rank
do ! circle over index of rank
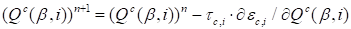
end
for
output
|
Such primitive structure
of the algorithm may be realized because the gradients are approximately
decomposable:
|
 . .
|
(14)
|
with the
tolerance of
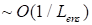 .
The choice of the ensemble of
points that are used for the estimation of the discrepancy functional is the
reason of the
decomposability.
.
The choice of the ensemble of
points that are used for the estimation of the discrepancy functional is the
reason of the
decomposability.
In
the paper the regularization gliding over the index of rank is applied, that is
based on the zero order Tikhonov regularization [9] with the regularizing
coefficient that increases along the rank index
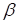 as
as
|
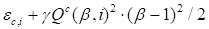
|
(15)
|
Herein
 is the basic regularizing coefficient.
is the basic regularizing coefficient.
Corresponding
iterations has the form:
|
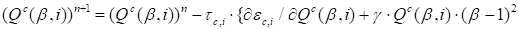
|
(16)
|
The general
optimization is reduced to local consequent optimization over
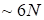 discrepancies.
The values
discrepancies.
The values
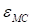 (5) and
(5) and
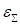 (10) are used
for the control of the convergence.
(10) are used
for the control of the convergence.
The
optimization of the cores components is terminated at
 ,
,
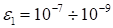 .
The process of
the determination of the canonical decomposition was broken at
.
The process of
the determination of the canonical decomposition was broken at
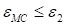 .
.
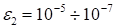 .
.
Let’s consider the
approximation of the six-dimensional function
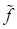 (more strictly
speaking the tensor
(more strictly
speaking the tensor
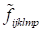 ,
which corresponds the
values of the function at nodes of the regular grid) by the canonical
decomposition and the corresponding set of cores
,
which corresponds the
values of the function at nodes of the regular grid) by the canonical
decomposition and the corresponding set of cores
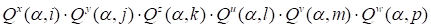 .
.
The grid containing 100
nodes along each coordinate was used in the numerical tests. Formally, the
storage of
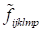 requires
requires
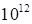 numbers on
this grid that is closely nonrealistic both from the necessary memory and the
computing time. As the illustration one should mark that, at the considered
case, the memory necessary to store cores with the rank 100 (rather great) is
numbers on
this grid that is closely nonrealistic both from the necessary memory and the
computing time. As the illustration one should mark that, at the considered
case, the memory necessary to store cores with the rank 100 (rather great) is
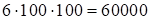 numbers. This illustrates the superhigh data
compression
(
numbers. This illustrates the superhigh data
compression
(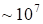 )
at the canonical decomposition.
)
at the canonical decomposition.
At debugging the
comparison of the numerical (obtained by the direct numerical differentiation)
and analytical (obtained using the expression (8)) gradients was performed that
demonstrates their practically perfect coincidence.
The results of
computations provide enough stable and reproducible estimates of errors.
At the first stage the
testing of the approximation of different functions using the canonical
decomposition was performed. The following multidimensional functions were
considered that are arranged in the order of the complexity increasing.
|
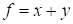
|
(17)
|
It
is utterly simple function, however its rank is not known a priori. 30 iterations
were used and the rank was varied from 1 to 10. The dependence of the
discrepancy value (5) on the rank magnitude is presented in Table 1.
Table
1. The dependence of the discrepancy value (5) on the rank for the function (17).
|
rank
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
10
|
|
discrepancy
|
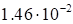
|
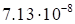
|
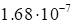
|
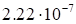
|
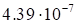
|
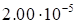
|
The rapid decreasing at
reaching true value of the rank (herein, 2) and slow increasing at further
growth of the rank is specific for the discrepancy. These results demonstrate
that, in general, the discrepancy magnitude may serve as an indicator of the
true rank of the tensor. As the rank increases the noise in the results grows.
We consider this circumstance as an evidence of instabilities occurring due to
the ill-posedness of the canonic decomposition [1,4].
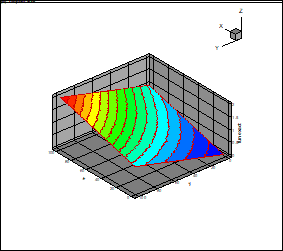
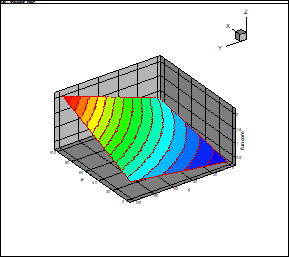
Fig. 2 and 3 provide the
true function (17) and its approximation at rank 2.
|
|
|
|
Fig. 2.
True function
|
Fig. 3. Approximation
via the canonical decomposition
|
Function (17) is
two-dimensional, let’s consider more complex true six-dimensional event
assigned by a Gaussian and a sum of sines along all directions in a form
|
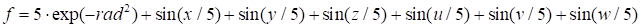
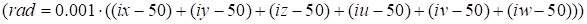 .
.
|
(18)
|
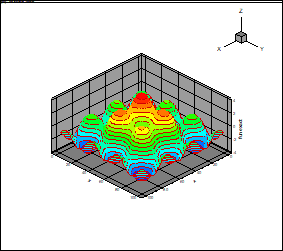
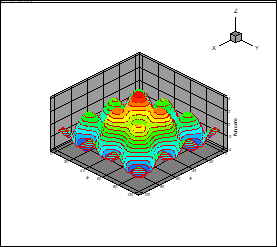
Figs. 4 and 5 present
results for the rank 10 and the ensemble of 1000 points in the plane
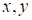 , other variables correspond to the middles of the
intervals at grid dimension 100. The results of approximation practically can’t
be distinguished from the true function. At decreasing of the ensemble
dimension the quality of the approximation deteriorates. In general, at
approximation of enough complex functions, the ensemble should be significantly
greater the a priori estimate of the rank. Fortunately, the application of the
zero order Tikhonov regularization in the gliding option enables to minimize
the current rank and leaves the necessarity of a priori knowledge of the rank
(or running over the ranks).).
, other variables correspond to the middles of the
intervals at grid dimension 100. The results of approximation practically can’t
be distinguished from the true function. At decreasing of the ensemble
dimension the quality of the approximation deteriorates. In general, at
approximation of enough complex functions, the ensemble should be significantly
greater the a priori estimate of the rank. Fortunately, the application of the
zero order Tikhonov regularization in the gliding option enables to minimize
the current rank and leaves the necessarity of a priori knowledge of the rank
(or running over the ranks).).
|
|
|
|
Fig. 4. Exact function (18)
|
Fig. 5. Approximation of
(18) by the canonical decomposition
|
The
Fig. 6 provides the behaviour of the different convergence criteria in the
dependence on the number of iterations. The discrepancies
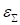 (10) (Eps), the global discrepancy estimated
using Monte-Carlo method
(10) (Eps), the global discrepancy estimated
using Monte-Carlo method
 (5) (Eps_MC) and the norm
of the discrepancy gradient (grad norm) are provided in the logarithmic form.
(5) (Eps_MC) and the norm
of the discrepancy gradient (grad norm) are provided in the logarithmic form.
Fig. 6. Different criteria
of the convergence in the dependence on the number of iterations
Discrepancy
 (10) (Eps) and the global discrepancy estimated
using Monte-Carlo
(10) (Eps) and the global discrepancy estimated
using Monte-Carlo
 (5) (Eps_MC) demonstrate
similar behaviour suitable for the convergence check. The norm of the gradient (grad
norm) is not monotonic at the start iterations that restrict its applicability
as the stopping criterion.
(5) (Eps_MC) demonstrate
similar behaviour suitable for the convergence check. The norm of the gradient (grad
norm) is not monotonic at the start iterations that restrict its applicability
as the stopping criterion.
In general, the considered
approach does not provide the monotonic minimization of the global criteria
since the minimization is performed by points. However, the numerical tests
demonstrate monotonic convergence for the global criteria. The considered
algorithm provides significantly more rapid convergence if compare with one
used by [10].
Really, in the
numerical tests we calculate not the true rank of the function (tensor), but
the approximation of the rank
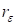 , providing the
discrepancy
, providing the
discrepancy
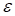 .
Fig. 7 demonstrates that the variant of
the Tikhonov regularization, used in the paper, enables to decrease the
effective rank by increasing regularizing parameter, however, the
regularization qualitatively changes cores.
.
Fig. 7 demonstrates that the variant of
the Tikhonov regularization, used in the paper, enables to decrease the
effective rank by increasing regularizing parameter, however, the
regularization qualitatively changes cores.
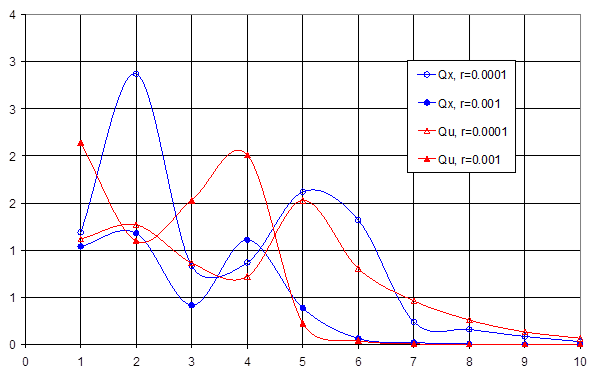
Fig. 7. The
dependence of the discrepancy on the rank for the function (18)
As
an example, we consider the two dimensional steady flowfield in the parameter
space of the dimension from one to three. It corresponds to the case of the
interaction of two supersonic air flow occurring at the flow around two
symmetric edges. The flow structure is described by the steady Mach and regular
modes of the shock waves interaction.
The
Mach number
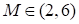 and flow
deflection angles
and flow
deflection angles
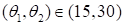 are the
parameters.
are the
parameters.
The ensemble
of the solutions on the same spatial grid with different parameters
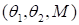 may be considered as the tensor
of the order
may be considered as the tensor
of the order
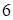 :
:
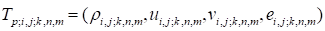 (
(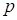 is
the number of the gasdynamical variables,
is
the number of the gasdynamical variables,
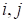 are the indices of the coordinate nodes,
are the indices of the coordinate nodes,
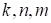 are the numbers of the parameters
are the numbers of the parameters
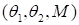 ).
).
Let’s
consider the formation of the canonical decomposition on such ensemble of
solutions that enables the radical compression of the data.
We
construct the canonical decomposition using the structure “umbrella”. One calculation
of the flowfield (elementary “building block”)
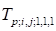 - it
is complete completed tensor of the order 3.
- it
is complete completed tensor of the order 3.
One may
relatively easy to form the tensor of the order 4 using the sequence of the
tensors of the order 3 (by the transition from
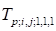 to
to
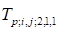 and so on). It
is enough laborious
(
and so on). It
is enough laborious
(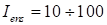 of the
separate computations), but realistic task. However, already at the generation
of the tensor of the order 5 the troubles appear. At the every layer one should
to determine the tensor of the order 4 from the scratch. It is highly laborious
from the computational standpoint and practically impossible for the tensor of
the following rank. So, the additional problem of the tensor completion using
incomplete data arises, which can be considered in the above described
optimization statement with the special selection of the support ensemble of
calculations.
of the
separate computations), but realistic task. However, already at the generation
of the tensor of the order 5 the troubles appear. At the every layer one should
to determine the tensor of the order 4 from the scratch. It is highly laborious
from the computational standpoint and practically impossible for the tensor of
the following rank. So, the additional problem of the tensor completion using
incomplete data arises, which can be considered in the above described
optimization statement with the special selection of the support ensemble of
calculations.
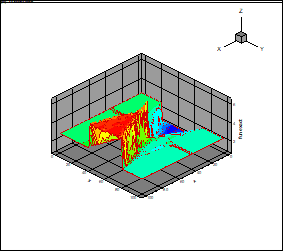
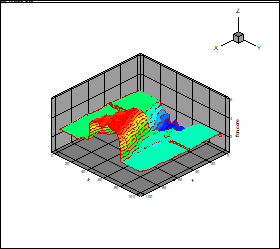
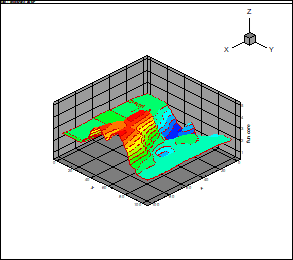
Fig. 8 and 9 provides
the results of the calculation of the flowfield (density) for
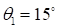 (the deflection of the upper flow),
(the deflection of the upper flow),
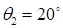 (the deflection of the down flow),
(the deflection of the down flow),
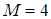 and corresponding approximation
by the canonical decomposition (rank 15, the number of point on the ensemble 2000).
The tensor
and corresponding approximation
by the canonical decomposition (rank 15, the number of point on the ensemble 2000).
The tensor
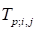 of the order
3 is used. The flow is directed from the right side. The zone of the high
density past crossing shock waves is presented in
the foreground.
of the order
3 is used. The flow is directed from the right side. The zone of the high
density past crossing shock waves is presented in
the foreground.
|
|
|
|
Fig. 8. Density field
calculation
|
Fig. 9. The
approximation of the density field using the canonical decomposition (third
order tensor)
|
The
results presented by Figs. 8 and 9 demonstrate the operationability of the
approximation (compression) of the flowfields using the canonical
decomposition.
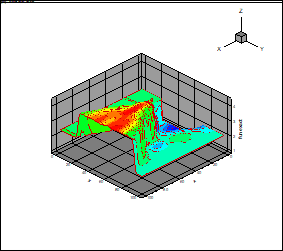
Fig. 10 and 11
present the results of the flow-field computations (density)
(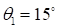 ,
,
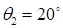 ,
,
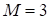 )
and corresponding approximation
using canonical decomposition (rank 3, the number of the points of the ensemble
-200). The tensor of the order 4:
)
and corresponding approximation
using canonical decomposition (rank 3, the number of the points of the ensemble
-200). The tensor of the order 4:
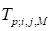 was
used, with five layers on
was
used, with five layers on
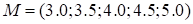 .
.
|
|
|
|
Fig. 10. Density field
calculation
|
Fig. 11. The
approximation of the density field using the canonical decomposition (fourth
order tensor)
|
The results presented in
Figs. 10 and 11 demonstrate the correctness of the approximation (compression)
of the one parameter flowfield using the canonical decomposition. The observed
oscillations of the approximation are possibly related with the ill-posedness
of the determination of the canonical decomposition. There exists some hope
that the quality of the solution may improve after the transition to the tensor
train format.
Due to the
ill-posedness of the problem of the estimation of the cores of the canonical
decomposition [4] the feasibility of the quadratic regularization of the zero
order (Tikhonov [9]) with the gliding regularization is provided. It enables to
compress the approximation of the rank
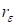 , ensuring the
discrepancy
, ensuring the
discrepancy
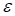 (to obtain the upper estimate of the rank).
(to obtain the upper estimate of the rank).
Tensor
decompositions are enough actively used for the visualization [11], since it
rather easy enable to engender a computable model that approximate the
difficult set of the data in the parameter space. Tensor decompositions
(canonical decomposition, tensor train, hierarchical Tucker) are used for
economic solving of the multidimensional problems such as the Boltzmann
equation [5,13,14]. The tensor train format and the cross-approximation [13]
are rather often used for these purposes. The above considered approach may be
easily expanded to the tensor train format and has no restrictions on the
computer resources specific for the cross-approximation (related with the
matrization of the tensor). The applied herein canonical decomposition enables
efficiently approximate and store the multidimensional functions.
The
computational time for the operations with the functions in the six-dimensional
space (at 100 nodes along every coordinates that formally requires to store and
operate with
 numbers) is about 1-3 minutes on
the personal computer (processor Intel I5, 2.66 GHz) at the required memory for
cores store (maximally) about
numbers) is about 1-3 minutes on
the personal computer (processor Intel I5, 2.66 GHz) at the required memory for
cores store (maximally) about
 numbers.
Some hope exists that the transition to the tensor train format may enable to
overcome part of the canonical decomposition drawbacks related to ill-posedness
and instability.
numbers.
Some hope exists that the transition to the tensor train format may enable to
overcome part of the canonical decomposition drawbacks related to ill-posedness
and instability.
The optimization algorithm for
the determination of the cores in canonical decomposition is offered, which
requires much less memory if compare with the standard methods using the
matrization of the tensor and the Khatri-Rao product. The gliding over rank
regularization is applied in the algorithm, which enables to reduce the
effective rank of the approximation for the sake of the reduction of the norm
of core layers with the higher indexes of ranks.
Numerical tests demonstrate that
the application of the above described algorithm for the realization of the
canonical decomposition enables to store and visualize functions in the
multidimensional space with moderate needs for the memory and the computational
time. This circumstance provides a special interest from the standpoint of
analyzing and treating results of the calculations for the multiparametric
problems of computational fluid dynamics.
1. W. Hackbusch. Tensor Spaces and Numerical Tensor Calculus.
Springer, 2012.
2. H. Yorick, S.
Willi-Hans, Matrix Calculus, Kronecker Product and Tensor Product: A
Practical Approach to Linear Algebra, Multilinear Algebra and Tensor
Calculus with Software I, WOS 2019
3.
Oseledets
I. V., Tensor- train decomposition, SIAM J. Sci. Comput., 33 (2011), pp.
2295–2317
4.
V. D. Silva
and L -H. Lim, Tensor rank and the ill-posedness of the best low rank
approximation problem, SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl., 30(3) 1084-1127, 2008.
5.
A. M. P.
Boelens, D. Venturi, D. M. Tartakovsky, Parallel tensor methods for high-dimensional
linear PDEs, J. Computat. Phys. 375 (2018) 519-539.
6.
Shuangzhe
Liu, Gaotz Trenkler, Hadamard, Khatri-Rao, Kronecker and other matrix products,
Int. J. Information and system Scienses, 2008, Volume 4, Number 1, Pages
160-177
7.
P. Comon, X. Luciani, and A.L.F. De Almeida, Tensor
decompositions, alternating least squares and other tales, Journal of
Chemometrics, vol. 23, no. 7-8, pp. 393–405, 2009.
A.
Uschmajew, Local convergence of the alternating least squares algorithm for
canonical tensor approximation, SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 33 (2) (2012)
639–652,
8.
S.
Rabanser, O. Shchur, S. Gunnemann, Introduction to Tensor Decompositions and
their Applications in Machine Learning, arXiv:1711.10781v1, 2017
9. Tikhonov, A.N.,
Arsenin, V.Y.: Solutions of Ill-Posed Problems. Winston and Sons,
Washington DC (1977).
10.
A.K. Alekseev,
A.E. Bondarev, Yu.S. Pyatakova,
On the visualization of multidimensional functions using canonical
decomposition, Scientific Visualization, 2022, volume 14, number 3, pages 73 -
91
11.
Yannis
Panagakis, Jean Kossaifi, Grigorios G. Chrysos, James Oldfield, Mihalis
A. Nicolaou, Anima Anandkumar and Stefanos Zafeiriou, Tensor Methods in
Computer Vision and Deep Learning, arXiv:2107.03436v1, 2021
12.
Oseledets I., Tyrtyshnikov
E., TT-cross approximation for multidimensional arrays, Linear Algebra Appl.,
432 (2010), pp. 70–88.
13.
Arnout M. P.
Boelens, Daniele Venturi, Daniel M. Tartakovsky, Tensor methods for the
Boltzmann-BGK equation, arXiv:1911.04904v2 2020
14.
A.V.
Chikitkin, E.K. Kornev, V.A. Titarev, Numerical solution of the Boltzmann
equation with S-model collision integral using tensor decompositions,
arXiv:1912.04582v1 2019