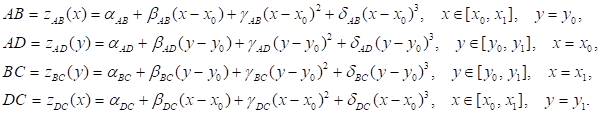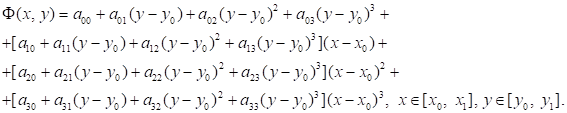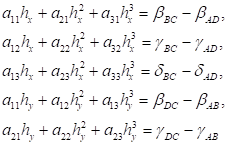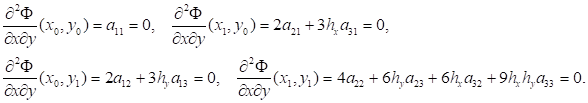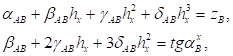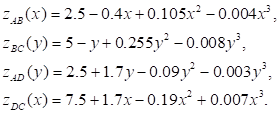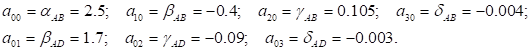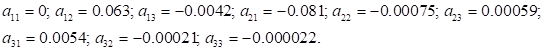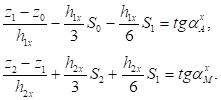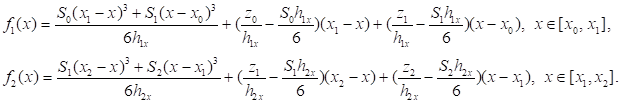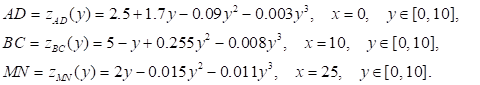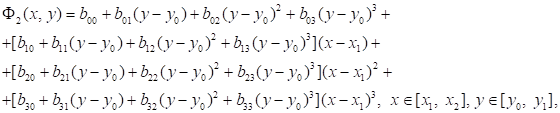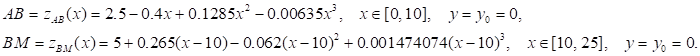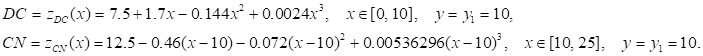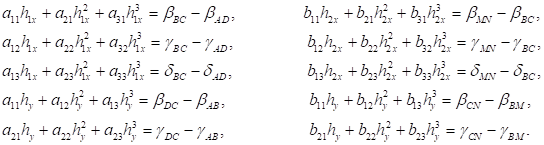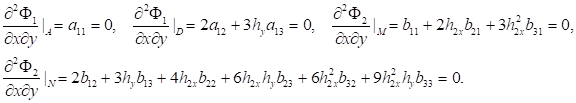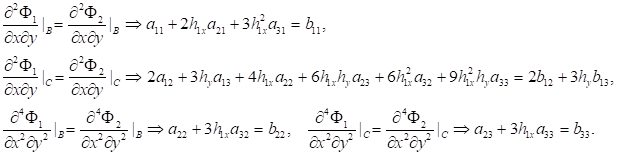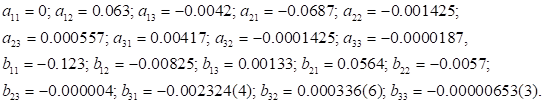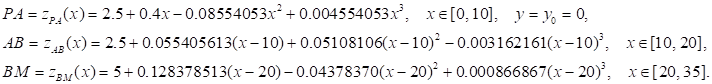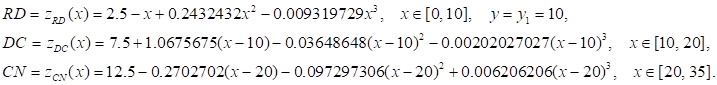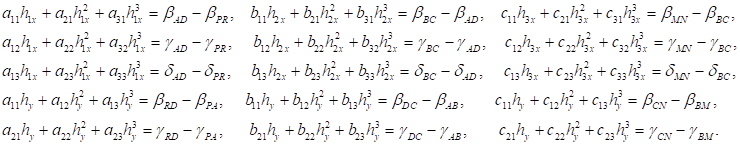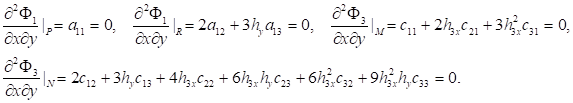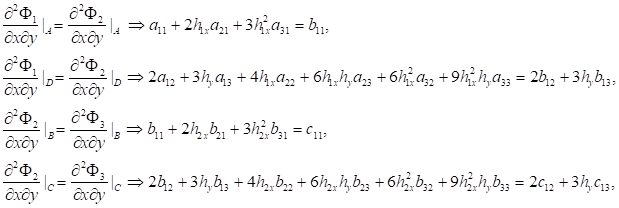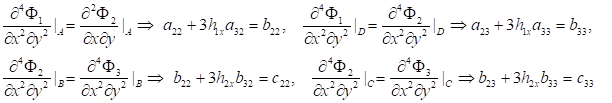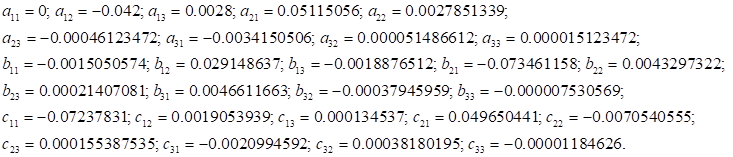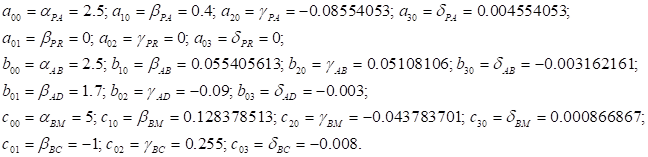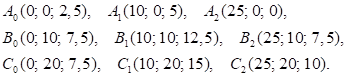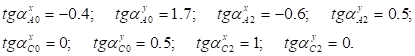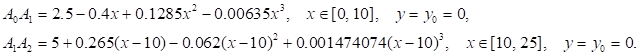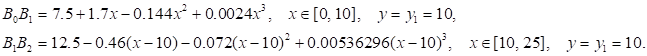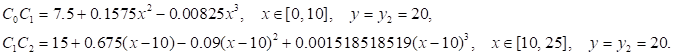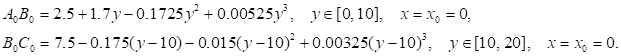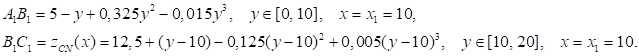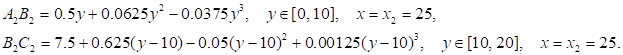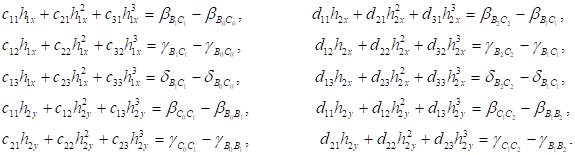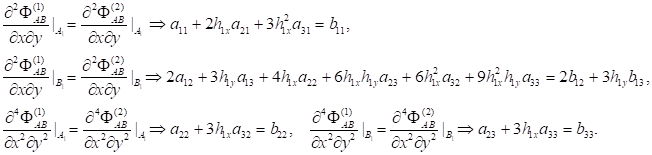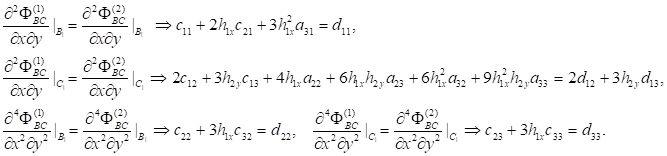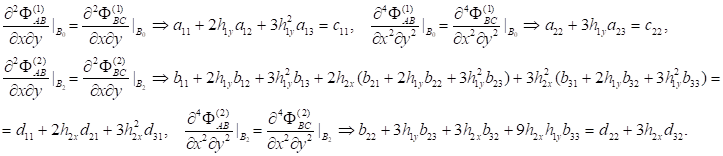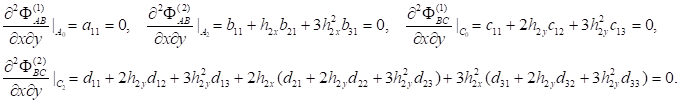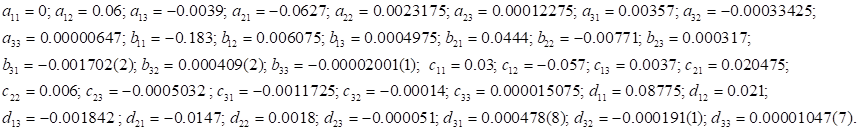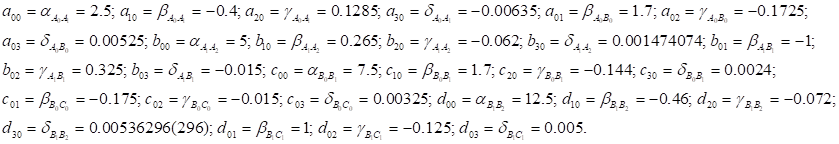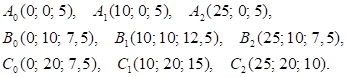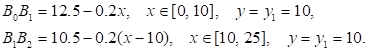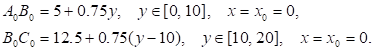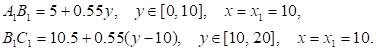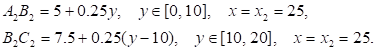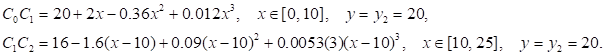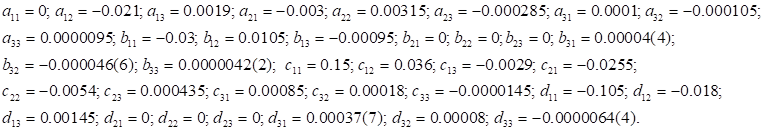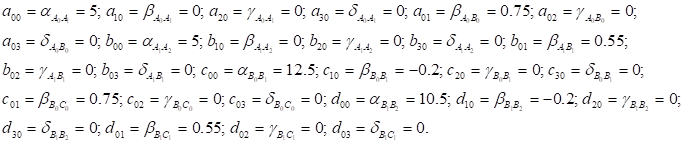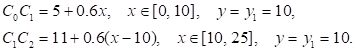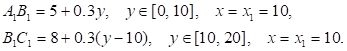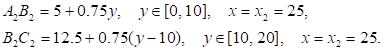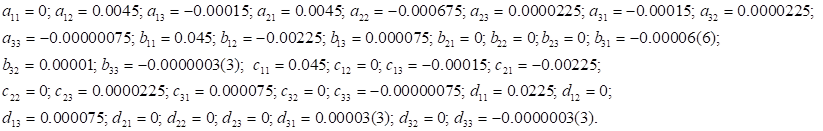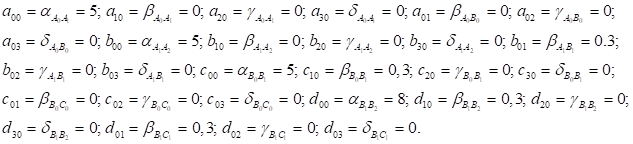A bicubic surface is formed by
bicubic portions
|
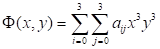 , ,
|
(1)
|
bounded by the cells of a rectangular grid
on the
xy
plane of the Cartesian coordinate system
Oxyz. Portions
(1) are interconnected and have a preset degree of smoothness.
The equation of each portion
contains 16 coefficients, which are determined based on the incidence,
smoothness, and boundary conditions. The surface on the
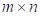 grid
consists of
mn
bicubic portions of form (1), each of which is determined
by its own set of 16 coefficients
aij. The calculation of the
coefficients is reduced to solving the system of linear algebraic equations
with a 16
mn
square characteristic matrix. For example, a system of 64
linear equations must be solved to calculate the coefficients of the equation
of a surface formed by four bicubic portions.
grid
consists of
mn
bicubic portions of form (1), each of which is determined
by its own set of 16 coefficients
aij. The calculation of the
coefficients is reduced to solving the system of linear algebraic equations
with a 16
mn
square characteristic matrix. For example, a system of 64
linear equations must be solved to calculate the coefficients of the equation
of a surface formed by four bicubic portions.
Scientific novelty.
The paper proposes an
algorithm which can nearly halve (from 16
mn
to 9
mn) the size of
the characteristic matrix. As opposed to known algorithms, the constructed
surface is considered as a set of longitudinal (elongated along the
x-axis)
bicubic tapes connected in the transverse direction with C2
smoothness (with continuous changes in curvature when crossing the common
boundary of the two tapes). Each tape is formed from sequentially connected
bicubic portions. We formulated and proved the algebraic conditions of C2-smooth
bicubic tape connection.
Practical significance.
Composite surfaces are often
modeled in modern architecture when designing structures with sufficient
spatial freedom. In particular, the search for new non-linear forms has led to
the appearance of “tent architecture” [1] and “fold architecture” [2], which
use overlaps with complex curvilinear outlines. If a constructed surface has no
large gradients relative to a base plane
xy, bicubic polynomials in the
scalar values
x, y
can be effectively used to model it [3, 4, 5].
A rectangular grid
 is marked on the
xy
plane. Points
with different elevations are indicated in the nodes of this grid. The angular
and boundary points have gradients (the slope angles of the constructed surface
to the
xy
plane) in the longitudinal (along the
x
axis) and
transverse (along the axis) directions. It is required to form a rectangular C2-smooth
surface with given gradients passing through the specified points. The C2
smoothness means a continuous (without “jumps”) change in the surface curvature
at any point and in any direction [6, 7].
is marked on the
xy
plane. Points
with different elevations are indicated in the nodes of this grid. The angular
and boundary points have gradients (the slope angles of the constructed surface
to the
xy
plane) in the longitudinal (along the
x
axis) and
transverse (along the axis) directions. It is required to form a rectangular C2-smooth
surface with given gradients passing through the specified points. The C2
smoothness means a continuous (without “jumps”) change in the surface curvature
at any point and in any direction [6, 7].
We will construct a surface from
bicubic portions of form (1) bounded by the cells of the rectangular grid
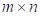 ,
where
m, n
are positive integers.
At
m=n
=1, we obtain a bicubic portion. At
m
≥2 and
n
=1,
we obtain a bicubic band. At
m=n
=2, we obtain the simplest compound
bicubic surface.
,
where
m, n
are positive integers.
At
m=n
=1, we obtain a bicubic portion. At
m
≥2 and
n
=1,
we obtain a bicubic band. At
m=n
=2, we obtain the simplest compound
bicubic surface.
Note.
A bicubic band is a rectangular-plan
surface elongated along the
x
axis, formed by a set of bicubic portions
interconnected by transverse joints (with C2
smoothness).
A rectangular cell is marked on
the
xy
plane of the Cartesian coordinate system
xyz, where
hx
=
x1
-
x0,
hy
=
y1
-
y0
(Fig. 1).
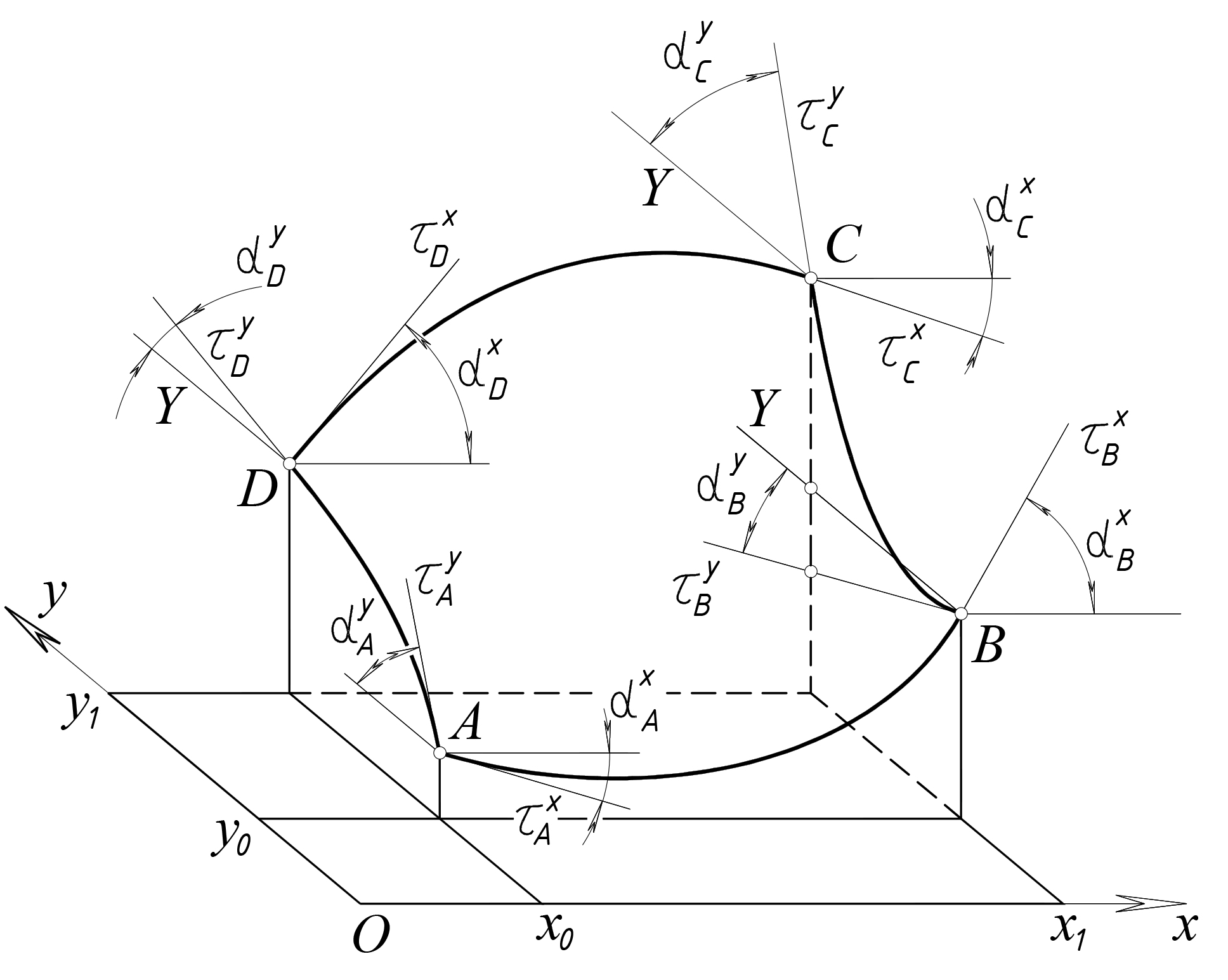
Fig. 1. Boundary conditions
The angular points
A(x0,
y0,
zA),
B(x1,
y0,
zB),
C(x1,
y1,
zC),
D(x0,
y1,
zD) are
specified and the equations of boundary curves (cubic parabolas) are given:
|
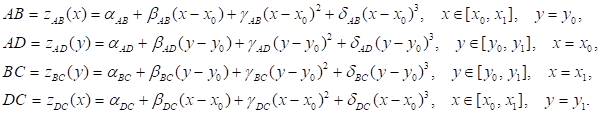
|
(2)
|
The free term of the cubic
parabola equation is hereinafter denoted by letter
α, and the
coefficients at the increasing degrees of the argument are denoted by letters
β,
γ, δ,
respectively. The subscripts indicate the boundary points
of the relevant parabolas. It is required to find the equation of the bicubic
surface (portion) Ô(x, y) =
ABCD
“stretched” along the given
boundary curves.
The expanded equation of bicubic
portion (1) is:
|
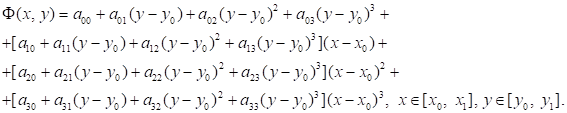
|
(1à)
|
Assuming that
y
=
y0,
we isolate the equation of boundary curve
AB
from (1a):
|

|
(3)
|
Equating the coefficients
included in the first equation from (2) and the coefficients included in
equation (3), we obtain:
|
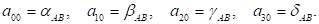
|
(4)
|
Similarly, assuming that
x
=
x0,
we isolate the equation of boundary curve
AD
from (1a) and equate the
coefficients at the identical degrees of the variable
y:
|
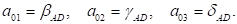
|
(5)
|
Assuming that
x
=
x1,
we isolate the equation of boundary curve
BC
from (1a). Assuming that
y
=
y1,
we isolate the equation of boundary curve
DC
from (1a). Equating the
coefficients of the obtained equations with the relevant coefficients from (2)
and taking into account (4), (5), we obtain the system of five linearly independent
equations
|
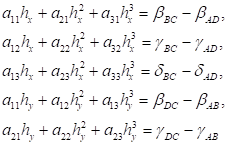
|
(6)
|
with respect to nine coefficients
a11,
a12,
a13,
a21,
a22,
a23,
a31,
a32,
a33.
Note.
Isolating the equations of the cubic
parabolas
BC, AD
from (1a) and equating the coefficients of these
equations to the relevant coefficients from (2) while taking into account (4)
and (5), we obtain not five, but six linear equations. We can show that any of
these six equations results from the five remaining equations so one equation,
namely
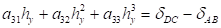 ,
is neglected.
,
is neglected.
Four boundary conditions should
be specified to determine the nine unknown coefficients included in (6). The
“plane angles” conditions can be taken as additional boundary conditions: the
first mixed derivatives of function (1a) are equal to zero at the angular
points of the constructed bicubic portion [8]. Differentiating (1a) and
equating the first mixed derivatives to zero, we obtain:
|
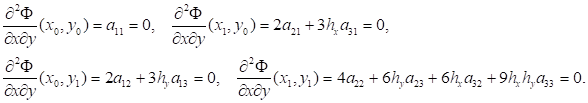
|
(7)
|
We find the coefficients
a11,
a12,
a13,
a21,
a22,
a23,
a31,
a32,
a33
from the system of equation (6), (7). The remaining seven coefficients of
equation (1a) are calculated according to (4), (5). The problem is solved.
Note.
Whereas bicubic portion is set
by the angular points
A, B, C, D
and the gradients (the slope angles of
the tangents
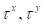 at the angular points), equations (2) of the
segment boundaries are determined by a simple calculation [9, 10]. For example,
if the slope angles
α
x
A,
α
x
B
of the tangents
at the angular points), equations (2) of the
segment boundaries are determined by a simple calculation [9, 10]. For example,
if the slope angles
α
x
A,
α
x
B
of the tangents
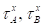 are set at the finite points of
boundary curve
AB(see Fig. 1), the coefficients
γAB,
δAB
included in the equation of this curve are
calculated from the system of equations
are set at the finite points of
boundary curve
AB(see Fig. 1), the coefficients
γAB,
δAB
included in the equation of this curve are
calculated from the system of equations
|
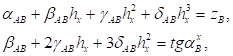
|
(8)
|
where
αAB
=
zA,
βAB
=
tgα
x
A. The
equations of other boundaries are determined similarly.
Example 1
We are given the coordinates of
the angular points
A(0; 0; 2,5),
B(10; 0; 5),
C(10; 10;
12,5),
D(0; 10; 7,5). Gradients are fixed at the angular points (see
Fig. 1):
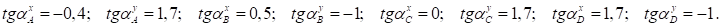
The boundary plane angles conditions (the
first mixed derivatives are equal to zero at the angles of the portion) are
additionally accepted. We must find equation (1a) of the bicubic portion
satisfying the conditions of the problem.
Solution
Substituting the values
hx
=
hy
=10
and the coordinates of points
A, B
in (8), we find the coefficients of
the equation of boundary curve
AB. Similarly, calculating the
coefficients of the equations of boundary curves
AD, BC
and
DC,
we obtain:
|
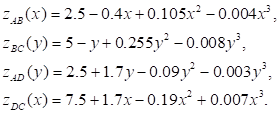
|
(9)
|
Substituting the coefficients of
equations (9) into (4), (5), we obtain:
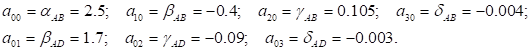
The remaining coefficients
included in (1a) are found from the system of equations (6), (7):
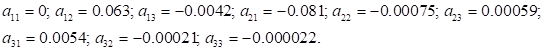
We determined all the
coefficients of equation (1a). Figure 2 shows the grid of generators of the
bicubic portion
BCD
constructed according to (1a).
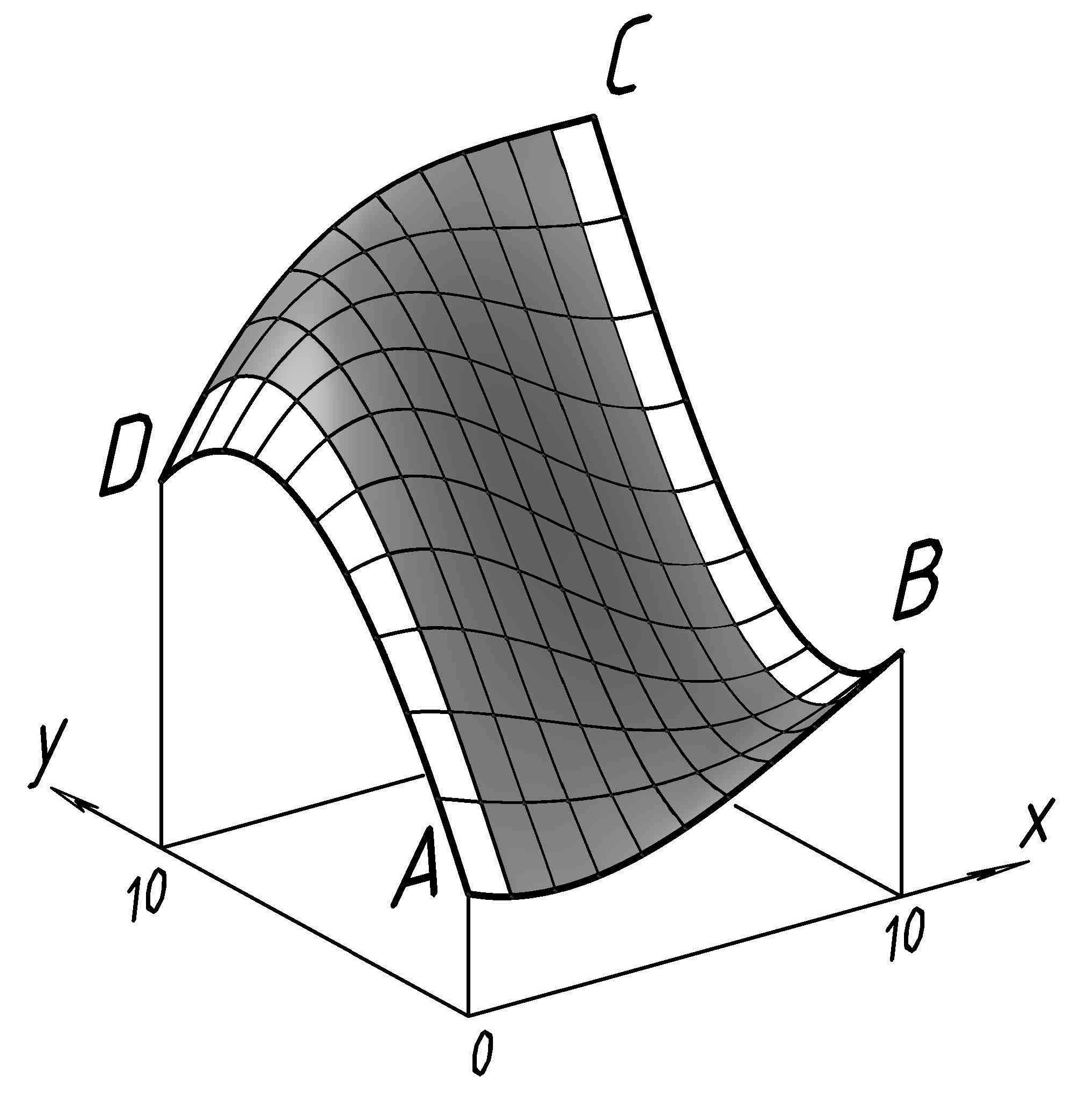
Fig. 2. Bicubic portion
A bicubic band consists of
series-connected (with C2
smoothness) bicubic portions. The bicubic
portions
ABCD
and
BMNC
must be connected along the joint
BC(Fig. 3).
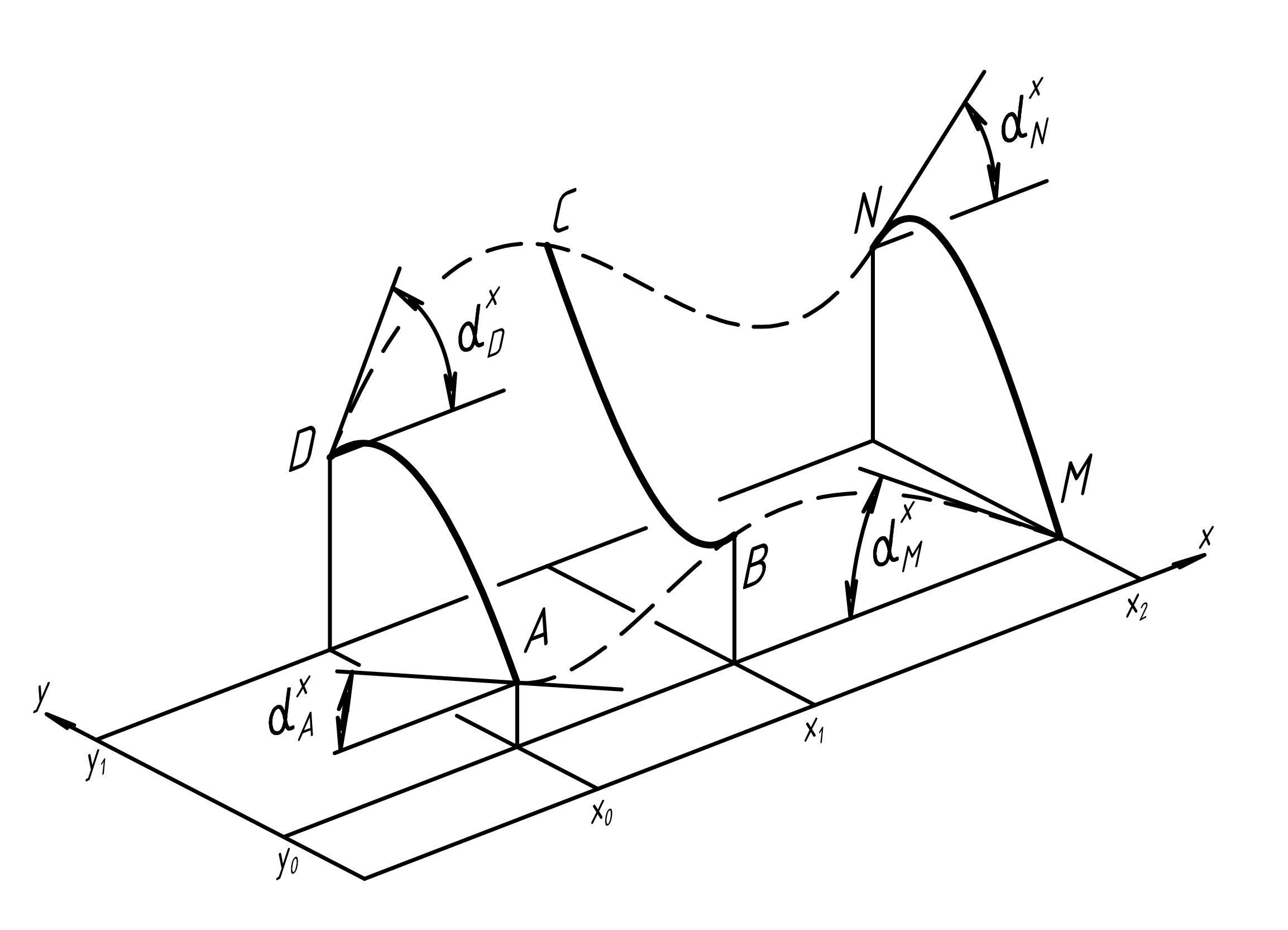
Fig. 3.
Connection of
bicubic portions (Theorem 1)
Let us show that C2
smoothness is achieved if the longitudinal boundaries of the band are C2-smooth
and the first and second mixed derivatives at the junction points
B, C
of the connected portions are equal.
Theorem 1.
To achieve C2-smooth
connection of the bicubic portions Ô1
(x,
y)=
ABCD
and Ô2
(x,
y)=
BMNC
along the transverse joint
BC,
it is sufficient to ensure that the longitudinal boundaries
ABM
and
DCN
are C2-smooth and that the first and second mixed
derivatives are equal at points
B, C:
|
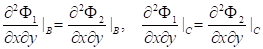 , ,
|
(10)
|
|
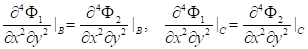 . .
|
(11)
|
Proof.
The requirement for C2-smoothness
of the band Ô1+Ô2 means that at any point of the joint
BC
the following
equalities should be met:
|
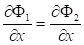 , ,
|
(12)
|
|
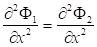 . .
|
(13)
|
Let us consider condition (12).
The cubic functions
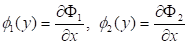 included in (12) are uniquely
determined by their values at the boundary points of the joint
B, C, as
well as by the values of the first derivatives
included in (12) are uniquely
determined by their values at the boundary points of the joint
B, C, as
well as by the values of the first derivatives
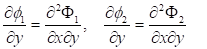 at
these points. According to (10), these values coincide; therefore, the
functions
at
these points. According to (10), these values coincide; therefore, the
functions
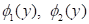 coincide along the joint
BC.
Condition (12) is satisfied.
coincide along the joint
BC.
Condition (12) is satisfied.
Let us consider condition (13).
The cubic functions
 included in (13) are uniquely
determined either by their values and first derivatives at points
B
and
C,
or by their values and second derivatives at these points. Therefore, to
fulfill requirement (13), in addition to the equality of the functions
included in (13) are uniquely
determined either by their values and first derivatives at points
B
and
C,
or by their values and second derivatives at these points. Therefore, to
fulfill requirement (13), in addition to the equality of the functions
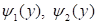 at points
B
and
C, we should
additionally ensure either the equality of the first derivatives
at points
B
and
C, we should
additionally ensure either the equality of the first derivatives
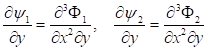 , or the equality of the second derivatives
, or the equality of the second derivatives
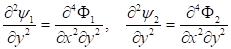 at these points. According to (11), the
second derivatives at points
B,
C
coincide. According to the C2-smoothness
condition for boundary curves
ABM
and
DCN, the values of the
functions
at these points. According to (11), the
second derivatives at points
B,
C
coincide. According to the C2-smoothness
condition for boundary curves
ABM
and
DCN, the values of the
functions
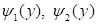 at points
B
and
C
also
coincide. Therefore, the functions
at points
B
and
C
also
coincide. Therefore, the functions
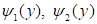 coincide along the joint
BC. Condition (13) is satisfied. The theorem is proven.
coincide along the joint
BC. Condition (13) is satisfied. The theorem is proven.
Let us construct a two-section C2-smooth
bicubic band with the fixed transverse guides
AD, BC, MN
and with the
given gradients
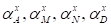 in the longitudinal direction (see
Fig. 3). According to the condition of Theorem 1, the longitudinal boundary
ABM
formed by the cubic parabolas
AB
and
BM
should be a C2-smooth
compound curve (cubic spline). The same requirement applies to the longitudinal
boundary
DCN. Let us consider an algorithm for constructing a cubic
spline with fixed end points (fixed tangents at the finite points).
in the longitudinal direction (see
Fig. 3). According to the condition of Theorem 1, the longitudinal boundary
ABM
formed by the cubic parabolas
AB
and
BM
should be a C2-smooth
compound curve (cubic spline). The same requirement applies to the longitudinal
boundary
DCN. Let us consider an algorithm for constructing a cubic
spline with fixed end points (fixed tangents at the finite points).
Points
A(x0,
y0,
z0),
B(x1,
y0,
z1),
M(x2,
y0,
z2)
are indicated in the vertical plane
y
=
y0
of the
Cartesian coordinate system
xyz. A composite C2-smooth curve
formed by the cubic parabolas
f1
(x)=
AB
and
f2
(x)=
BM(cubic spline) must be drawn through these points. The slope angles
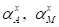 of the tangents to the constructed curve
(“fixed end points”) are indicated at boundary points
A
and
M.
of the tangents to the constructed curve
(“fixed end points”) are indicated at boundary points
A
and
M.
The condition for the C2-smooth
connection of the parabolas
f1
(x) and
f2
(x)
has the form [11, 12]
|
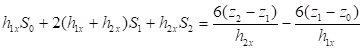 , ,
|
(14)
|
where
S0,
S1,
and
S2
are the values of the second derivatives of the
functions
z
=
f1
(x) and
z
=
f2
(x)
at the nodes
A, B, and M. The designations
h1
x
=
x1
-
x0
and
h2
x
=
x2
-
x1
are
used hereinafter.
Condition (14) should be
supplemented with the fixed end points conditions:
|
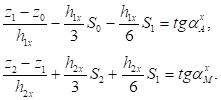
|
(15)
|
We find the values of
S0,
S1,
S2
from the system of equations (14),
(15) and substitute them into the equations
|
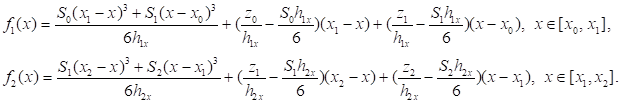
|
(16)
|
The computational algorithm of
(14), (15), (16) makes it possible to find equations of a cubic spline with
fixed end points. If the spline is formed from
m
segments (m-1
junction points), the specified algorithm will contain
m-1 smoothness
conditions of form (14) and
m
equations of form (16).
Let us construct a band
consisting of
m
bicubic portions
ABCD,
BMNC,
MKLN,
… (Fig. 4).

Fig. 4. Transverse guides of the
bicubic band
We will assume that the
equations of the frame transverse lines
AD, BC, MN, KL, … are either
preset or found according to (8). To solve the problem, 16
m
coefficients
included in equations (1) of connected portions must be calculated.
Step 1.
We find the equations of the
longitudinal boundaries of the band formed by composite C2-smooth
m-sectional
cubic curves (cubic splines) using algorithm (14) ... (16).
Step 2.
We create a system of 5
m
equations with (6). We supplement this system of equations with four boundary
conditions with (7) plane angles and 4(m-1) smoothness conditions of
(10) and (11) (see Theorem 1). We obtain a system of 9
m
linear
equations, from which we find 9
m
coefficients.
Step 3.
Using direct calculation by
formulas (4) and (5), we find 7
m
coefficients included in the equations
of portions. Jointly with the previously found 9
m
coefficients, we
obtain 16
m
coefficients included in the equations of connected portions.
The problem is solved.
Example 2
Let us construct a C2-smooth
bicubic band passing through fixed transverse guides
|
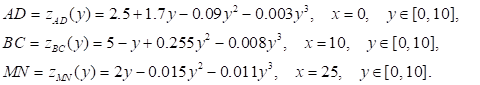
|
(17)
|
Longitudinal gradients
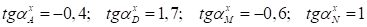 are set in the angular points (see Fig. 3).
are set in the angular points (see Fig. 3).
Solution
We will find the equation of the
portion Ô1
=
ABCD
in form (1a). We will find the equation of
the portion Ô2
=
BMNC
in the form
|
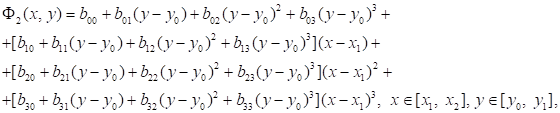
|
(1b)
|
where
x0
=
y0
=0,
x1
=
y1
=10,
x2
=25.
Step 1.
According to (14), (15), and
(16), we find the equations for the segments of the longitudinal boundary
ABM
connected at point
B
with Ñ2
smoothness:
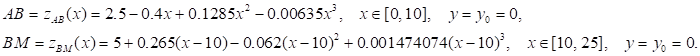
Similarly, we find the equations
of the segments of boundary curve
DCN
connected at point
C
with Ñ2
smoothness:
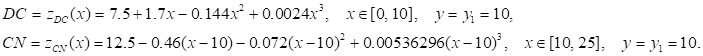
Step 2.
We make a system of ten
equations of form (6) with respect to the unknown coefficients
aij,
bij
included in equations (1a), (1b) of the required bicubic
portions:
|
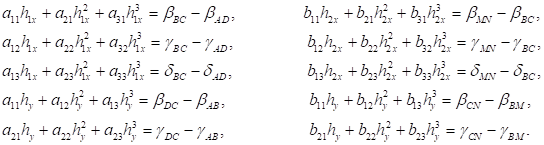
|
(18)
|
Here,
hy
=
y1
-
y0
=10,
h1
x
=
x1
-
x0
=10,
h2
x
=
x2
-
x1
=15.
We write down the plane angles condition:
|
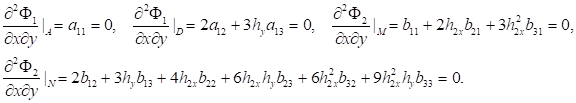
|
(19)
|
The system of equations (18) and
(19) is supplemented by the requirements for a C2-smooth connection
of the bicubic portions Ô1, Ô2
along the joint
BC(see Theorem 1):
|
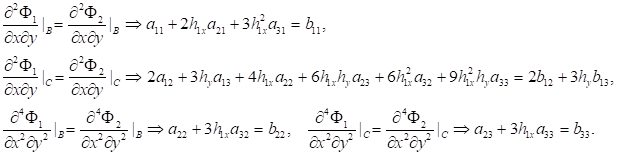
|
(20)
|
We obtained a system of eighteen
equations (18), (19), and (20). We find 18 coefficients from this system of
equations:
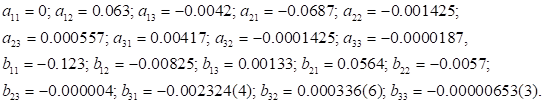
Step 3.
We find the remaining 14
coefficients according to (4) and (5):

We determined all the
coefficients of equations (1a), (1b) of the bicubic segments Ô1
and
Ô2
with a Ñ2-smooth connection. Figure 5 shows the grid
of generators of the bicubic band Ô1+Ô2
constructed
according to (1a) and (1b).
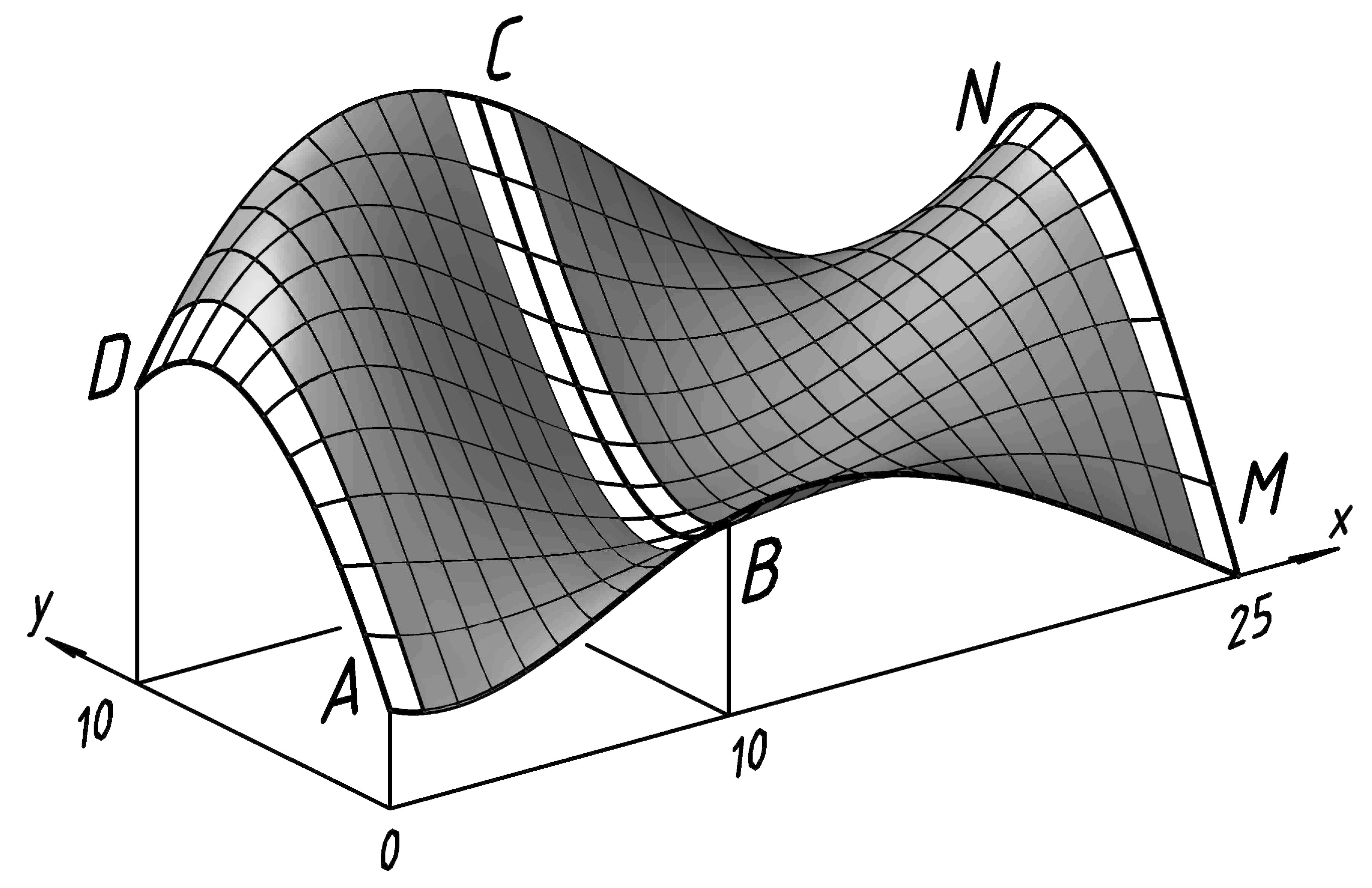
Fig. 5. Ñ2-smooth band (Example
2)
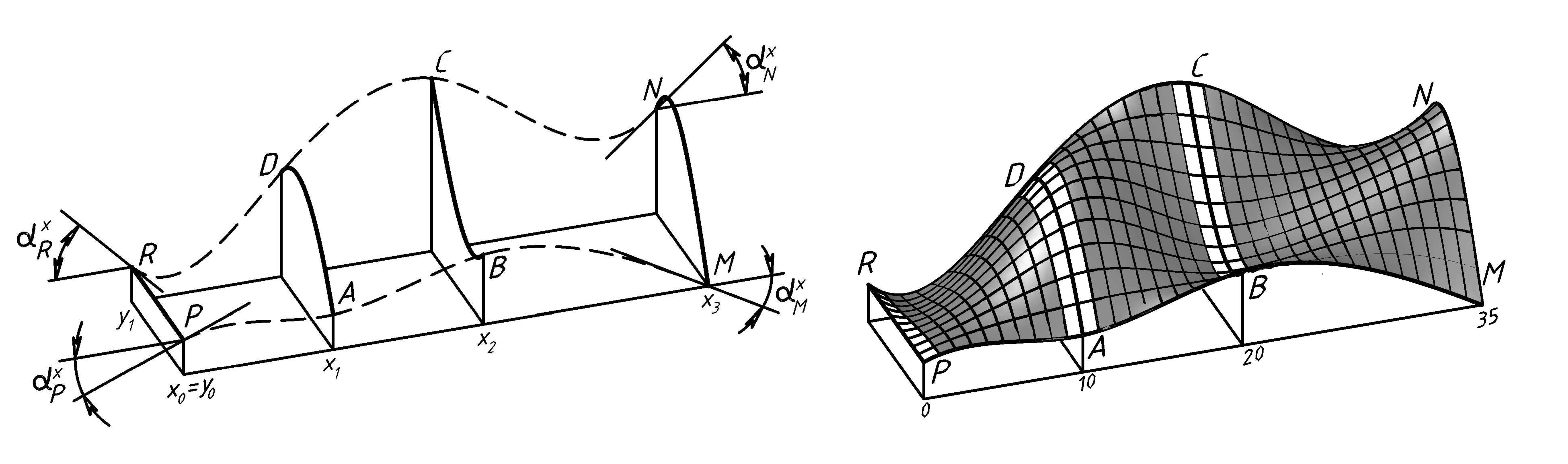
Example 3
Let us attach the section
PADR
with a horizontal guide
PR
located at a height of
z
=2.5 to the
two-section band
ABCD + BMN
considered in example 2 (Fig. 6a).
|
|
|
(a)
|
(b)
|
Fig. 6. Three-section Ñ2-smooth
band (Example 3): à - boundary conditions; b - grid of generators
We will assume we are given the
coordinates of the grid nodal points:
x0
=
y0
=0,
x1
=y1
=10,
x2
=20,
x3
=35.
The equations for the transverse guides
AD, BC, MN
are shown in example
2. The equation for the guide line
PR
degenerates into the equation
zPR
=2.5. The longitudinal gradients
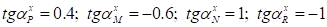 are set at the angular
points
P, M, N, R
of the constructed band.
are set at the angular
points
P, M, N, R
of the constructed band.
Solution
Let us find the equations of the
bicubic portions Ô1
=
PADR
and Ô2
=
ABCD
with
(1à) and (1b), assuming that
x0
=
y0
=0,
x1
=
y1
=10,
x2
=20 and the equation of the
portion Ô3
=
BMNC
in the following form
|

|
(1c)
|
assuming that x3=35.
Step 1.
According to algorithm (14)
... (16), we find the equations of the segments of the longitudinal boundary
PABM.
We obtain a set of C2-smoothly connected cubic parabolas satisfying
the “fixed end points” conditions:
|
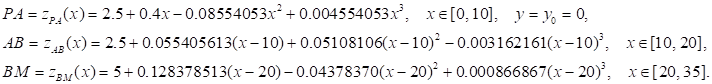
|
(21)
|
Using the same algorithm, we
find the equations for the segments of the longitudinal boundary
RDCN:
|
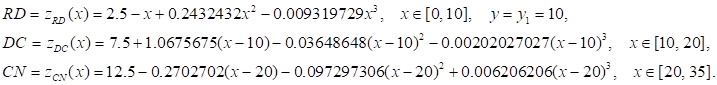
|
(22)
|
Step 2.
We make a system of 5
m
=15
equations of form (6) with respect to
aij,
bij,
and
cij:
|
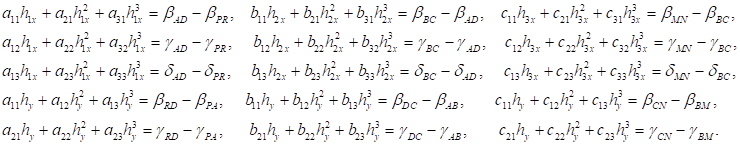
|
(23)
|
The values
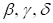 included in (23) are determined according
to (17), (21), and (22). For example, it follows from (17) that
included in (23) are determined according
to (17), (21), and (22). For example, it follows from (17) that
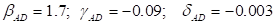 .
Line
PR
is a horizontal segment, so
.
Line
PR
is a horizontal segment, so
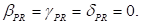
We supplement the system of
equations (23) with the conditions of form (7) (plane angles):
|
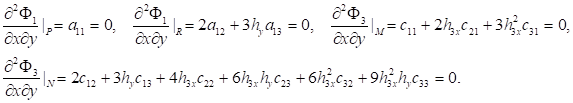
|
(24)
|
We write down 4(m-1)=8
smoothness conditions: the conditions for the equality of the first mixed
derivatives
|
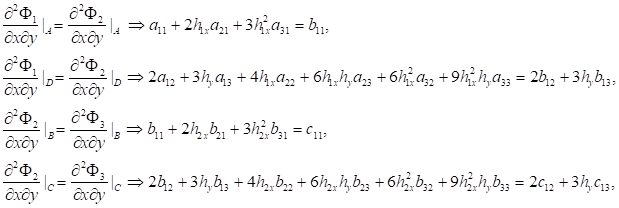
|
(25)
|
and the conditions for the equality of the
second mixed derivatives
|
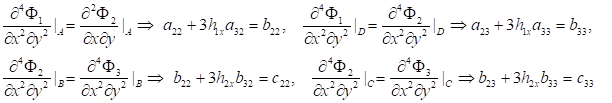
|
(26)
|
at the junction points
A, D, B,
and
C(see Theorem 1).
We find 27 coefficients from the
system of 27 linear equations (23) ... (26):
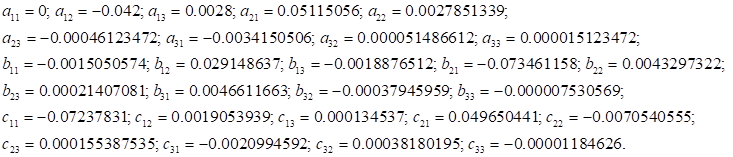
Step 3.
We find the remaining coefficients using
the formulas of (4), (5):
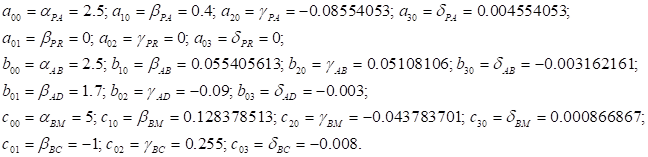
We determined all 48
coefficients of equations (1a), (1b), and (1c) of the bicubic portions Ô1,
Ô2, and Ô3. Figure 6b shows the grid of generators of the
bicubic band Ô=Ô1
+Ô2
+Ô3.
Let us construct a bicubic
surface consisting of
mn
bicubic portions:
m
portions in the
longitudinal direction (along the
x
axis) and
n
portions in the
transverse direction (along the
y
axis). The longitudinal and transverse
frame lines of the surface are formed by cubic splines. We will assume that the
constructed surface consists of
n
bicubic bands, each of which consists
of
m
bicubic portions. The bicubic bands should be C2-smoothly
interconnected (along the longitudinal lines of the frame). Let us consider the
conditions for the smooth connection of bicubic bands.
Let the bicubic surface consist
of two bands (Fig. 7).

Fig. 7. Bicubic surface frame
Band ÔAB
formed by the bicubic portions
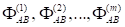 is bounded by the cubic
splines
A0
A1
…
Am
and
B0
B1
…
Bm.
B and ÔBC
formed by the bicubic portions
is bounded by the cubic
splines
A0
A1
…
Am
and
B0
B1
…
Bm.
B and ÔBC
formed by the bicubic portions
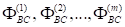 is bounded by the cubic splines
B0
B1
…
Bm
and
C0
C1
…
Cm.
is bounded by the cubic splines
B0
B1
…
Bm
and
C0
C1
…
Cm.
Theorem 2.
To achieve C2-smooth
connection of the bicubic bands ÔAB, ÔBC
along the longitudinal joint
B0
…
Bm, it is
sufficient to ensure the equality of the first and second mixed derivatives at
the initial
B0
and finite
Bm
points of the
longitudinal joint in addition to the C2-smoothness of the frame
lines:
|
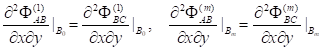 , ,
|
(27)
|
|
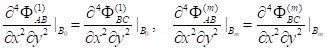 . .
|
(28)
|
Proof
. The requirement for the C2-smooth
connection of bicubic bands means that the following equalities are met at any
point of the joint
B0
…
Bm
|
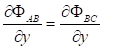 , ,
|
(29)
|
|
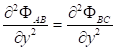 . .
|
(30)
|
Let us consider condition (29).
The cubic Ñ2-smooth composite functions
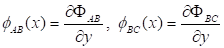 included
(29) are determined by their values at nodal points
B0,
B1,
…,
Bm
and the values of the first derivatives
included
(29) are determined by their values at nodal points
B0,
B1,
…,
Bm
and the values of the first derivatives
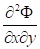 at finite points
B0,
Bm
of the longitudinal joint
B0
…
Bm. The
numerical values of the functions
at finite points
B0,
Bm
of the longitudinal joint
B0
…
Bm. The
numerical values of the functions
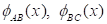 at points
B0,
B1, …,
Bm
are equal to the tangents of the
slope angles of the tangents to the transverse lines of the frame. Due to the
smoothness of the transverse lines of the frame, the values of the functions
at points
B0,
B1, …,
Bm
are equal to the tangents of the
slope angles of the tangents to the transverse lines of the frame. Due to the
smoothness of the transverse lines of the frame, the values of the functions
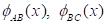 at these points coincide. According to
condition (27), the values of the derivatives of these functions at the finite
points
B0
and
Bm
also coincide; therefore,
the functions
at these points coincide. According to
condition (27), the values of the derivatives of these functions at the finite
points
B0
and
Bm
also coincide; therefore,
the functions
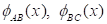 coincide along the joint
B0
….
Bm.
Condition (29) is satisfied.
coincide along the joint
B0
….
Bm.
Condition (29) is satisfied.
Let us consider condition (30).
The cubic Ñ2-smooth composite functions
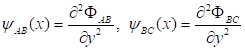 included
in (30) are determined by their values at points
B0,
B1,
…,
Bm
and the values of the second derivatives
included
in (30) are determined by their values at points
B0,
B1,
…,
Bm
and the values of the second derivatives
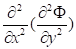 at boundary points
B0,
Bm
of the longitudinal joint
B0
…
Bm.
The values of the functions
at boundary points
B0,
Bm
of the longitudinal joint
B0
…
Bm.
The values of the functions
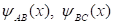 at points
B0,
B1, …,
Bm
are proportional to the curvature
of the transverse joints at these points. Due to the C2-smoothness
of the transverse lines of the frame, these values coincide. According to
condition (28), the values of the second derivatives of these functions at
boundary points
B0,
Bm
also coincide;
therefore, the functions
at points
B0,
B1, …,
Bm
are proportional to the curvature
of the transverse joints at these points. Due to the C2-smoothness
of the transverse lines of the frame, these values coincide. According to
condition (28), the values of the second derivatives of these functions at
boundary points
B0,
Bm
also coincide;
therefore, the functions
 coincide along the joint
B0
….
Bm. Condition (30) is satisfied. The
theorem is proven.
coincide along the joint
B0
….
Bm. Condition (30) is satisfied. The
theorem is proven.
The calculation is reduced to
calculating 16
mn
coefficients of the equations of the bicubic portions
forming the constructed surface. We assume that the surface consists of
n
longitudinal bicubic bands, and each band consists of
m
bicubic
portions. Each portion is described by an equation of form (1).
Step 1.
Using the algorithm from (14),
(15), and (16), we find the equations of the longitudinal and transverse lines
of the frame (cubic splines).
Step 2.
We make a system of 5
m
equations of form (6) for each bicubic band. We add 4(m-1) smoothness
conditions for the band (see Theorem 1). We obtain 9
m-4 equations. We
obtain
n(9
m-4) equations for
n
bands. We supplement the
resulting equations with 4(n-1) conditions (27), (28) for the smooth
band connection (see Theorem 2), as well as 4 “plane angles” conditions. We
obtain the system of 9
mn
linear equations used to find 9
mn
coefficients included in the equations of bicubic portions of the constructed
surface.
Step 3.
Using direct calculation of
formulas (4) and (5), we find 7
mn
coefficients included in the equations
of portions. Along with the previously found 9
mn
coefficients, we obtain
16
mn
coefficients included in the equations of connected portions. The
problem is solved.
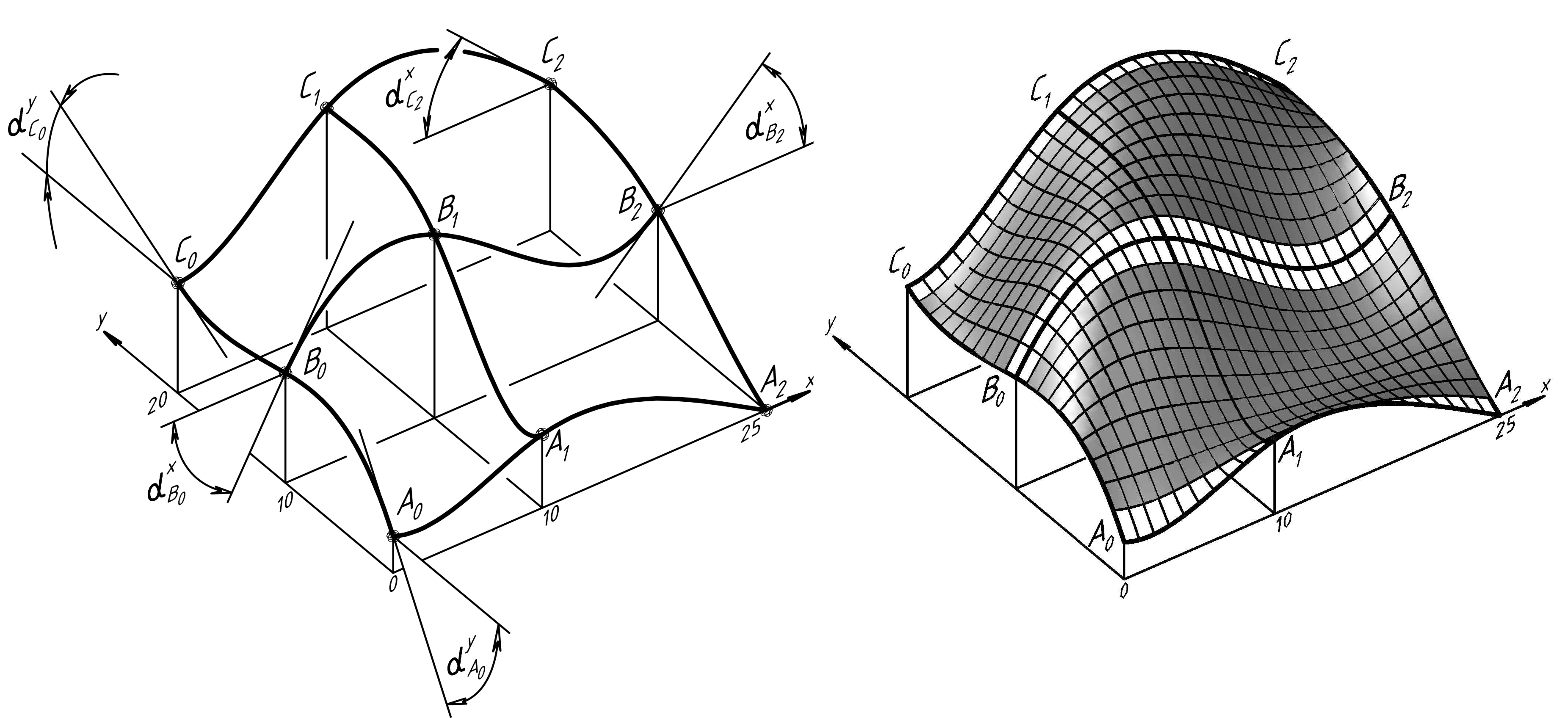
Example 4
Let us construct a C2-smooth
bicubic surface passing through points
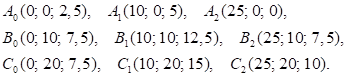
The gradients in the
longitudinal and transverse directions are fixed at the angular points
A0,
A2,
C0,
C2:
The longitudinal gradients
 are given at boundary points
B0,
B2. The transverse gradients
are given at boundary points
B0,
B2. The transverse gradients
 are
given at boundary points
A1,
C1
(Fig. 8à).
are
given at boundary points
A1,
C1
(Fig. 8à).
|
|
|
(a)
|
(b)
|
Fig. 8. Bicubic surface (Example
4): a - fixed frame; b - grid of generators
Solution
Step 1.
Per (14), (15), and (16) we
find the equations of the frame lines satisfying the conditions of the problem.
The equation of the longitudinal
boundary line
A0
A1
A2:
|
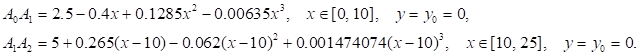
|
(31)
|
The equation of the longitudinal
line
B0
B1
B2:
|
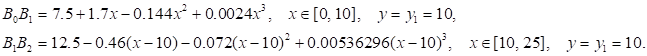
|
(32)
|
The equation of the longitudinal
boundary line
C0
C1
C2:
|
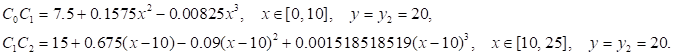
|
(33)
|
(31) … (33) take into account
that
x0
=
y0
=0,
x1
=10,
x2
=25.
Similarly, we find the equations
of the transverse lines of the frame. The equation of the transverse boundary
line
A0
B0
C0:
|
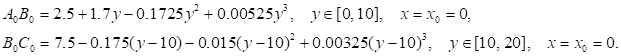
|
(34)
|
The equation of the transverse
line
A1
B1
C1:
|
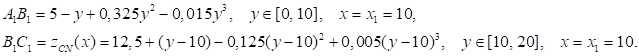
|
(35)
|
The equation of the transverse
boundary line
A2
B2
C2:
|
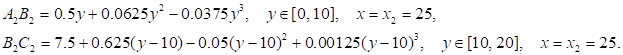
|
(36)
|
The surface frame is fixed.
Step 2.
The constructed surface consists
of two bicubic bands ÔAB
and ÔBC
smoothly
interconnected along the joint
B0
B1
B2.
The band ÔAB
is formed by the portions
|
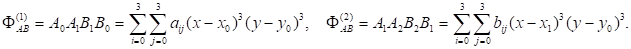
|
(37)
|
The band ÔBC
is formed by the portions
|
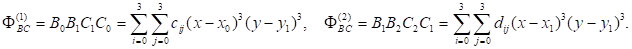
|
(38)
|
We make a system of 10 equations
of form (6) for each band.
For the band ÔAB
we obtain:
|

|
(39)
|
Here,
h1
x
=
x1
-
x0
=10,
h1
y
=
y1
-
y0
=10, and
h2
x
=
x2
-
x1
=15.
For the band ÔBC
we obtain:
|
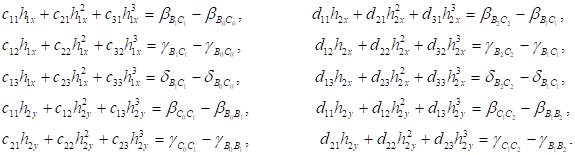
|
(40)
|
Here,
h2y
=10.
The values
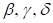 included in (39) and (40) are determined
according to (31)…(36). For example, it follows from (34) that
included in (39) and (40) are determined
according to (31)…(36). For example, it follows from (34) that
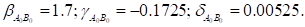
We write down the smoothness
conditions for each bicubic band (see Theorem 1). For band ÔAB,
we obtain four conditions for a smooth connection of portions
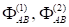 (the equality of the first and second mixed
derivatives at points
A1,
B1):
(the equality of the first and second mixed
derivatives at points
A1,
B1):
|
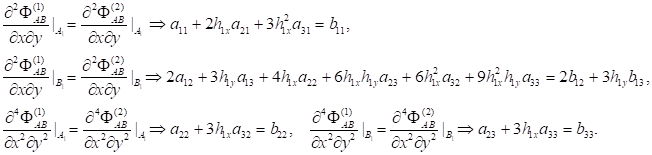
|
(41)
|
For band ÔBC
we also obtain four conditions for a smooth connection of portions
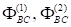 (the equality of the first and second mixed
derivatives at points
B1,
C1):
(the equality of the first and second mixed
derivatives at points
B1,
C1):
|
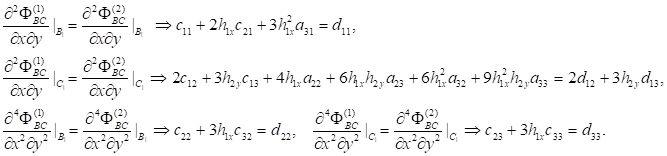
|
(42)
|
We write down the conditions for
the smooth connection of the bicubic bands ÔAB
and ÔBC
at the junction points
B0
and
B2
(see
Theorem 2):
|
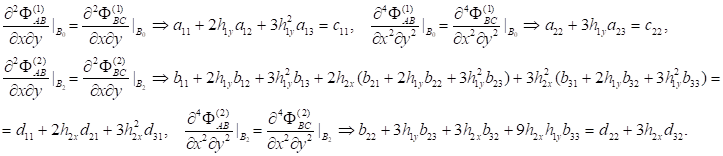
|
(43)
|
We write down the plane angles
condition:
|
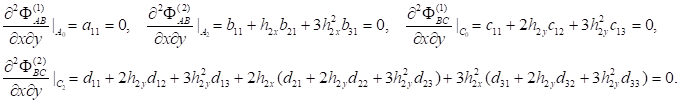
|
(44)
|
The system of equations (39) …
(44) contains 36 equations with respect to 36 coefficients
aij,
bij,
cij, and
dij
included in equations (37) and (38). Solving this system of equations, we
obtain:
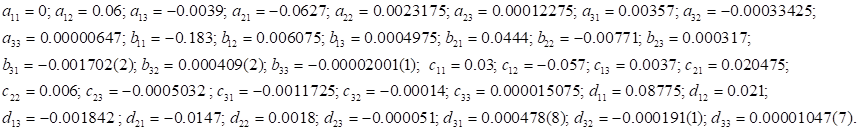
Step 3.
Using direct calculation of
formulas (4) and (5), we find the remaining 28 coefficients included in
equations (37), (38):
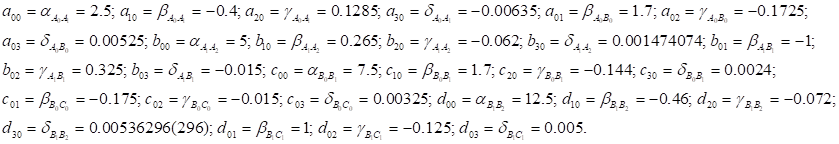
We determined all 64
coefficients included in equations (37) and (38). Figure 8b shows the grid of
the generators of the bicubic surface ÔAB+ÔBC.
The computational algorithm
based on preliminary fixing of the surface frame is valid when the frame is
formed by a mixed set of cubic splines.
Example 5
The surface frame is set by the
straight lines
B0
B1
B2
and
A1
B1
C1. The surface
boundaries are set by the straight lines
A0
A1
A2,
A0
B0
C0, and
A2
B2
C2
and the cubic spline
C0
C1
C2
with the longitudinal gradients
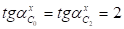 (Fig. 9à).
(Fig. 9à).
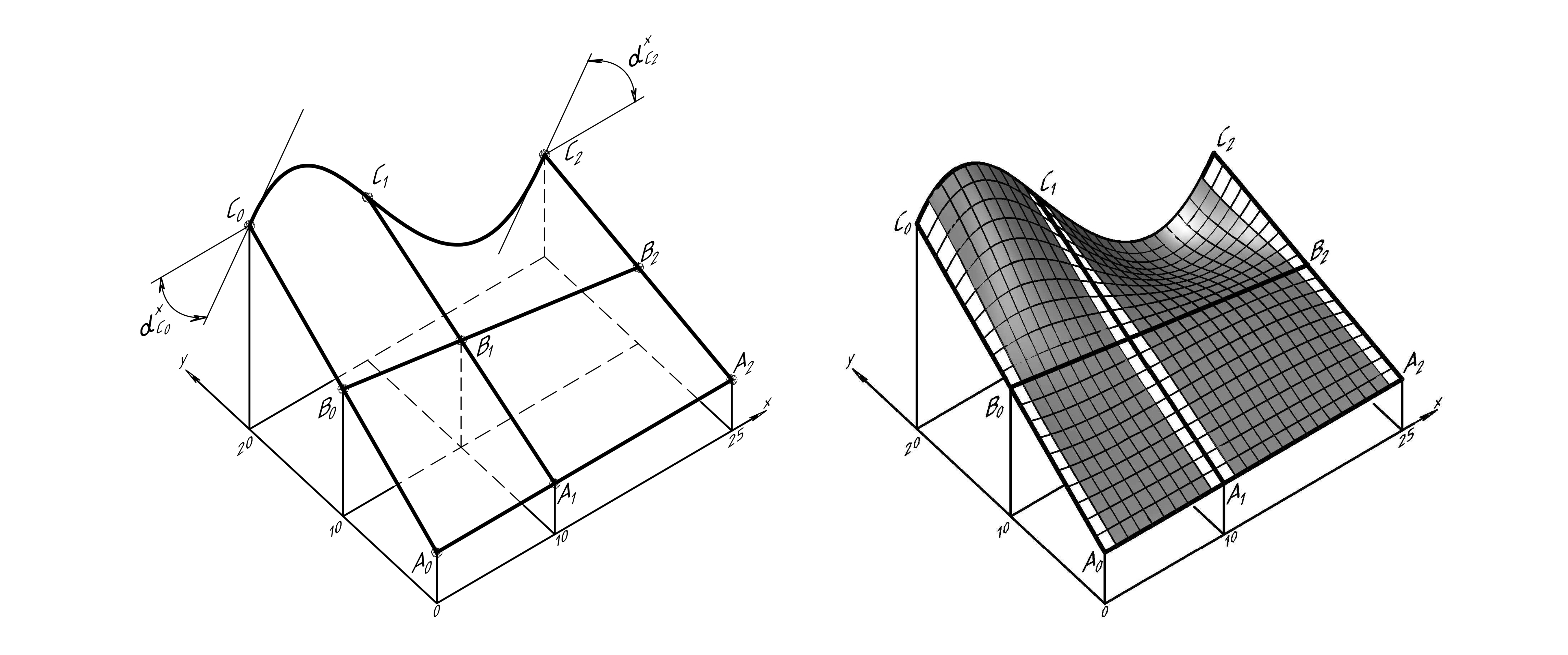
Fig. 9. Bicubic surface on a
frame of straight lines and cubic splines (Example 5):
a - fixed frame; b - grid
of generators
We are given the coordinates of the
following nodal points:
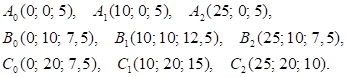
Let us construct a C2-smooth
bicubic surface satisfying the conditions of the problem.
Solution
We will assume that the
constructed surface consists of the bicubic bands ÔAB
and ÔBC
smoothly interconnected along the straight joint
B0
B1
B2.
Each band, in turn, consists of bicubic portions (37), (38).
Step 1.
We find the equations of the
frame lines satisfying the conditions of the problem.
The equation of line
A0
A1
A2:
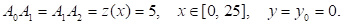
The equation of line
B0
B1
B2:
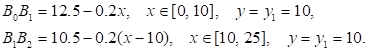
The equation of line
A0
B0
C0:
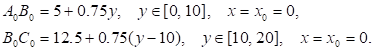
The equation of line
A1
B1
C1:
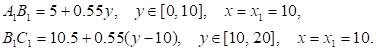
The equation of line
A2
B2
C2:
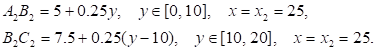
Following the algorithm in (14),
(15), and (16), we find the equation of the Ñ2-smooth boundary curve
C0
C1
C2
with the gradients
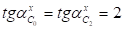 :
:
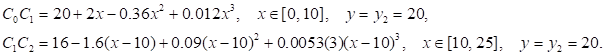
Step 2.
We write down the system of
equations (39) ... (44) containing 36 equations for 36 coefficients
aij,
bij,
cij, and
dij
included in equations (37) and (38). In equations (39) and (40) we substitute
the values of the coefficients
α,
β,
γ, and
δ
corresponding to the equations of frame lines. For example, it
follows from the equation of boundary line
A0
B0
C0
that
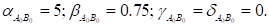
Having solved the system of
equations (39) ... (44), we find 36 coefficients included in equations (37),
(38):
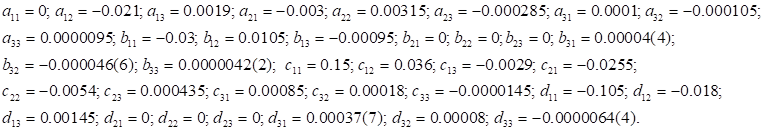
Step 3.
Using direct calculation of
formulas (4) and (5), we find the remaining 28 coefficients included in
equations (37) and (38):
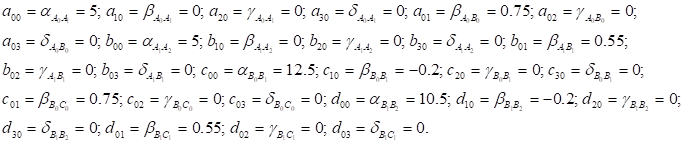
We determined all 64
coefficients included in equations (37) and (38). Figure 9b shows the grid of
generators of the bicubic surface ÔAB+ÔBC.
Example 6
The surface frame is set by a
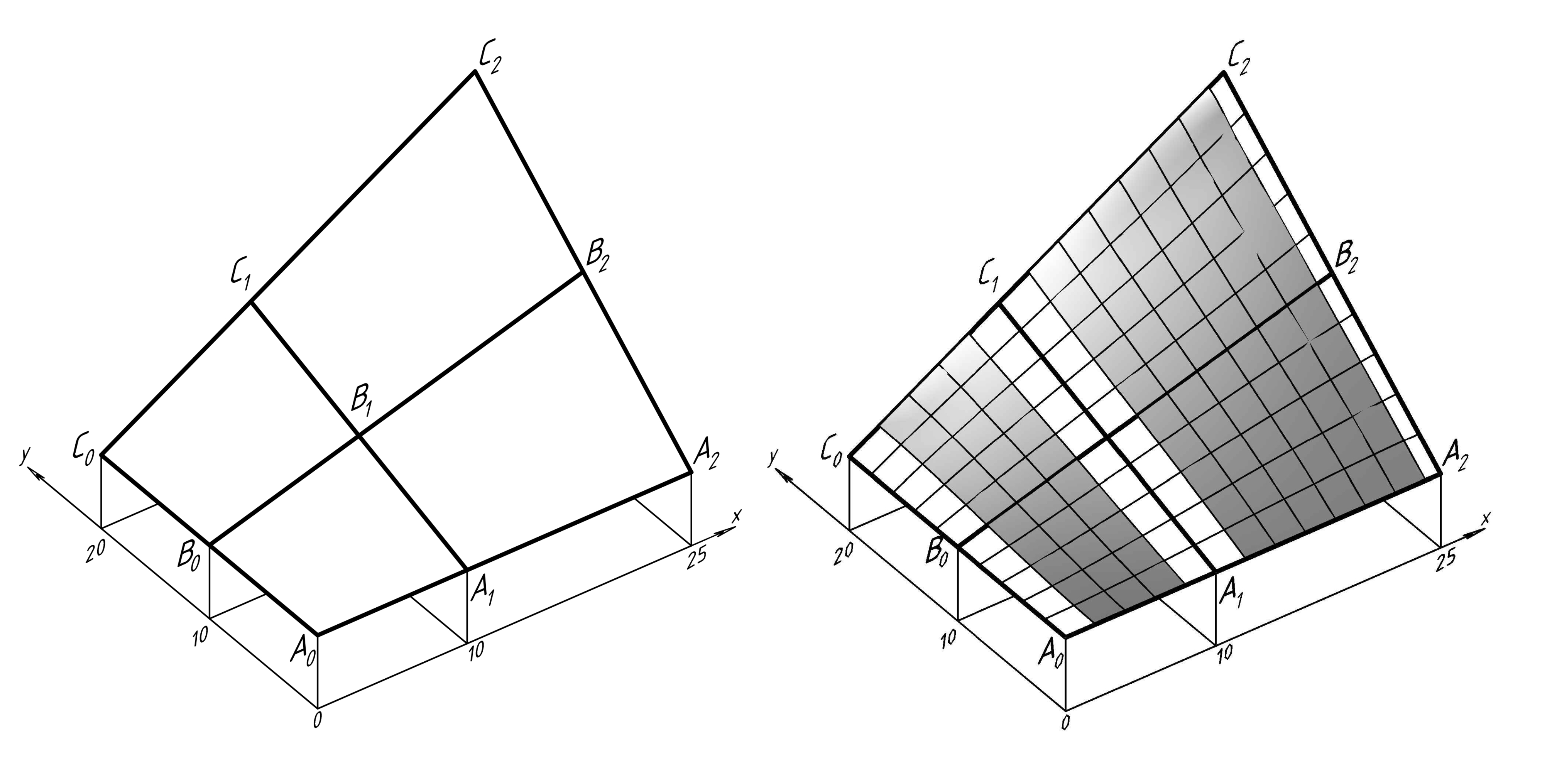
spatial quadrilateral with the angular points
A0
(0; 0; 5), A2
(25;
0; 5), C2
(25; 20; 20), and C0
(0; 20; 5) and the straight
guides B0
B1
B2
and A1
B1
C1
lying in the vertical planes
y
=10 and
õ
=10 (Fig. 10à).
|
|
|
(a)
|
(b)
|
Fig. 10. Bicubic surface on a
straight line frame (Example 6):
à - fixed frame; b - grid of generators
Let us construct a bicubic
surface “stretched” on a given frame.
Solution
We will assume that the
constructed surface consists of the bicubic bands ÔAB
and ÔBC
smoothly interconnected along the straight joint
B0
B1
B2.
Each band, in turn, consists of bicubic portions (37), (38).
Step 1.
We find the equations of the
frame lines.
The equation of line
A0
A1
A2:
The equation of line
B0
B1
B2:

The equation of line
Ñ0
Ñ1
Ñ2:
The equation of line
A0
B0
C0:
The equation of line
A1
B1
C1:
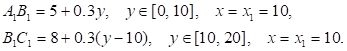
The equation of line
A2
B2
C2:
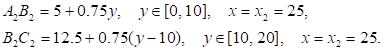
Step 2.
We write down the system of
equations (39) … (44) substituting values of the coefficients
α,
β,
γ,
δ
corresponding to the equations of frame lines. For
example, it follows from the equation of boundary line
A0
B0
C0
that
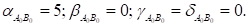 Having solved the system of equations (39)
… (44), we find the coefficients of equations (37) and (38):
Having solved the system of equations (39)
… (44), we find the coefficients of equations (37) and (38):
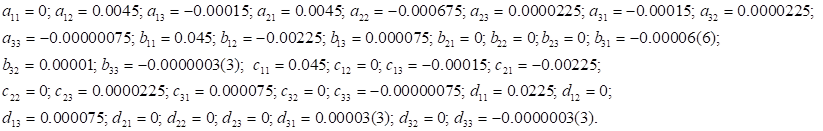
Step 3.
Using direct calculation of
the formulas (4) and (5), we find the remaining 28 coefficients included in
equations (37) and (38):
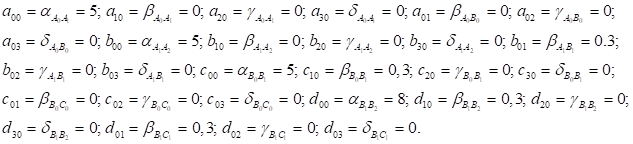
We determined all the
coefficients included in the equations of bicubic portions (37) and (38).
Figure 10b shows the grid of the generators of the bicubic surface ÔAB+ÔBC.
The resulting surface slightly differs from the oblique plane
A0
A2
C2
C0.
For example, at
x
=6,
y
=4, the elevation marks of the points on
the bicubic surface and on the oblique plane are
z
=5.623232 and
z
=5.720,
respectively, differing by 1.7%.
Matrix calculations (solving the
systems of linear equations) were performed using the freely distributed
software SMath Studio. The grid of the bicubic surface generators was
calculated and visualized in all examples using the AutoLISP programming
language in the AutoCAD environment [13]. The transparency of the examples is
ensured by indicating the numerical values of all the calculated magnitudes
with an accuracy of nine significant figures.
We aimed to avoid the classical
idea of a composite bicubic surface as a set of bicubic portions meeting certain
conditions for the border of a surface (incidence of given points, fixed
gradients, etc.) and for the smooth interconnection of portions.
Our proposed approach creates a
surface frame made of algebraic cubic splines. Constructing a cubic spline that
interpolates a given set of points is a trivial task which was fully solved in
the second half of 20th century [14, 15]. The work of Kazan mathematicians
Kornishin M.S. et. al [16] is noteworthy in Russian literature.
A distinctive feature of the
proposed algorithm for calculating a composite C2-smooth bicubic
surface consists in the conventional decomposition of the constructed surface
into separate bicubic tapes bounded by longitudinal frame lines. Calculating a
tape is much easier than calculating a surface [17]. We believe that this
approach, which divides the problem into simple calculation blocks, is most
consistent with engineering practice.
The proposed algorithm was
illustrated with 3D surface models. As P. Bezier said, the widespread use of
some systems is adversely affected by the fact that, despite the sophistication
of applied mathematical methods, users have difficulty in their assimilation
[8]. One method to overcome these difficulties is to demonstrate the applied
methods and algorithms based on specific examples, as we did in this article.
The paper proposes an algorithm
for calculating a composite bicubic surface with a continuous change in
curvature stretched on a fixed frame. In the proposed algorithm, the problem is
divided into two stages: first, the frame equations are found, and then the
coefficients included in the equations of the bicubic portions forming the
bicubic surface are calculated. According to the specified boundary conditions,
the frame lines are described by cubic splines with fixed end points.
This approach to modeling a
bicubic surface reduces the size of the characteristic matrix of the system of
linear equations with respect to the coefficients included in the bicubic
surface equation. The matrix size is reduced from 16
mn
to 9
mn,
where
m
and
n
are the number of bicubic portions along the
x,
y
axes. Surface visualization is reduced to building a grid of longitudinal
and transverse generators, the equations of which are formed from the bicubic
surface equation by substituting
y
=const (longitudinal generators) or
x
=const
(transverse generators).
1. Udler E. M., Tostov E. Design
of tent shells // CADmaster #1(6) / 2001, pp. 43−47.
2. Kirichkov I.V. Refraction of
the fold category through the prism of architecture // Architecture and Design.
- 2018. – # 3. – P. 1–11. DOI: 10.7256/2585-7789.2018.3.29422
3. Jarke J.V. Bicubic patches
for approximating non-rectangular control-point meshes / / Computer Aided
Geometric Design. - 1986. - Vol. 3, # l. - P. 456-459.
4. Levner G., Tassinari P.,
Marini D. Simple general methods for ray tracing bicubic surfaces //
Theoretical Foundations of Computer Graphics and CAD. – New York:
Springer-Verlag, 1988. – P. 805–820.
5. Fox A., Pratt M.
Computational geometry. Application in design and production. Moscow: Mir,
1982. 304 p.
6. Panchuk, K. Spline Curves
Formation Given Extreme Derivatives / K. Panchuk, T. Myasoedova, E. Lyubchinov.
– Mathematics
2021, 9(1), 47.
https://doi.org/10.3390/math9010047
7. Gallier, J. Curves and
Surfaces in Geometric Modeling: Theory and Algorithms; University of
Pennsylvania: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018; P. 61–114.
8. Bezier P. Geometric methods //
Mathematics and CAD. Vol. 2. Moscow: Mir, 1989. P. 96–257.
9. Korotkiy V.A. Irregular
curves in engineering geometry and computer graphics // Scientific
Visualization, 2022. Vol. 14, No. 1. P. 1–17. DOI: 10.26583/sv.14.1.01
10. Korotkiy V.A. Cubic curves in
engineering geometry // Geometry and Graphics. – 2020. Vol. 8, No. 3. – P.
3–24. – DOI: 10.12737/2308-4898-2020-3-24
11. Shikin E.V., Plis A.I.
Curves and surfaces on a computer screen. User guide to splines. Moscow:
Dialog-MEPhI, 1996. 240 p.
12. Golovanov N.N. Geometric
modeling. Moscow: DMK-Press, 2020. 406 p.
13. Gotovtsev A.A. Autodesk
alias: where to start? // CADmaster #5 (66) / 2012, P. 42–44.
14. 318 ñ. Ahlberg J., Nilson
E., Walsh J. The theory of splines and their applications. Moscow: Mir, 1972.
318 p.
15. C. de Boor. A practical
guide to spline. Moscow: Radio and Communication, 1985. 303 p.
16. Kornishin M.S., Paimushin
V.N., Snigirev V.F. Computational geometry in problems of shell mechanics.
Moscow: Nauka, 1989. 208 p.
17. Korotkiy V.A, Usmanova E.A.,
A bicubic tape surface // Omsk Scientific Bulletin. 2023. #. 2 (186). pp.
19–27. DOI: 10.25206/1813-8225-2023-186-00-00.