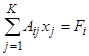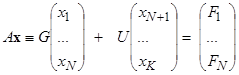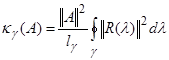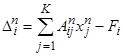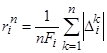The creation of software products for the digital
nutrition involves the solution of both theoretical and practical computational
problems.
The first task is to digitally transform data on human
physiological needs
in
food and
biologically active substances and energy, the chemical composition of basic food
and
the
creation
a computer program to process this data
in order to create personalized recommendations for optimal nutrition [1].
The second task is
in
developing
the
combined deterministic and statistical
models according to the peculiarities of nutritional characteristics, taking
into account
the
medical
recommendations, the forecast of quantitative and age-related changes in the
population structure, the environmental situation, and
national characteristics. This is also important for predicting
the
regional food needs.
The third task is less global, but the accuracy of
forecasts and recommendations depends on its solution, and this will
be
discussed
in this paper. This
task consists in creating an algorithm for automatic selection of dishes and
calculating the size of their portions under given linear constraints
(equalities and inequalities), based on some not completely formalized
principle of optimality, which takes it out of the classical field of linear
programming. The point is that there is no formal functionality in this task
that needs to be minimized.
Optimization in this context will be understood as
minimizing the amount of time required to achieve a given nutrient intake in
the average daily equivalent. For example, the average annual protein intake recommended
in [2] is about 100 g per day for an adult, of which 50 % is of animal origin,
and 50 % is of vegetable origin (cereals, vegetables, fruits).
At the same time consumption of
fish
and poultry
meat is about 20 % the total
consumption of meat food, and 60 % is accounted for by animal meat. Then the
average daily protein intake from meat products is 10 g
of
poultry
meat, 10 g of fish meat and 30 g of beef (or lamb, pork, etc.). However, it is
not very natural to eat every day products that make up the average daily set. It
would also be strange to eat only fish for the first quarter of the year, the
second quarter
to eat
poultry
and then animal meat.
We will
understand
the
optimality as a
variety of menus, in which the average daily intake of nutrients is achieved
with a given accuracy in a minimum time. This requires the development
of a
specific algorithm for selecting foods
and dishes in accordance with their chemical composition [3] and frequency of
nutrition.
Since this problem does not have an unambiguous
solution, it is necessary to
formalize
the algorithm for selecting dishes from the existing database [4, 5] and
calculating the portion size depending on the user's parameters.
The current state of the
problem being solved is contained, in particular, in the review [6]. According
to [6], there are quite similar programs, such as "Assessment of actual
nutrition", "Individual diet", "Dietitian",
"Nutrilogic", "Idealnutrient" and a number of others, the
initial data for which are the data obtained from the patient's survey: age and
anthropometric data, physical activity data, information about eating habits.
For each product
in
the
program enters the portion size and frequency of consumption. As a result, we
get information about the average daily consumption. The final protocol of the
program contains the calculated level of the value of the main exchange,
recommendations for caloric content, the structure of indicators of food value
by food groups, as well as a graph of the characteristics of food value in
relation to the norms. The standards usually comply with
the recommendations of the Ministry of health [2]. However, there
is no description of the rules for selecting certain dishes in the daily menu
in these programs.
It should also be noted
that existing software products do not assume the possibility of automatically
creating a menu for an arbitrary time period. At the same time, for users with
a specific schedule of daily withdrawals (various types of
fastings
and
traditional holidays), such a schedule is a practical
necessity.
Note that there are
accounting programs for preparing menus and accompanying accounting documents
for public catering establishments that automate the functions of a dietitian,
accountant-calculator or storekeeper for calculating food and accounting for
the preparation of meals in the food units of medical and preventive
institutions of stationary type. Such programs cannot be used for research
purposes, since they do not involve menu variations in relation to the user’s
request.
The main computational
component of software algorithms is filling the daily menu in conditions of
restrictions on the total content of nutrients. The other algorithms are related
to working with databases. The optimization problem does not arise in this
context.
Instead of solving the
ambiguous task of creating a menu, the available programs contain
the
options for standard daily
diets and differ mainly in the volume of databases on products and nutrients.
There are three major
blocks that make up any software implementation of a particular model in the
field of nutrition.
The first block is
the
set of models for the assimilation of
food by human body (or animal, if the task relates to animal husbandry, etc.),
which has certain characteristics. The basic characteristics include gender,
age, height, body weight, fat mass and physical activity. Additional parameters
that affect the choice of food are diseases that (if the user has them)
introduce restrictions or, conversely, certain menu items, as well as the
region of residence, cultural traditions, and individual preferences for
certain products.
The second block is
a
database on the chemical composition
of food. This block includes both the actual nutrient composition of the
products, and the calculation of the corresponding composition, which is
obtained for a dish consisting of a given set of ingredients after its
preparation in a certain way. It should be emphasized that there are no
reliable estimates of the accuracy of the data used. They are only available
for specifically performed experiments, many of which relate to the irrelevant
historical past. It is not clear how well the data used meets modern realities,
even in terms of average values and variance. As a result, a priori
requirements
on
the accuracy of incoming data for
performing computational procedures,
they
are practically important. They show the upper limit of the
error resulting from
calculations
of
portion sizes and menu composition.
An effective tool
to
find accuracy limits in
computational linear algebra problems is the matrix’s
spectral portrait of the
corresponding linear operator, the which construction of which is used in this
work.
The third block is a combined software package of
computational algorithms necessary to solve the following problem: select from
the second block a
set of
products and dishes and determine the amount of their portions necessary to
meet the vector of daily nutrient needs, which are determined in the first
block by the specified anthropometric and other characteristics of the user.
This section also includes
a
set of
the
statistical functions’
set that allow you to perform a comparative analysis of the
various menu options, determine the
accuracy of solving the specified task, classify users by preferred menu types and
solve other statistical problems related to nutrition science.
One of the aspects of the computational program
developed by the authors, related to evaluating of the accuracy of forming a
rational nutrition menu, is presented in this article.
Thus, the calculated menu should be, on the one hand,
quite diverse, i.e. in some sense random, and on the other
– contain the necessary daily calories in
the form of macronutrients. In this paper, an approach to solving such a
problem
is
formulated
and
it
describes
some computational difficulties
encountered along the way.
Let
K
be a total daily consumption of
food and dishes. Usually their number varies from 10 to 20.
Let’s
introduce the following notation. The
vector of nutrient needs
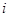 is
considered a given value and is denoted by
is
considered a given value and is denoted by
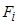 . Both the composition of the products and the ingredients of the
dishes are known. Then it is known the nutrition matrix
. Both the composition of the products and the ingredients of the
dishes are known. Then it is known the nutrition matrix
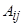 of mass component of
nutrient
of mass component of
nutrient
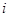 in the dish
in the dish
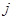 at the rate of 100 g of
the dish. Let us designate
at the rate of 100 g of
the dish. Let us designate
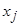 the
value of
the
value of
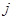 dish portion. Then
the equation to be solved for determining the coefficients
dish portion. Then
the equation to be solved for determining the coefficients
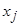 has the form of a linear
system
has the form of a linear
system
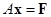 or
or
|
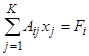 ,
,
|
(1)
|
which must be solved under condition
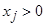 . The matrix
. The matrix
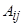 presents
the main characteristics of
the
digital nutrition data base. Its basic minor determines the accuracy
which the weight composition of the menu items is determined.
presents
the main characteristics of
the
digital nutrition data base. Its basic minor determines the accuracy
which the weight composition of the menu items is determined.
Formally, the solution of equation (1) is carried out by
means of the computational linear algebra apparatus, depending on the structure
of the matrix
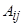 . However, in
practice
there
may
be
difficulties
related
to poor conditioning of the food
matrix.
. However, in
practice
there
may
be
difficulties
related
to poor conditioning of the food
matrix.
The purpose of this paper is to describe a method that
allows you to get a solution in a mathematically correct form and with
reasonable coefficients. Depending on the structure of the food matrix the
following solutions to the equation (1) are possible.
Variant 1.
The number of
menu items is exactly equal to the number of balanced nutrients
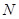 . The matrix
. The matrix
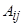 in this case is square
in this case is square
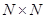 . If this matrix is
nondegenerate, then there is an inverse matrix
. If this matrix is
nondegenerate, then there is an inverse matrix
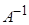 , that is also considered to be known, after which the formal
solution of equation (1) has the form
, that is also considered to be known, after which the formal
solution of equation (1) has the form
|
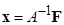 .
.
|
(2)
|
The essence of the problem in this case is to select a
menu for which the components of the found solution (the proportion of dishes
in the menu) are strictly positive and are within some natural dimensions of
the dish, a priori known.
Variant 2.
The number
menu items is less than the number of balanced nutrients. Then the matrix
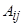 has dimension
has dimension
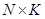 and the basis minor has a
rang
and the basis minor has a
rang
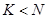 . In general the system is
incompatible in other words, it is impossible to get a solution for all the
nutrients. Necessary condition for the existence of a solution is that rang
A
= rang [A,F], where [A,F] is an extended matrix,
obtained from matrix
A
by adding the vector
F
as an additional
column.
. In general the system is
incompatible in other words, it is impossible to get a solution for all the
nutrients. Necessary condition for the existence of a solution is that rang
A
= rang [A,F], where [A,F] is an extended matrix,
obtained from matrix
A
by adding the vector
F
as an additional
column.
If this condition, which is known from the standard
course of linear algebra, is not met, you can proceed
in the following way.
Since the immediate
goal of a daily diet is to balance calories, not microelements, the three
components (protein, fat, and carbohydrate) can be determined if the number of
meals is at least three. In this case, the remaining components should be
determined by a wider range of consumption times – a week, two weeks, or a
month. Therefore, instead of the original problem, you can solve an equation
with respect to the values of portions, for example, for a menu for a week that
contains at least N dishes, and then divide these dishes by day, taking into
account the daily calorie limit. Thus, the case of the General situation in
this way of solving the problem is the following variant 3.
Variant 3.
The number of
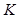 menu items is greater than
the number of balanced nutrients. Then the matrix
menu items is greater than
the number of balanced nutrients. Then the matrix
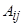 has rectangular dimensions
has rectangular dimensions
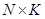 , the basis minor has a
rang
, the basis minor has a
rang
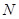 , and a system (1) in
general has more than one solution. If we present the matrix
, and a system (1) in
general has more than one solution. If we present the matrix
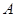 in block form and
designate basis minor
in block form and
designate basis minor
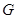 and
remain sub-matrix
and
remain sub-matrix
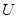 :
:
 .
.
Then the equation (1) has the form:
|
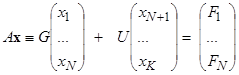 .
.
|
(3)
|
Thus, the coefficients of using the first
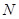 dishes
of the menu depend on randomly selected
non-negative coefficients of the remaining
dishes
of the menu depend on randomly selected
non-negative coefficients of the remaining
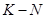 dishes, provided that the solution is non-negative with respect to
all components of
dishes, provided that the solution is non-negative with respect to
all components of
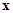 .
.
Therefore, the algorithm of actions for making a daily
menu consists in bringing the number of nutrients and the number of dishes to
an equality. It appears as follows. Let the daily menu ha
s
K
dishes and let
n
be the nearest integer to the ratio of the
number of nutrients to the number of dishes
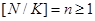 . If
. If
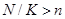 , then some
dishes from the n-day menu are crossed out so that the condition is met
, then some
dishes from the n-day menu are crossed out so that the condition is met
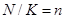 . If
. If
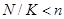 , then some dishes are
added to the menu of the last day. Crossing out and adding is a formal process
and is not a change in the menu, but a formal change in the recipe of some dishes.
, then some dishes are
added to the menu of the last day. Crossing out and adding is a formal process
and is not a change in the menu, but a formal change in the recipe of some dishes.
These actions lead to the formation of a menu for
n
days, based on the calculation that the total number of dishes is equal to the
number of balanced nutrients, so
N.
A matrix is created for each such menu and calculated the inverse
matrix
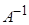 . These objects are the
database’s characteristics
for the chemical
composition of products and dishes, and are not consumer properties, so they
can be calculated in advance. After that, the problem is solved by the formula
(2). However, such standard actions in practical calculations are often
impossible. The reasons for this are discussed below.
. These objects are the
database’s characteristics
for the chemical
composition of products and dishes, and are not consumer properties, so they
can be calculated in advance. After that, the problem is solved by the formula
(2). However, such standard actions in practical calculations are often
impossible. The reasons for this are discussed below.
Let's consider the problem of creating a menu for a
healthy person with certain anthropometric parameters that correspond to a
given daily intake of nutrients and, in particular, calories. In Fig. 1 we
present an example of the accumulated daily caloric content for macronutrients.
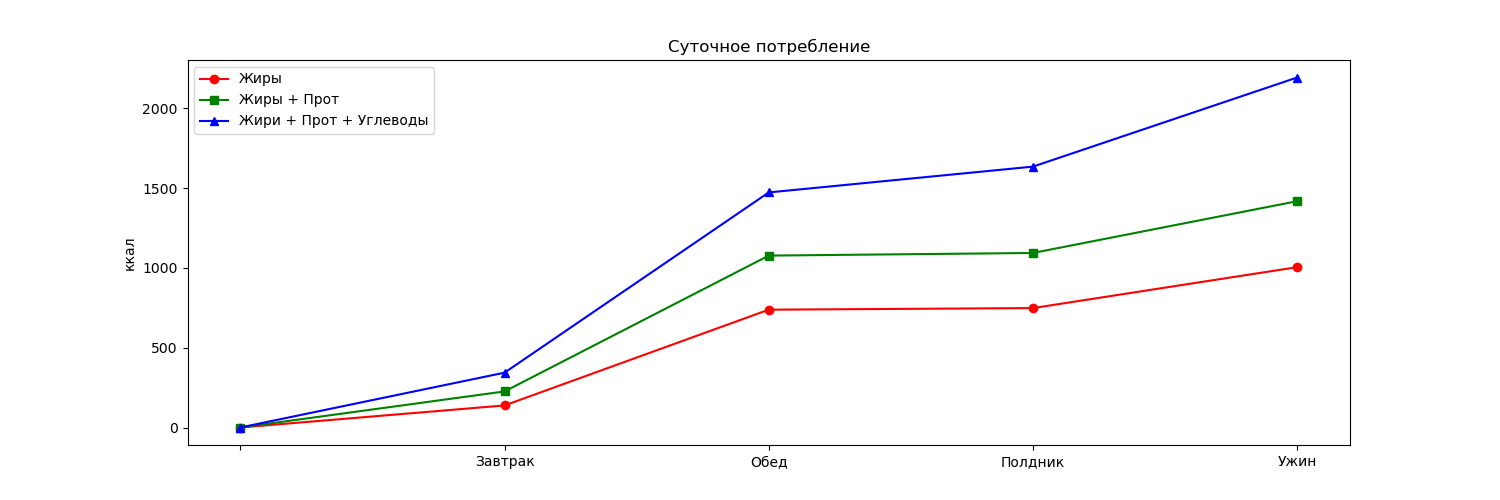
Fig. 1. Typical daily intake of essential
nutrients:
fat, protein and carbohydrates.
When modeling the needs vector, the following list of
nutrients is used.
Macronutrients: 1-fat, 2-protein, 3-carbohydrates.
Micronutrients: 4-vitamin C, 5-vitamin B2, 6-vitamin PP,
7-K (potassium), 8 – Ca (calcium), 9 – P (phosphorus), 10 – Na (sodium).
Micronutrients of small concentrations: 11-vitamin B1,
12-vitamin A, 13-carotene, 14-Mg (magnesium), 15 – Fe (iron).
Let's create a menu in which the number of dishes is
exactly equal to the number of balanced nutrients, without discussing the
method of selecting dishes from the database. An example of this menu is shown
below. Breakfast: 1-semolina porridge with milk, 2-cheese sandwich (sliced
loaf, butter), 3-apricot jam, 4-black tea without sugar. Lunch: 5-Moscow
borscht with meat and sour cream, 6-grain bread, 7-salad of fresh cucumbers and
tomatoes with green onions and mayonnaise, 8-Lula-beef kebab with rice, 9-dried
fruit compote with sugar. Afternoon tea: 10-cappuccino coffee without sugar, 11
- pastry. Dinner: 12-vegetable stew, 13-pistachios, 14-honey, 15-black tea
without sugar.
However, after performing formal calculations using the
formula (2), we get a vector with a negative part of its components as a
solution for the portion size of such a menu, which does not make sense. The
reason for this strange behavior of the solution for a seemingly acceptable menu
is that the nutrition matrix is poorly defined, while the elements of the
database on the chemical composition of dishes are known with relatively low
accuracy (about 10-15 %), which significantly deviates from the accuracy
requirements for the matrix elements for dividing spectrum points.
The computational meaning of dividing the spectrum
points is the following. Assume that all eigenvalues
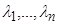 of the matrix
A
are
different. Corresponding eigenvectors
of the matrix
A
are
different. Corresponding eigenvectors
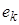 with the conditions
with the conditions
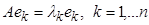 form a linearly independent system of vectors that can be
decomposed both vector F
from
(1) and the desired solution vector x.
Suppose that the coefficients
form a linearly independent system of vectors that can be
decomposed both vector F
from
(1) and the desired solution vector x.
Suppose that the coefficients
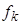 of the expansion of the right-hand side vector are found, so that
of the expansion of the right-hand side vector are found, so that
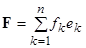 .
Analogously
.
Analogously
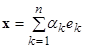 .
Substituting the
expansions for F and x
in equation (1), we obtain
a system for determining of the values
.
Substituting the
expansions for F and x
in equation (1), we obtain
a system for determining of the values
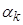 . The solution has the form
. The solution has the form
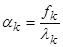 .
However, if the uncertainty in the elements of the matrix is such
that, when calculated with this accuracy, the points of the spectrum are
indistinguishable, then the eigenvalues are considered multiples, and a
different formula is required to construct the solution. Spectral portrait is
an effective method for determining the sufficient accuracy of input data on
the studied matrix’s structure to apply the above formulas.
.
However, if the uncertainty in the elements of the matrix is such
that, when calculated with this accuracy, the points of the spectrum are
indistinguishable, then the eigenvalues are considered multiples, and a
different formula is required to construct the solution. Spectral portrait is
an effective method for determining the sufficient accuracy of input data on
the studied matrix’s structure to apply the above formulas.
To determine what accuracy requirements should be
applied to the elements of the food matrix, we will build a spectral portrait
of it. The construction of spectral portraits of matrices is based on the
procedure described in the book [6]. The portrait shows the areas where the
eigenvalues of matrices lie, if the elements of these matrices are known with
the precision that the decimal exponent of which is specified in the legend.
In terms of resolvent of nutrition matrix
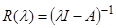 the corresponding
the corresponding
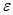 -spectrum is defined as
follows: the value
-spectrum is defined as
follows: the value
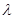 is
belonged to
is
belonged to
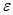 -spectrum
-spectrum
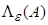 , if
, if
|
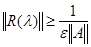 .
.
|
(4)
|
In the studying the location of the spectrum points it
is convenient to consider a closed smooth curves
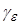 , representing the contours of
, representing the contours of
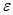 -spectrum. The quality of the dichotomy
-spectrum. The quality of the dichotomy
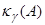 is estimated by the norm
of the square of the resolvent (4) on this curve:
is estimated by the norm
of the square of the resolvent (4) on this curve:
|
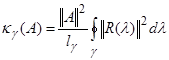 .
.
|
(5)
|
Here
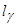 is a contour length
is a contour length
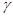 . The value of
. The value of
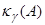 can be considered an
indicator of the accuracy of spectrum separation. If there are no spectrum
points
can be considered an
indicator of the accuracy of spectrum separation. If there are no spectrum
points
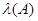 on a certain
curve
on a certain
curve
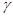 , then the norm of the
resolvent on such a curve is finite
, then the norm of the
resolvent on such a curve is finite
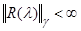 , as is the integral of it on this curve. This representation is
used for numerically finding the
, as is the integral of it on this curve. This representation is
used for numerically finding the
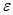 -spectrum of the matrix. The algorithm is arranged as follows. The
complex plane is divided into concentric circles in increments
-spectrum of the matrix. The algorithm is arranged as follows. The
complex plane is divided into concentric circles in increments
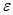 . For each circle the
integral (5) is calculated numerically. The logarithmic growth of this integral
during the transition from one circle to another indicates an approximation to
the eigenvalue of the matrix
A. The subsequent decrease in the integral
(5) allows us to determine the ring, in which the eigenvalue of the matrix
lies, estimated with a given accuracy
. For each circle the
integral (5) is calculated numerically. The logarithmic growth of this integral
during the transition from one circle to another indicates an approximation to
the eigenvalue of the matrix
A. The subsequent decrease in the integral
(5) allows us to determine the ring, in which the eigenvalue of the matrix
lies, estimated with a given accuracy
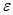 . Comparing the values of the integral (5) obtained when dividing
the complex plane into curves, the color of the corresponding points of this
plane, we get a spectral portrait of the matrix.
. Comparing the values of the integral (5) obtained when dividing
the complex plane into curves, the color of the corresponding points of this
plane, we get a spectral portrait of the matrix.
The food matrices’ typical spectral portraits of the
traditional food’ daily menu and vegan menu are shown in Fig. 2-3. From this it
follows that in order to correctly solve the food equation (1), the elements of
the matrix
A
must be known at least with accuracy
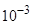 (when the eigenvalues of
the matrix are separated), which is not actually realized.
(when the eigenvalues of
the matrix are separated), which is not actually realized.
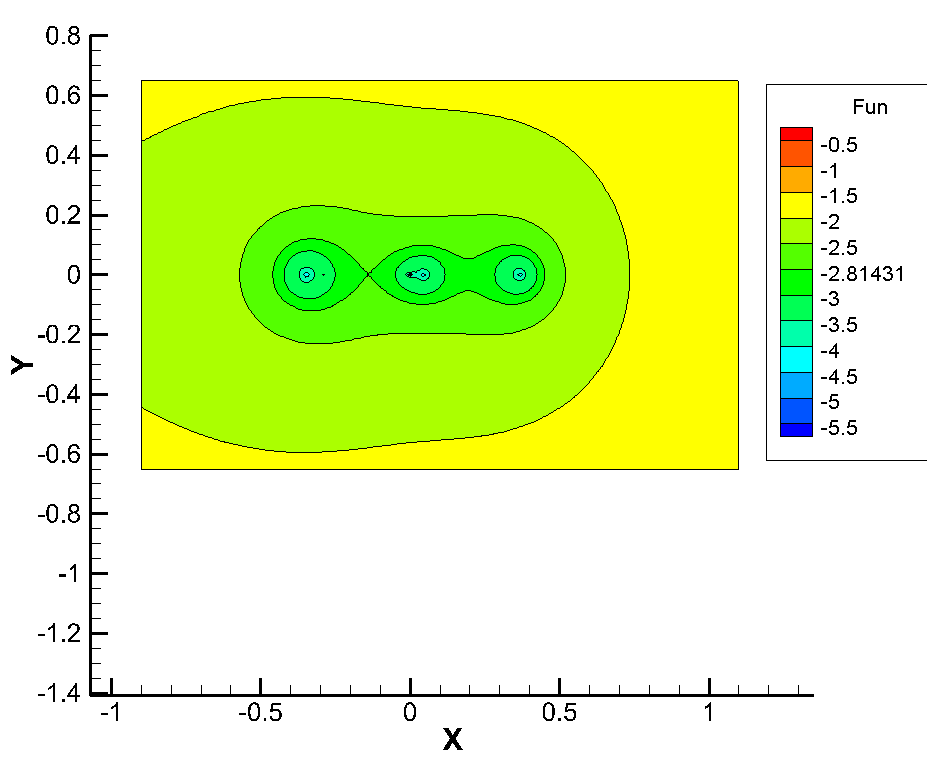
Fig. 2. Spectral portrait of traditional
nutrition matrix.
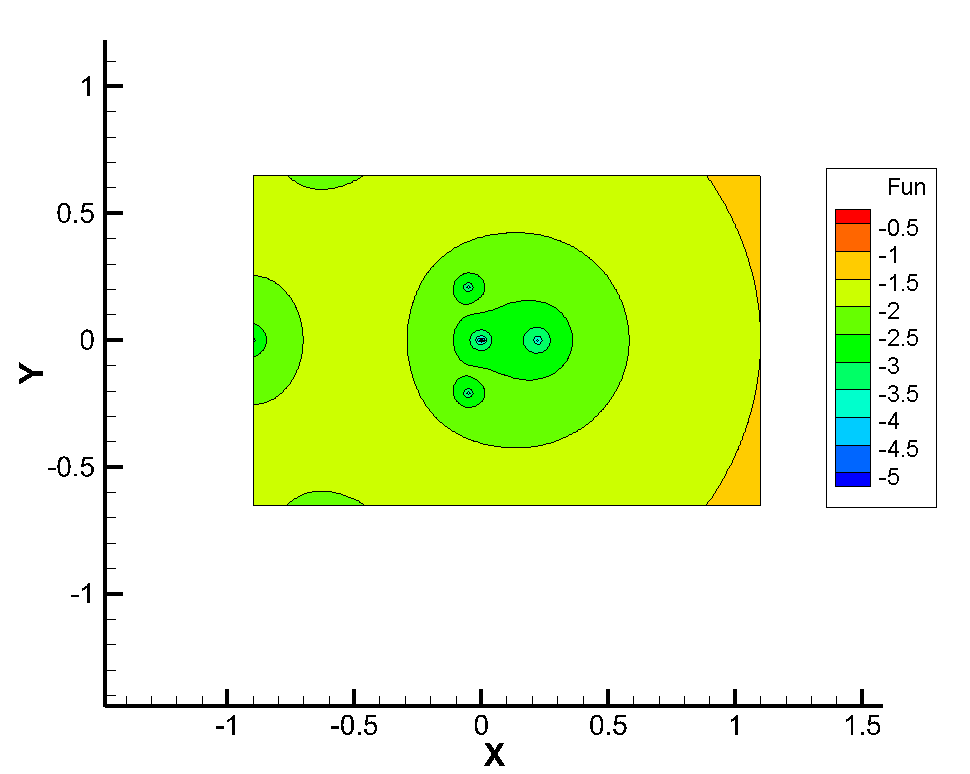
Fig. 3. Spectral portrait of vegan nutrition
matrix.
The meaning of these drawings is following. If the
relative accuracy of the matrix elements is
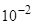 (yellow background), then the matrix has one eigenvalue (or rather,
15 matching ones) that are located somewhere in the marked square. With the
accuracy
(yellow background), then the matrix has one eigenvalue (or rather,
15 matching ones) that are located somewhere in the marked square. With the
accuracy
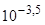 in Fig. 2 one
can see three bluish circles containing all 15 eigenvalues, which are perceived
as three in this case. In Fig. 3 the division of the spectrum points (already
into four bluish circles) occurs with accuracy
in Fig. 2 one
can see three bluish circles containing all 15 eigenvalues, which are perceived
as three in this case. In Fig. 3 the division of the spectrum points (already
into four bluish circles) occurs with accuracy
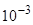 , i.e. the nutrition matrix of a vegan is somewhat better
conditioned than that of a meat eater. However, this matrix is not applicable
for calculating menu portions, since, as mentioned above, the accuracy of the
matrix data of the chemical composition of dishes is no better than
, i.e. the nutrition matrix of a vegan is somewhat better
conditioned than that of a meat eater. However, this matrix is not applicable
for calculating menu portions, since, as mentioned above, the accuracy of the
matrix data of the chemical composition of dishes is no better than
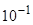 .
.
From this consideration, it also follows that increasing
the number of days when calculating the menu will not change the proportion
between nutrients, and therefore simultaneous calculation of the values of
portions of dishes under conditions of control of all 15 nutrients at a given
level of accuracy is not possible. Indirectly, this state of Affairs is
evidenced by the absence of a description of the calculation algorithm in
existing software products, i.e. the menu in these programs is actually built
not by calculation, but by selection. The accuracy of the selection is also not
specified, as is the characteristic deviation of the percentage of nutrients in
certain products from the standard prescribed in the database.
From a computational point of view, the problem is that
the menu contains dishes with a high content of macronutrients, as a result,
the proportion of micronutrients in their background can’t be determined with
the necessary accuracy. Let's proceed as follows. Let's select the rows of the
system (1) with the dominant elements related to macronutrients, and combine
the menu items so that instead of a poorly conditioned matrix 15*15, we get a
"good" matrix 3*3. Note that the idea of balance only for
macronutrients is used in some calculations (see, for example, [8]), but
without explaining the reasons for this choice.
Grouping dishes allows you to analyze the food matrix
only in part of macronutrients. The spectral portrait of such a matrix is shown
in Fig. 4.
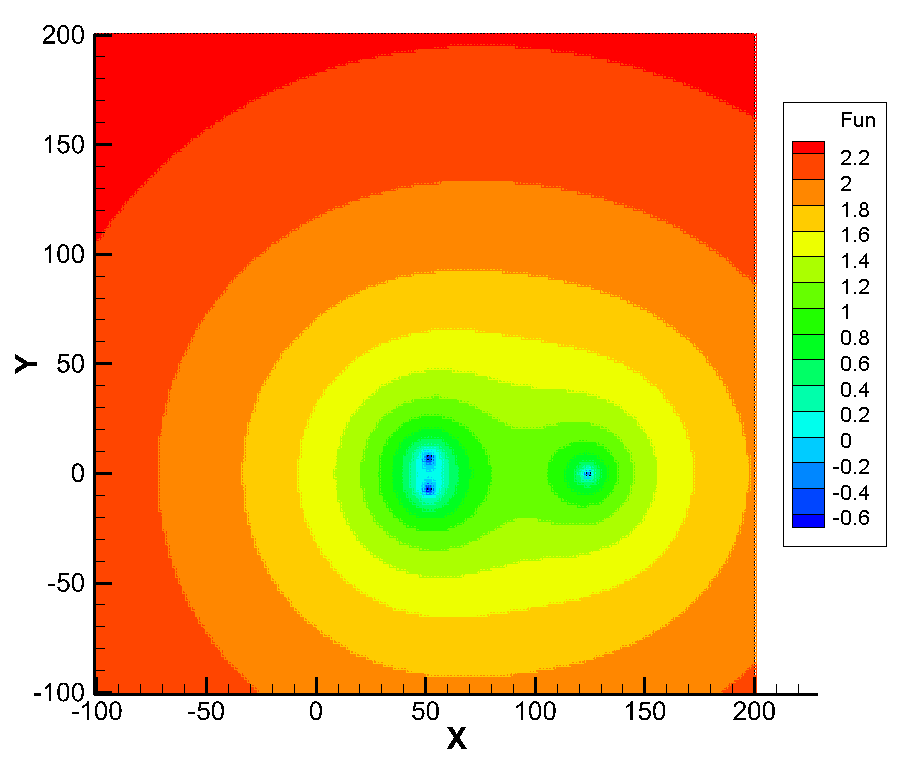
Fig. 4. Spectral portrait of the enlarged
nutrition matrix.
Coordinates
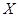 and
and
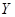 in the Fig 4 correspond to
the points of the complex plane where the spectrum of the matrix
in the Fig 4 correspond to
the points of the complex plane where the spectrum of the matrix
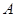 can be located. Red,
orange, yellow and light green areas correspond to a consistently decreasing
inaccuracy (from 10 000% to 400%) in the matrix elements, in which its
three eigenvalues are still not recognized. At an inaccuracy level of 160 %,
the spectrum splits into two blue regions. Three eigenvalues of this matrix are
identified, starting with an error of approximately 0,4 (
can be located. Red,
orange, yellow and light green areas correspond to a consistently decreasing
inaccuracy (from 10 000% to 400%) in the matrix elements, in which its
three eigenvalues are still not recognized. At an inaccuracy level of 160 %,
the spectrum splits into two blue regions. Three eigenvalues of this matrix are
identified, starting with an error of approximately 0,4 (
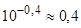 ). This means that even for
very inaccurate measurements of the dishes’ chemical composition, the solution
of the problem for macronutrients will be correct.
). This means that even for
very inaccurate measurements of the dishes’ chemical composition, the solution
of the problem for macronutrients will be correct.
Let's consider the selection of dishes. A special
feature of our algorithm is to create a menu with a planning horizon
significantly longer than one day. It is convenient to consider a month as a
planning unit. Then, based on the actual data of Rosstat
the
annual food consumption, you can
determine their average monthly consumption. For a certain type of user, taking
into account their age, gender, anthropometric and other data, these average
values are corrected based on statistical models that are not discussed here.
After that, the number of food types consumed during the month (meat dishes,
poultry dishes, etc.) is determined, each of which is the main supplier of one
of the macronutrients. Since the daily menu of the dishes’ types is known, it
remains to choose representatives of these types. To do this, a random set of
numbers is generated –
the
dishes’
IDs of this type
in the database. Then, after combining them into groups,
the
equation (1) for the enlarged food
matrix is solved. As a result, macronutrients are precisely balanced, but
micronutrients may have noticeable deviations from the set standards. For each
nutrient we will enter a daily deviation of the calculated consumption from the
set one:
|
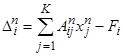 .
.
|
(6)
|
We also introduce the accumulated average modulus of
relative deviation
|
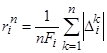 .
.
|
(7)
|
Menu optimization is a search of options within the
types of dishes in the database, in which the value
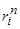 reaches the specified
level of accuracy in the minimum number of days
n. This ensures both the
preservation of a given level of nutrient consumption, and a sufficient variety
of nutrition. If the database on the chemical composition of dishes is
sufficiently diverse and contains about a thousand different dishes, then each
of the remaining micronutrients can be balanced with a relative accuracy of
0,10 in less than two weeks.
reaches the specified
level of accuracy in the minimum number of days
n. This ensures both the
preservation of a given level of nutrient consumption, and a sufficient variety
of nutrition. If the database on the chemical composition of dishes is
sufficiently diverse and contains about a thousand different dishes, then each
of the remaining micronutrients can be balanced with a relative accuracy of
0,10 in less than two weeks.
Note that in conditions of special restrictions
(exceptions), the balancing of micronutrients occurs somewhat later than for
food without restrictions, although the food matrix is better conditioned for
menus with exceptions. We emphasize that vitamins in tablets are not considered
as possible products.
In this paper, an algorithm for selecting database
components and calculating the corresponding weight coefficients of these
components under conditions of poor conditionality of the linear relationship
matrix is constructed. In relation to the challenges of the digital nutrition
this algorithm is applied to build daily food menu for freely definable
planning horizon. The calculation visualization method used in this work
is
based on the construction of a spectral
portrait of the nutrient matrix, has led to the need to segment the calculation
in such a way as to reduce the computational error. It is shown that the
optimization problem in terms of nutrition diversity can be solved by the
proposed method.
1. David A. Bender
An introduction to nutrition and metabolism // CRC Press, 2014
2. Methodical
recommendations of MP 2.3.1.2432-08 “Norms of physiological requirements for
energy and nutrients for various groups of the population of the Russian Federation”
(approved by the chief state sanitary doctor of the Russian Federation on
December 18, 2008).
3. Tutelian V.A.,
Samonov M.A., Kaganov B.S., Baturin A.K., Sharafetdinov H.H., Plotnikova O.A.,
Pavluchkova M.S. Cardboard dishes of dietary (therapeutic and prophylactic)
nutrition optimized composition. - M.: National Association of Clinical
Nutrition, 2008. - 448 p.
4. Tutelian V.A.
The chemical composition and calorie content of Russian food. Directory. - M.:
DeLi print, 2012 .-- 284 p.
5. Raper N.,
Perloff B., Ingwersen L., Steinfeldt L., Anand J. An overview of USDA’s Dietary
Intake Data System // J Food Compos Anal, 2004.17 (3–4).
6. Portnov N.M.
Electronic Doctor // Practical Dietetics, 2012, 2 (6).
7. Godunov C.K.
Modern aspects of linear algebra. - Novosibirsk: Scientific Book, 1997. – 388p.
8. Grashchenkov
D.V. Mathematical modeling of formulations for the organization of baby food //
Food Industry, 2018, 3 (4).