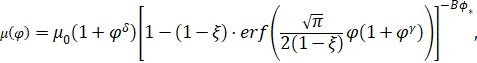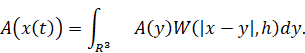During volcanic eruptions,
the spread of lava flows poses a significant risk to nearby communities, homes,
and infrastructure. In effusive eruptions, a lava flow begins to form when
molten rock erupts onto the Earth’s surface and slowly spreads across the
surface from a volcanic vent. Thus, various gravitational flows arise,
depending on the chemical composition and temperature of igneous rocks, the
quantitative content of crystals in the lava, and also on the topography of the
surface along which the lava flows [1, 2]. Making timely lava flow forecasts
is
critical
for volcano monitoring and emergency
management during volcanic
eruptions [3].
The core of the procedure
is
the
creation of
mathematical lava flow models
for
prediction of
combination of lava flow direction, velocity,
propagation, and duration of dangerous lava flows.
Modern HPC
hardware and software
allows carrying
out computer
experiments to obtain a numerical solution of such mathematical models [4].
Although thermal effects play an important role in the flow of lava flows,
simplified isothermal analytical and numerical models have demonstrated how
lavas flow in the absence of cooling [2, 5].
A key requirement for
computer code for lava flow simulation is that it must be able to provide
timely forecasts in real time, that is, during a real natural process. At
present, numerical simulation of viscous fluid flows is widely used in the
study of volcanic processes and plays an important role in understanding the
dynamics, morphology, and thermal evolution of lava flows [6]. In the past few
decades, a new class of meshless SPH methods
has been
developed
as an alternative to traditional mesh-based methods.
The
method considers
a continuous medium
discretization
by
a set of particles that move freely along the characteristics of the advection
equation. Thus, it is natural to consider the equations of dynamics of a
continuous medium in Lagrangian coordinates, and after discretization, partial
differential equations for determining the speed, location, temperature, and
other characteristics of the medium are transformed into ordinary differential
equations for the evolution of each particle. The number of such differential
equations corresponds to the number of particles in the discretization of the
problem. SPH methods are used for mathematical modeling of lava flows due to
the fact that this approach is able to describe a free surface flow, a
multicomponent medium (namely, a multiphase gas-liquid-solid medium).
As a spreading surface, we
use the generated topography, which is a realistic slope of a mountainous area,
formed taking into account natural geological processes. Numerical simulation
is carried out using the meshless SPH method. The results of several model
cases of lava flows over the surface are presented.
Mathematical model
The
process
of
spreading
of a viscous inhomogeneous incompressible Newtonian fluid under gravitational
force will be used to describe the lava flow
motion.
The
mathematical model
for such process
is
outlined
by the
Navier-Stokes equation and the continuity equation, which in Lagrangian
coordinates have the form
|
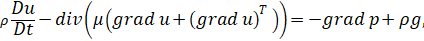
|
(1)
|
|
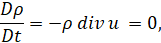
|
(2)
|
with the initial
condition:
 (0,
(0,
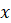 ) =
) =
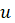 0
(
0
(
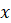 ), where
), where
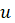 (
𝑡,
(
𝑡,
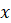 ) = (
𝑢1,
𝑢2,
𝑢3)
is the
velocity vector,
) = (
𝑢1,
𝑢2,
𝑢3)
is the
velocity vector,
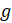 = (0, 0, −9.81) is the
acceleration vector due the gravitational force,
𝑝(𝑡,
= (0, 0, −9.81) is the
acceleration vector due the gravitational force,
𝑝(𝑡,
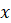 ) is the pressure,
𝜌(𝑡,
) is the pressure,
𝜌(𝑡,
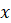 ) is the lava density,
𝜇(𝑡,
) is the lava density,
𝜇(𝑡,
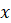 ) is the dynamic lava viscosity,
𝑡
is the time,
) is the dynamic lava viscosity,
𝑡
is the time,
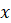 =
=
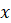 (𝑡) =
(𝑢1, 𝑢2, 𝑢3)
is the
characteristic of the advection equation
(𝑡) =
(𝑢1, 𝑢2, 𝑢3)
is the
characteristic of the advection equation
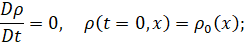
𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑑
and
𝑑𝑖𝑣
are the
gradient and divergence operators, respectively.
We assume that the viscosity of lava depends on
the volume fraction of crystals [7, 8]
|
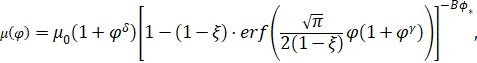
|
(3)
|
where
𝜑
=
𝜙
/
𝜙∗,
𝜙
∈
[0, 1] is the
volume fraction of crystals and
𝜙∗
is the specific
value of the volume fraction of crystals;
𝜇 0
is is the
specific lava viscosity factor,
𝐵
is the theoretical value
of the Einstein coefficient (it has been experimentally established that the
Einstein coefficient ranges from 1.5 to 5 [9]);
𝛿
= 7.24,
𝛾
= 5.76 and
𝜉
= 4.63 ×
10
−4; erf(
⋅) is the error
function.
Any melt consists of a
liquid phase, gas and solid crystals, which tend to an equilibrium state. The
volume fraction of crystals is determined from the evolution equation
describing the simplified kinetics of the crystal growth during the
crystallization due to magma degassing
|
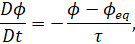
|
(4)
|
with the initial condition
𝜙(𝑡
= 0,
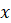 ) = 0. Here
𝜙𝑒𝑞
is the volume
fraction of crystals in the equilibrium state, which depends on the amount of
the water dissolved in the magma and on temperature;
𝜏
is the crystal
growth time. The smaller
𝜏,
the faster the
crystallization process converges to its equilibrium state.
) = 0. Here
𝜙𝑒𝑞
is the volume
fraction of crystals in the equilibrium state, which depends on the amount of
the water dissolved in the magma and on temperature;
𝜏
is the crystal
growth time. The smaller
𝜏,
the faster the
crystallization process converges to its equilibrium state.
As a spreading surface, we
use the generated topography
𝐺
(see the figure 1), which
is a realistic slope of a mountainous area, formed considering natural
geological processes. At this surface the viscous friction condition is
satisfied:
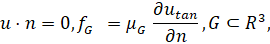
where
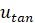 is the projection of the velocity vector
onto the tangent plane at the points of
𝐺,
is the projection of the velocity vector
onto the tangent plane at the points of
𝐺,
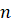 is the normal vector to some surface. A
volcanic crater (vent) with a diameter of 30 meters has been formed on this
surface, in which a particle emitter is located, which generates particles with
a constant boundary velocity
is the normal vector to some surface. A
volcanic crater (vent) with a diameter of 30 meters has been formed on this
surface, in which a particle emitter is located, which generates particles with
a constant boundary velocity
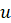 =
=
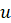 𝑐
and the volume
fraction of crystals
𝜙
=
𝜙𝑐.
𝑐
and the volume
fraction of crystals
𝜙
=
𝜙𝑐.
The
values
of
initial
parameters of a particle
that leaves
a crater
are
presented
in the table 1. These parameters correspond to the average
values of eruptions with basaltic lavas.
Table 1. Initial
parameters of a particle emerging from a crater
|
Parameter
|
Value
|
Dimension
|
|
Density
|
𝜌0
= 2600
|
𝑘𝑔
⋅
𝑚−3
|
|
Boundary viscosity
|
𝜇𝐺
= 1010
|
𝑃𝑎
⋅
𝑠
|
|
Volume of cristal’s fraction
|
𝜙𝑐
= 0.4
|
|
|
Specific value of the volume fraction of crystals
|
𝜙∗
= 0.384
|
|
|
Equilibrium state of the crystal
|
𝜙𝑒𝑞
= 0.83
|
|
|
Crystal growth time
|
𝜏
= 3 × 3600 × 24
|
sec
|
|
Velocity magnitude
|
|u𝑐| = 0.01
|
𝑚
⋅
𝑠−1
|
SPH method of the model
approximation
In the SPH approach, a continuous medium is represented as a
set of
𝑁
particles
interacting with each other under the application of various forces
F.
According to (1), Newton’s law is valid for each particle. The particle with
the number
𝑖(𝑖
= 1, ...,
𝑁)
at the moment
of time
𝑡
is located at
the point
x𝑖(𝑡),
moves at the
velocity
v𝑖(𝑡)
and has
physical values, namely the pressure
𝑝𝑖|, mass
𝑚𝑖,
density
𝜌𝑖,
viscosity
𝜇𝑖,
volume
fraction of crystals
𝜙𝑖.
The influence
of a single particle on the properties of a liquid is estimated in accordance
with the distance from it to the point of interest. Discrete particles have a
characteristic radius
ℎ
> 0 (sometimes this
parameter is called the distance of influence of a particular particle on its
neighbors). In the direction of increasing distance of influence, the
properties of the particle are smoothed using a symmetric kernel function
𝑊.
That is, the
approximation of the value of a physical quantity A at the coordinate
x(𝑡)
has the form:
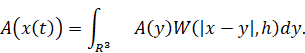
Integration (1) by volume
𝑉𝑖
=
𝑚𝑖
/
𝜌𝑖
allows us to
write Newton’s second law for the i- th particle in the form
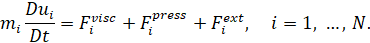
Mathematical justification
and implementation of the SPH method are described in [10].
The
software
for this numerical experiment
have been
developed
with
SPlisHSPlasH,
an open-source
C++
library for the physical modeling of
liquids. The main features of the package are described in [11]. To simulate
lava dynamics,
software
was written
with
consideration of
variable viscosity,
also
changes were
made to the solver pressure
calculation stage,
and kinetics of crystal
growth and viscosity
have been added.
The calculations were
implemented on a personal computer running OS Ubuntu 14.10 without the use of a
GPU. Parallelization is based on the OpenMP interface, which is designed for
programming multithreaded applications on multiprocessor systems with shared memory.
Surface topography
Several test scenes were
generated to simulate lava flow. One of the scenes represents a section of a
mountain surface created in the Wold Machine package [12]. This scene has
sections of steep and gentle descents for expert assessment of the correctness
of the flow behavior under various conditions, as well as formed active and
inactive craters. Hydro- and wind- erosion parameters characteristic of
Hawaiian-type volcanoes was used for formation. An example of such a surface is
shown in figure 1.
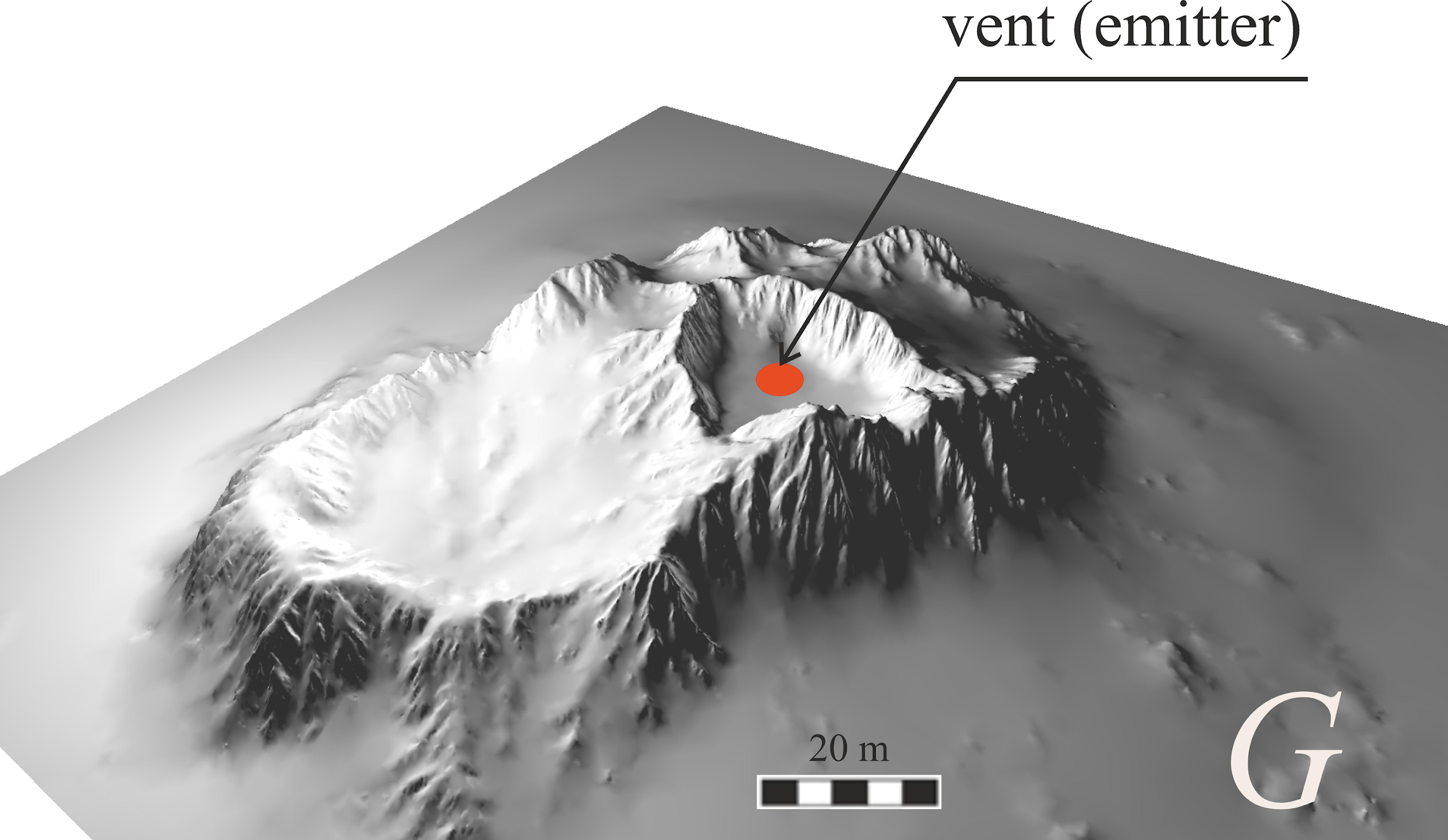
Figure 1:
Artificial lava flow surface, generated
considering the features inherent in Hawaiiantype volcanoes
To organize a
computational experiment, it is necessary to set the following initial data for
calculations:
•
Topography of
the area over which lava flows will spread;
•
Eruptive input
conditions: volumetric velocity of lava extrusion, geometry of the vent from
which lava will erupt;
•
Boundary
condition on topography and interaction of lava with the environment along its
free boundary;
•
Physical
properties of lava: the density, crystal contents, rheology.
Computational
experiments were carried out for the specific lava viscosity factor
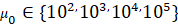 𝑃𝑎
⋅
𝑠
on the time
interval [0; 2.5 × 106]
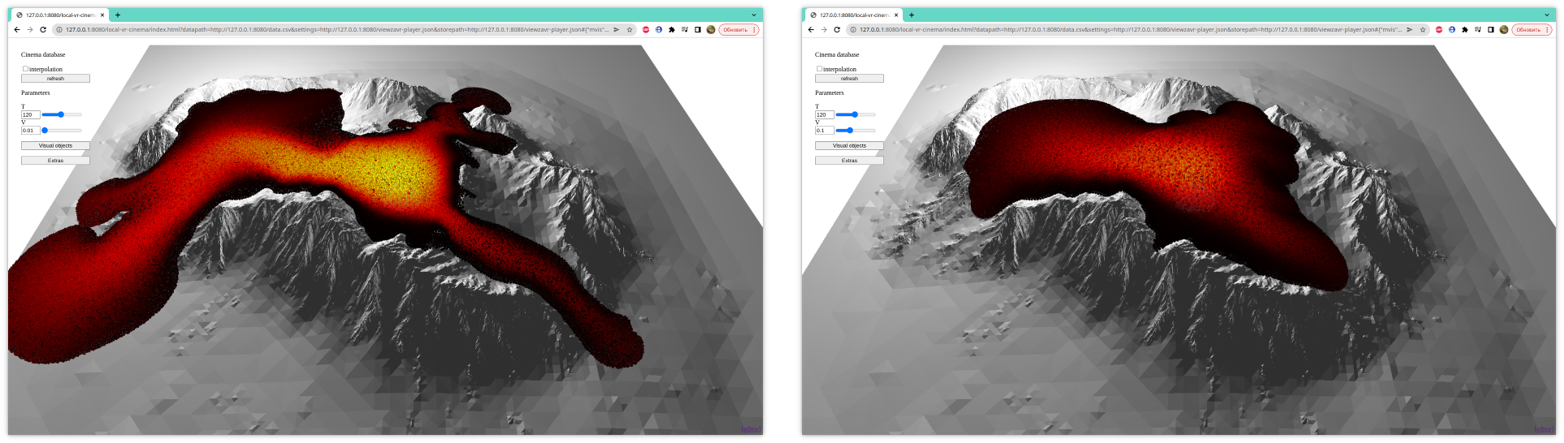
sec. The figures 2 show results of
numerical simulations.
𝑃𝑎
⋅
𝑠
on the time
interval [0; 2.5 × 106]
sec. The figures 2 show results of
numerical simulations.
|
|
|
(a)
𝜇0
= 102
|
(b)
𝜇0
= 103
|
|
|
|
(c)
𝜇0
= 104
|
(d)
𝜇0
= 105
|
|
|
Figure 2:
The figure shows the dynamics of lava spreading
with dynamic viscosity depending on the level of crystals in the melt according
to the formula (3) at the time moment 2.5 × 106
sec.
In addition to the
numerical calculations themselves, there was also the task of visualizing the
results of the simulation. This task is relevant, since the visual method for
evaluating the results of numerical modeling is very common in volcanology. The
following aims were set for visualization:
•
Show the
dynamics of lava spreading over time;
•
Within one
visualization, show the results of several series of calculations with
different initial parameters;
•
Show the
internal structure of the lava flow.
The first aim is of
primary interest to an expert volcanologist, since it allows one to
qualitatively assess the dynamics of spreading and the morphology of the
resulting dome, and thus assess the overall “quality” of the simulation. The
second aim is born from the frequent impossibility of specifying the exact
values of the initial lava parameters. According to indirect data, a
volcanologist can indicate parameters in a certain range. Therefore, a frequent
request is the variation of some of the modeling parameters in one of the
directions. The third aim is more ‘cosmetic’, as many rendering packages allow
to slice object with a plane. To assess the dynamics of the distribution of
some parameter (for example, the level of crystals or the distribution of
relict particles) in space, a larger number of such slices may be required.
An approach
to
3D
visualization developed at the Krasovskii Institute [13]
has
been
chosen as the
main
visualization tool. It was based on
CinemaScience [14]. It allows a custom 3D visualization to be programmed using
simple CSV file [15]. In this file, which describes a table in a text format,
three things are defined:
1.
a
list of parameters,
2.
a
list of visual artifacts, including their types,
3.
a
mapping between parameters values and artifact files.
Both parameters and visual
artifacts are abstract to CinemaScience approach. The following model is used:
when user selects some parameters values in graphical interface, a
corresponding visual artifact files are loaded and presented in 3D space. Thus
a wide range of visualizations may be programmed, including time-based.
To solve the first of two
visualization aims defined above, the paradigm of describing the results of
calculations in the CinemaScience format is perfect, since it allows to
represent each variable condition as a visualization parameter. For the stated
visualization task, a CSV file of the following form was generated. An example
of such a file is shown in the table 2.
Table 2. An example of the CSV file for the
stated visualization task
|
T,
|
ViscoStep,
|
FILE_vtkpoints_lava,
|
FILE_obj_vulkan,
|
FILE_obj_emmiter
|
|
4,
|
10e2,
|
10e2/ParticleData_4.vtk,
|
vulk.obj,
|
emit.obj
|
|
5,
|
10e2,
|
10e2/ParticleData_5.vtk,
|
vulk.obj,
|
emit.obj
|
|
|
|
…
|
|
|
|
4,
|
10e3,
|
10e3/ParticleData_4.vtk,
|
vulk.obj,
|
emit.obj
|
|
5,
|
10e3,
|
10e3/ParticleData_5.vtk,
|
vulk.obj,
|
emit.obj
|
|
|
|
…
|
|
|
|
4,
|
10e4,
|
10e4/ParticleData_4.vtk,
|
vulk.obj,
|
emit.obj
|
|
|
|
…
|
|
|
|
1999,
|
10e5,
|
10e5/ParticleData_1999.vtk,
|
vulk.obj,
|
emit.obj
|
•
There
are two parameters defined,
T
and
ViscoStep. While the first one
is a simulation time step, the second one is the computational parameter
representing viscosity. We put into one CSV file the results of series of
computations with different
ViscoStep.
•
There
are three visual objects defined,
𝐹𝐼𝐿𝐸_𝑣𝑡𝑘𝑝𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑠_𝑙𝑎𝑣𝑎,
𝐹𝐼𝐿𝐸_𝑜𝑏𝑗_𝑣𝑢𝑙𝑘𝑎𝑛
and
𝐹𝐼𝐿𝐸_𝑜𝑏𝑗_𝑒𝑚𝑖𝑡𝑡𝑒𝑟.
The first one
has ‘type’
𝐹𝐼𝐿𝐸_𝑣𝑡𝑘𝑝𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑠,
which
corresponds to VTK file format [16]. The latter two have type
𝐹𝐼𝐿𝐸_𝑜𝑏𝑗,
which
corresponds to the OBJ file format.
•
An
input file for
𝐹𝐼𝐿𝐸_𝑣𝑡𝑘𝑝𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑠_𝑙𝑎𝑣𝑎
visual object
changes when parameters
(𝑇
and
𝑉𝑖𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑆𝑡𝑒𝑝)
change. Input
files for
𝐹𝐼𝐿𝐸_𝑜𝑏𝑗_𝑣𝑢𝑙𝑘𝑎𝑛
and
𝐹𝐼𝐿𝐸_𝑜𝑏𝑗_𝑒𝑚𝑖𝑡𝑡𝑒𝑟
do not change.
We create a directory
where we put the CSV file of the structure presented above, among with
referenced data files. Then we run a visualization system which loads that
file. From the first line of CSV file, it determines parameters and artifacts.
Graphical controls are generated for all parameters. Their values, selected by
a user, determine current input files for visual objects.
These
visual objects are displayed in 3D scene, and user might change
the
position of
the camera, zoom in and out, so on. Thus, user navigates both in geometry space
using a camera
and in parameter space by
selecting
a
current combination of parameter values.
As stated above,
a
user
is free to select any available combination of parameter values. For example,
a
user
may slide among some
parameters
(T
or
ViscoStep)
while keeping other
parameters
constant.
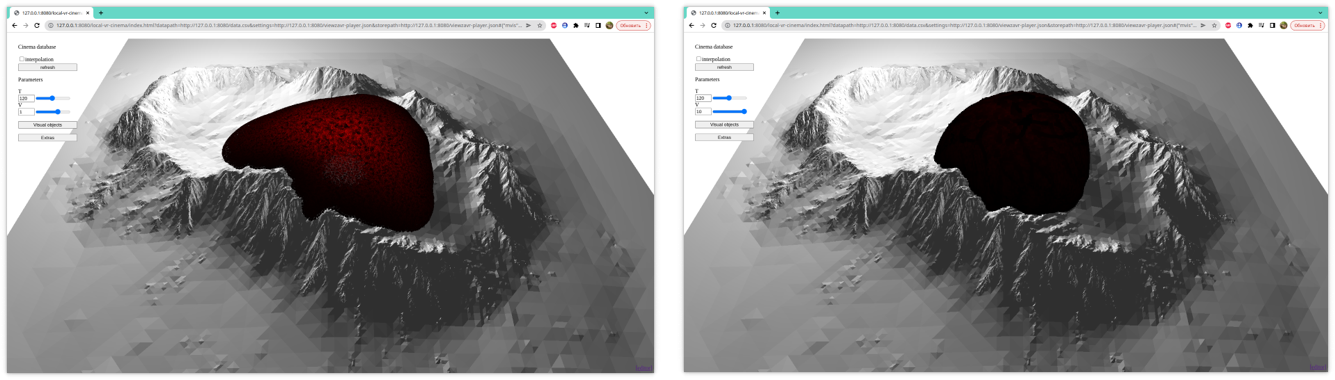
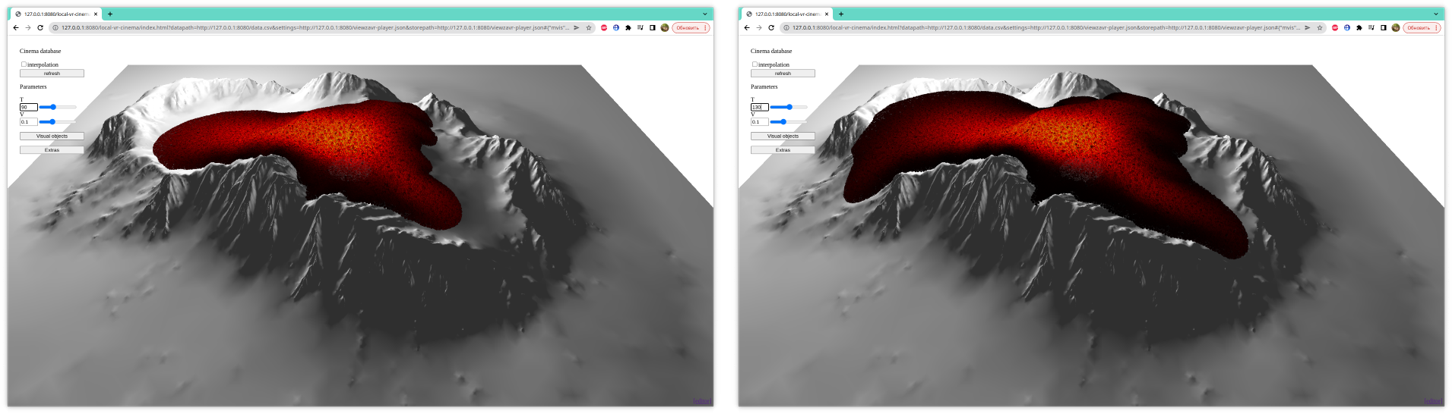
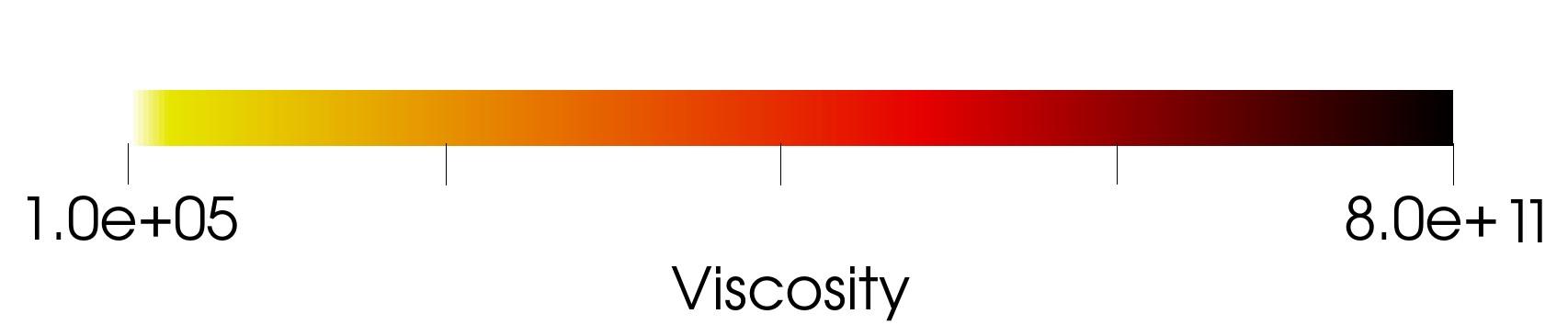
The figure 2 shows
different initial calculation parameters (variation of the initial viscosity
parameter) for a fixed time parameter. On the contrary, the figure 3 shows the
spreading dynamics at different moments of time for a fixed parameter
𝜇0.
|
|
|
(a) 1 hour;
|
(b) 8 hours;
|
|
|
|
(c) 25 hours;
|
(d) 36 hours;
|
|
|
Figure 3:
The dynamics of lava spreading with dynamic
viscosity depending on the level of crystals in the melt according to the
formula (3) with viscosity
𝜇0
= 103
at
different times
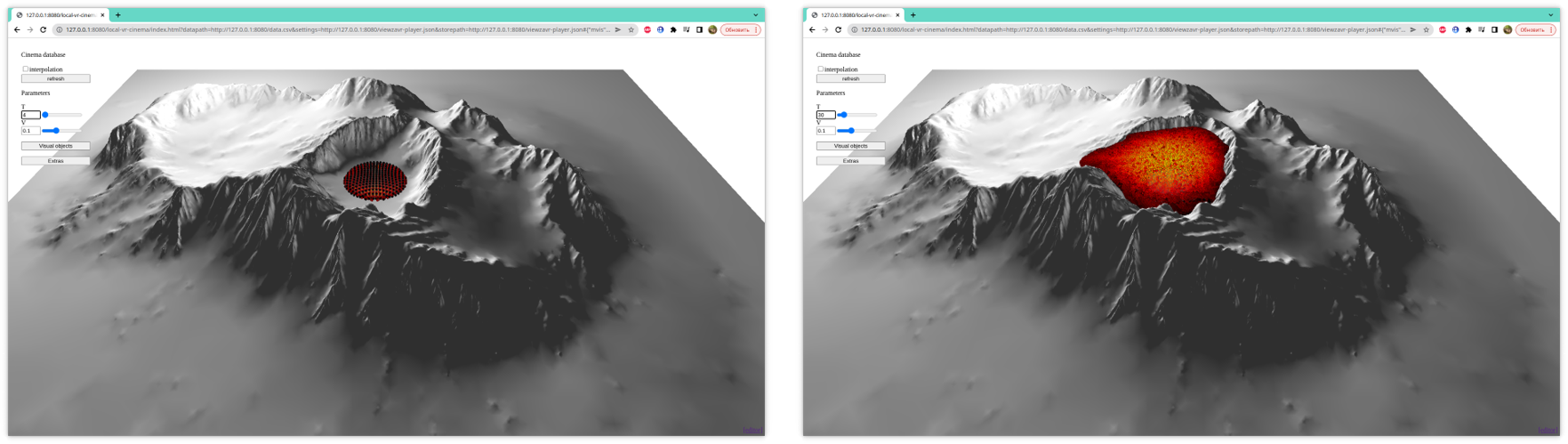
The last aim was achieved
by using sets of “modifiers” – relatively simple scripts that allow to modify the
behavior of the scene. The figure 4 shows the Clip serie modifier, which allows
to make a regular set of sections parallel to the plane and with a given
thickness. This makes it possible to evaluate the distribution of parameters
within the flow over the entire volume, simultaneously.
Summarizing, using the
CinemaScience 3D approach for scientific visualization, we got the following
results:
Firstly, thanks to the
simple description of the scene in CSV format, we are able to display
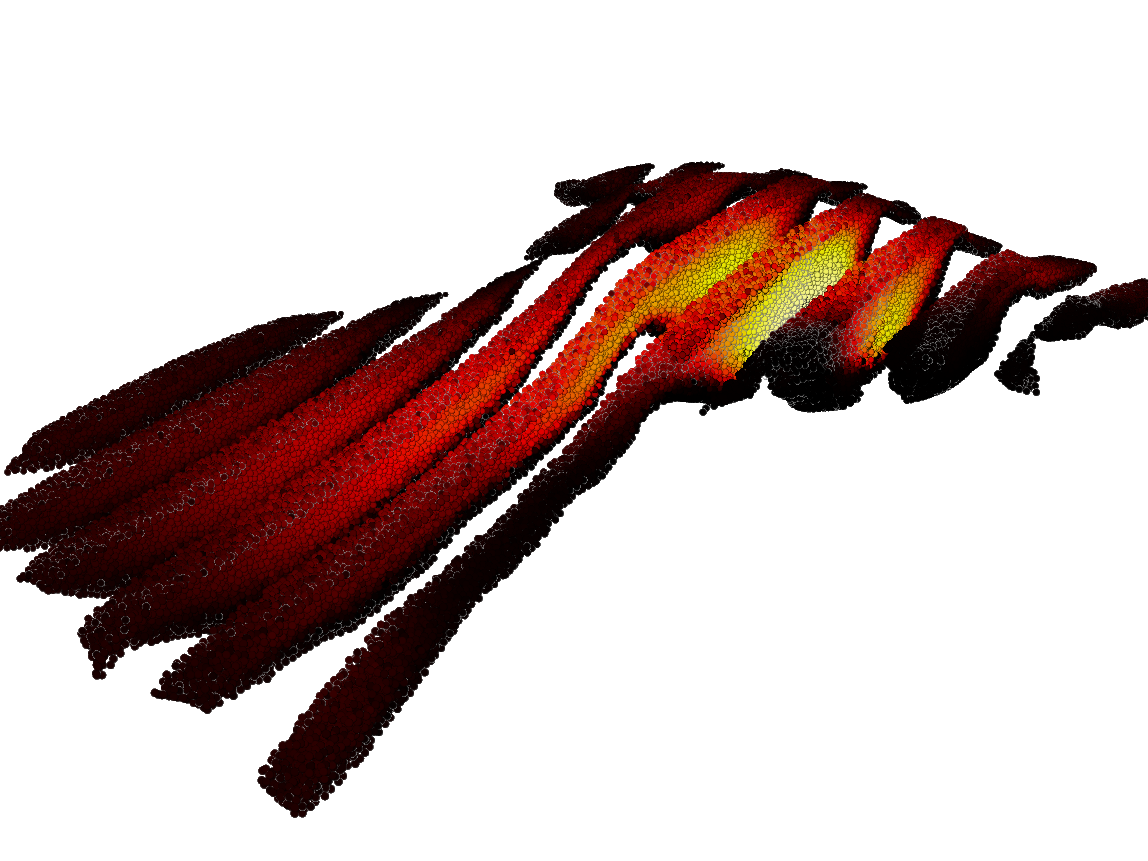
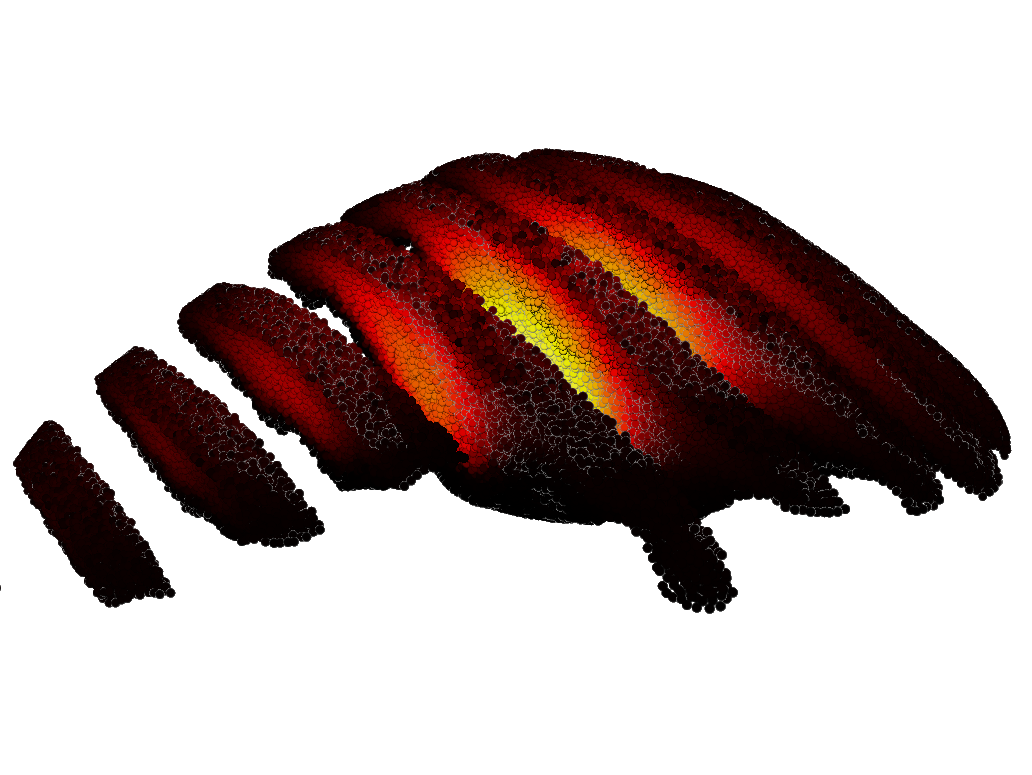
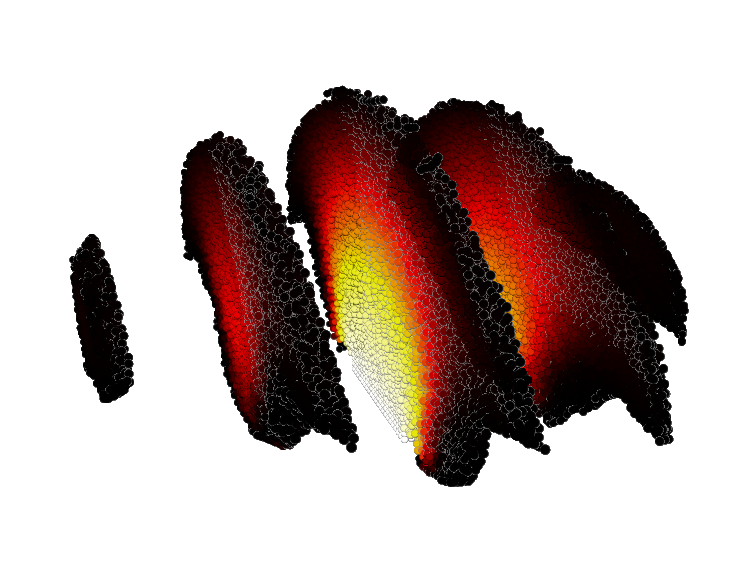
Figure 4:
The figure shows a lava flow sliced with the Clip
serie modifier. The color indicates the fraction of crystals, from 0.6 (yellow)
to 0.8 (black).
(a)
clearly shows the formation of a “channel” of the
flow, during which the lava adhering to the surface thickens and forms a
trough.
(b)
shows how a solid crust is formed and a relatively liquid
flow underneath, which can lead to the formation of lava “tubes” or cracking of
the crust.
(c)
shows the formation of a lava dome with hard crust, which
is formed during the outflow of highly viscous lava several computational
results corresponding to the same model time in one scene. Thus,
both static
time slices and animated sequences can be displayed, that
is very
important for retrospective and comparative analysis. So, we can specify the
calculation parameters as a visualization parameter and view the progress of
the simulation process for different computational processes at one point in
time.
Secondly, the description
of the scene is not static and may change during the visualization process.
This makes it possible to build the complex of online visualization. When new
numerical results appear, new entries are added to the scene description. This
allows the researcher to monitor the progress of the simulation and, if
necessary, make changes to the model parameters or stop the calculations
without waiting for the end of the numerical simulation. This is important
because it can significantly save computing time. Another advantage of online
visualization is the ability to process results directly from the
supercomputer’s storage, without the need to move all amounts of data.
And thirdly, the use of
the modifiers system allows you to quickly create the necessary types of
displays, including filters and additional entities that allow
a
full exploration of
a
visual object.
So, the Clip serie modifier described above allows you to literally cut a point
cloud into plates of the required thickness and with a convenient step,
literally with one click, which allows you to see the internal structure of the
flow.
The stated visualization
task also might be solved in universal visualization systems, for example in
Paraview [17]. However, we prefer CinemaScience-based approach. It allows
defining
scene
dynamics using CSV file syntax and simple semantics.
In a current
task the
required dynamics is simple. The corresponding state of the lava flow is shown
by selecting
𝑇
and
𝑉𝑖𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑆𝑡𝑒𝑝
value. In
ongoing tasks, it may be more sophisticated. Even current dynamics is not easy
to implement in ParaView. It allows
importing
series of files
and play animations among them. Thus, to emulate our solution, user may
manually open different groups of VTK files, each for different
𝑉𝑖𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑆𝑡𝑒𝑝,
and manage
their visibility by turning them on and off. However, this is usable only for
small amount of different
𝑉𝑖𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑆𝑡𝑒𝑝𝑠.
To program
more sophisticated dynamics, some kind of programmable filter will be required.
It definitely requires more efforts than generating a CSV file.
We
believe the creation of
CinemaScience 3D import plugin for Paraview
can
allow getting the
best of two
software
solutions.
Another problem of Paraview is an absence of required visual
modifiers, exactly Clip series modifier.
It
can
be implemented
using programmable filter in Paraview. In our system we implemented this
modifier using OpenGL shaders, adding it to user library of available
modifiers.
A
three-dimensional model of lava flow evolution was considered under the
assumption that the lava viscosity depends only on the volume fraction of
crystals, and this fraction, in turn, depends on the characteristic time of
crystal growth. Lava flows are modeled using the SPH method. The visualization
of the numerical results was performed using CinemaScience 3D approach. Using
the visualization tool compatible with that approach, various slices of lava
flows were examined. The distribution and formation of crystals were analyzed
depending on the initial viscosity. This information is used for short-term and
long-term forecasts of the eruption of real volcanoes by employees of volcanological
observatories.
It is also necessary to
add that, although the above results were obtained on synthetic data, they are
as close as possible to real data. Now, numerical simulations are being carried
out on real topologies obtained by satellite scanning.
The
research described here was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic
Research and DFG (grant no. 20-51-12002). During the work, the supercomputer
“Uranus” IMM URO was used RAS.
The authors are grateful
to Alik Ismail-Zadeh and Alexander Korotkii for their help in developing the
mathematical model.
[1]
R. W.
Griffiths, The dynamics of lava flows, Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics 32
(2000)
477–518. doi:
10.1146/annurev.fluid.32.1.477.
[2]
I. Tsepelev, A.
Ismail-Zadeh, O. Melnik, A. Korotkii, Numerical modeling of fluid flow with
rafts: An application to lava flows, Journal of Geodynamics 97 (2016) 31–41.
doi:
10.1016/ j.jog.2016.02.010.
[3]
A.
Ismail-Zadeh, K. Takeuchi, Preventive disaster management of extreme natural
events, Natural Hazards 42 (2007) 459–467. doi:
10.1007/s11069-006-9075-0.
[4]
V. Zago, G.
Bilotta, A. Hérault, R. A. Dalrymple, L. Fortuna, A. Cappello, G. Ganci,
C. Del Negro, Semi-implicit 3d sph on gpu for lava flows, Journal of Computa
tional Physics 375 (2018)
854–870. URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/
S002199911830593X.
doi:
10.1016/j.jcp.2018.07.060.
[5]
H. E. Huppert,
The propagation of two-dimensional and axisymmetric viscous gravity currents
over a rigid horizontal surface, Journal of Fluid Mechanics 121 (1982) 43–58.
doi:
10.1017/S0022112082001797.
[6]
B. Cordonnier,
E. Lev, F. Garel, Benchmarking lava-flow models, in: Detecting, Modelling and
Responding to Effusive Eruptions, Geological Society of London, 2016. doi:
10.1144/ SP426.7.
[7]
A. Costa, L.
Caricchi, N. Bagdassarov, A model for the rheology of particle-bearing
suspensions and partially molten rocks, Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems 10
(2009).
doi:
10.1029/2008GC002138.
[8]
A.-M. Lejeune,
P. Richet, Rheology of crystal-bearing silicate melts: An experimental study at
high viscosities, Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 100 (1995)
4215–4229.
doi:
10.1029/94JB02985.
[9]
D. J. Jeffrey,
A. Acrivos, The rheological properties of suspensions of rigid particles, AIChE
Journal 22 (1976) 417–432. doi:
10.1002/aic.690220303.
[10]
I.S.
Starodubtsev, I.A.Tsepelev, The numerical modeling of lava dome evolution at
volcán de colima using vof and sph methods, Computational Continuum
Mechanics 15 (2022)
263–273. doi:
10.7242/1999-6691/2022.15.3.20.
[11]
Splishsplash,
2022. URL:
https://splishsplash.readthedocs.io/en/2.9.0/about.html,
accessed:
2022-11-14.
[12]
W. M. S. LLC,
World machine, 2022. URL:
https://www.world-machine.com,
accessed:
2022-11-14.
[13]
P. Vasev, S.
Porshnev, M. Forghani, D. Manakov, M. Bakhterev, I. Starodubtsev, An experience
of using cinemascience format for 3d scientific visualization, Scientific
Visualization 13 (2021) 127 – 143. doi:
10.26583/sv.13.4.10.
[14]
J. Ahrens, S.
Jourdain, P. O’Leary, J. Patchett, D. H. Rogers, M. Petersen, An image-based
approach to extreme scale in situ visualization and analysis, in: SC ’14:
Proceedings of the International Conference for High Performance Computing,
Networking, Storage and Analysis, 2014, pp. 424–434. doi:
10.1109/SC.2014.40.
[15]
Y.
Shafranovich, Common format and mime type for comma-separated values (csv)
files., RFC 4180 (2005) 1–8. URL:
http://dblp.uni-trier.de/db/journals/rfc/rfc4100-4199.html,
accessed:
2022-11-14.
[16]
W. Schroeder,
K. Martin, B. Lorensen, The Visualization Toolkit–An Object-Oriented Approach
To 3D Graphics, fourth ed., Kitware, Inc., 2006.
[17]
J. Ahrens, B.
Geveci, C. Law, ParaView: An End-User Tool for Large Data Visualization,
Visualization Handbook, Elsevier, 2005.
You can take a look at the
ViewZavr project (which is an implementation of the described approach) and
example scenes via
https://github.com/viewzavr/vr-cinema