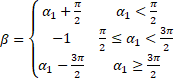The process of constructing virtual cities and
populate them with virtual agents is increasing as a research area in computer
graphics and artificial intelligence. Developing environments with intelligent
agents implies several challenges, for instance, rendering thousands of objects
within any given scene with geometric and topological variety is complex and
many computational resources such as memory and processing power are required.
A wide range of areas such as games movies, or urban simulation require virtual
3D city models with detailed geometry.
Additionally, Agent-based simulation of
credible actors in large-scale urban environments is a growing research domain,
with numerous applications ranging from security to crisis management,
entertainment, urban planning and virtual training [Navarro11].
Simulating hundreds of thousands of individual agents within a very large
environment like an airport, a crowded train or station or a whole mega city
requires significant computational power. The generation of large urban
environments typically involves different stages. Heavily simplifying this
model based on a fixed grid layout, a city of finite extent can be generated
for a single view on the CPU and rendered efficiently on a GPU. Level of detail
techniques work properly. Those techniques tend to adapt the complexity of the
3D models based on the viewpoint of the observer by limiting the number of
polygons displayed by the graphic engine in each frame of simulation.
Therefore, meshes with a high polygon count often must be simplified to achieve
acceptable display rates [Sullivan02].
The creation of urban
environments involves a lot of different but related tasks such as the
processing of geographic information, the visualization of crowds and the
generation of steering behaviors [Silverira2006]. All above with the
goal of producing a simulation useful and plausible. In the following
paragraphs we discuss some of the relevant works that addresses the tasks enlisted
previously.
The rising of geographic information
systems and data acquisition have led to increase the demand of visualization
software in terms of 3D globe-based interfaces, consequently the need for
develop algorithms to reconstruct 3D data using primarily 2D objects was increased
in the same order. An example of this is the work presented by Essen which
describes a method to produce 3D maps taking as a base 2D city maps containing
relevant features. [Essen2008], by using GPS traces we were able to
extract urban and city information to create complex environments using real
data and combining them with an interactive crowd, on figure 1 it can be seen a
visualization of people’s average flow registered by GPS sensors, the greener
the street, the higher the stream of people walking on the street.
On the other hand, the work of Thomsen
et al. [Thomsen2008] introduces a general approach for modeling in 3D
GIS addressing the problem of using 3D data in comparison with traditional 2D
and 2.5D and how the context of topological abstraction influences the result,
depending on the operations to a certain set of data. Using a cell layout,
hierarchies are created, and geometry can have a mesh representation.
The kind of videogames with detailed urban
virtual worlds where the players can explore, and approach objectives freely
has become a success in the market. The process of creating such environments also
known as Open Worlds takes many hours of work. To face this scenario researchers
have used procedural modeling via shape grammars with production rules that
iteratively evolve a design by increasing the details. The main advantage of
this kind of techniques is that the creation of the hierarchical structure is
specified in the modeling process. This semantic information allows to reuse
design rules bringing forth procedural variations and then creating a large
variety of architecture flooding a whole city. However, the completion of this process
can take hours and consumes a huge amount of memory (tera-bytes of storage),
when rendering a city like Manhattan, which consists of more than 100,000 buildings
[Loviscach06].
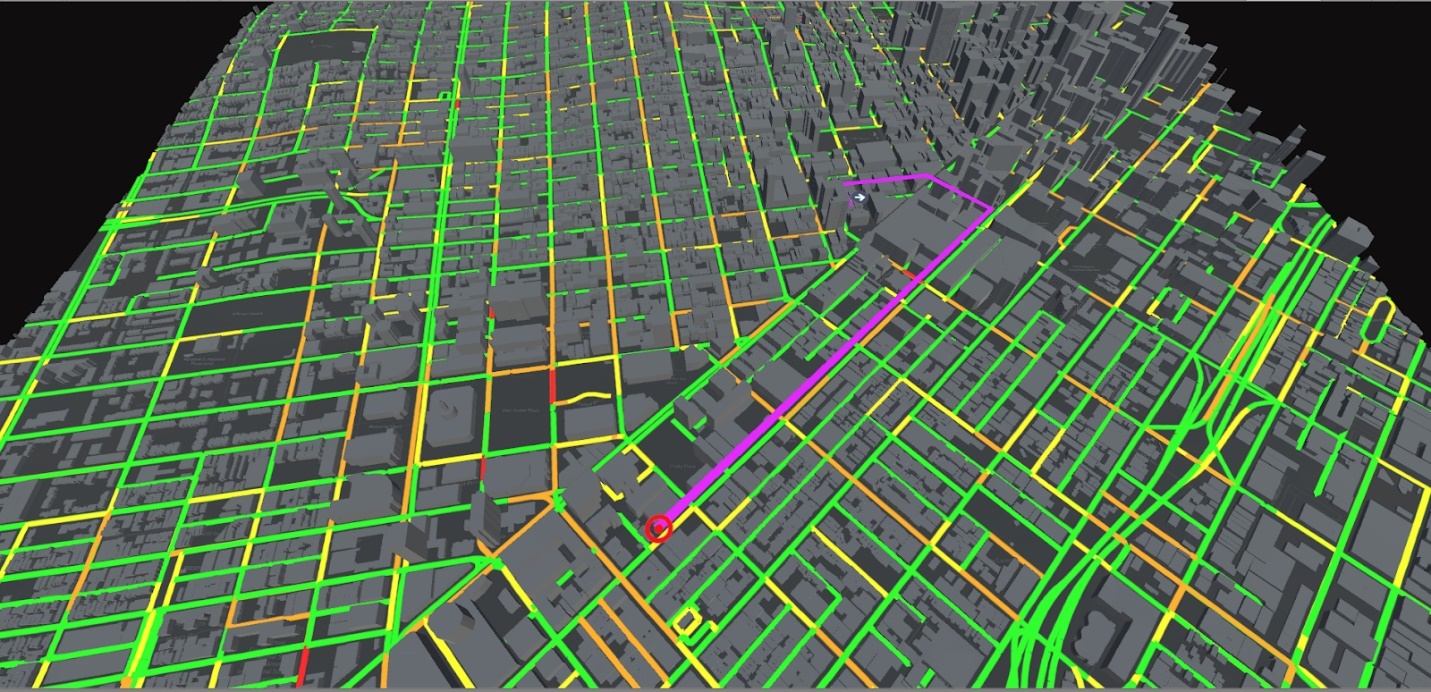
Figure 1. Visualization of people’s average flow registered by GPS.
Some researchers have introduced parallel
architectures such as graphics processing unit (GPU). These works take into
consideration account visibility and different level of detail. This way faster
rendering is achieved. An adaptive level of detail is used as well and a
dynamic vertex buffer and index buffer that allows geometry to be generated at
any point during grammar derivation on the GPU. It is important to address that
this simulation must run at interactive frame rates (at least 30 frames per
second). Thalmann and Boatright [Thalmann09, Boatright2013] stated that
additional challenges such as Variety in both appearance and animation and
behaviors.
Pedestrian steering behaviors or pedestrian
motion involves the behavior of an individual by considering the other members
of the crowd. According to Pettre [Pettre2009], steering has a big
influence to get a plausible and a realistic crowd, and that is the main
motivation behind being included as a part of the simulation workflow.
To address steering behavior, researchers have
proposed different approaches following two alternatives. The first one is to
deal the crowd as macroscopic phenomena. In this case, the crowd is simulated
by using PDEs (Partial Differential Equations) with physic models treating the
crowd as a whole [Shinohara2011].
However, physics models have problems in
simulating complex behaviors, since a fluid particle does not have a preferred
direction of motion, does not have goals and cannot make decisions [Dai2013].
An alternative to the macroscopic approach is to deal with every agent in the
crowd individually. This approach is called microscopic. Among the microscopic
algorithms used to simulate dense crowds we have three main categories: vector
based, agent based and data-driven techniques. One of the first research
centered on microscopic simulation of autonomous virtual agents and their
steering behaviors was presented by [Reynolds1987]. Several years later
Helbing et al. presented the social forces model, where each agent tends to
move at a desired velocity while applying friction and repulsion forces against
obstacles and other agents [Helbing1995]. According to the authors,
social forces are well suited for pedestrians in normal, or known, situations.
The social forces model has been extended to support social groups of related
pedestrians by Moussaïd et al. [Moussaid2010].
These kinds of methods can produce realistic
results for specific situations or do not provide group steering behaviors. To
do so, many finely tuned specific rules are required. As an example of the
later, the work of [Lakoba2005] presented a modified version of
Helbing's social force model proposed up to 24 parameters to set up. Sometimes tuning
several parameters is a challenging task and often requires a lot of trial and
error, this being an impediment to using this kind of methods for authoring
tools. Particularly in the cases when it is necessary to add new behaviors and
a new set of rules needs to be defined. Data-driven techniques generate behavior
models by recording real pedestrian trajectories in video sequences. This
approach generates several example situations and actions for the characters.
Lerner et al. [Lerner2007] used video samples to construct a large
example database. This database contains the data necessary to simulate
individual trajectories. The amount of memory required to store the examples it
ranges between 50MB to 150 MB. Containing up to 42K of trajectories. On the
other hand, Lee et al. [Lee2007] used the environment and the motion of
nearby agents observed in video sequences to determine the moving trajectories
of each simulated agent. Focusing its work on recreating groups dynamics rather
than individual steering. In addition [Sun2011] presented a data-driven
collision avoidance algorithm and recently Charalambous et al. [Charalambous2014]
presented a method for the synthesis of steering behaviors by abstracting the
pedestrians steering behaviors in a structure called perception-action graph.
Data-driven works usually don't model social group behavior and when they do
the database grows significantly. In conclusion, data-driven models create very
realistic results but require many examples and large amounts of memory to
cover the complexity of social human behavior.
As mentioned before, the process of
creating a complex urban environment is not a trivial task, many variables are
involved in the process. Computational resources must be addressed when
creating large scenes in consequence memory consumption becomes bigger for
every additional element added to the virtual world. Nevertheless, memory is
not the only problem, since these scenarios also consider high density crowds
within, thus the time consumed by processing the simulation must be properly
bounded to ensure an acceptable performance.
Our goal in this proposed workflow is
to ensure the simulation and the visualization of the virtual urban environment
runs at interactive frame rate (at least 30 frames per second), to achieve this
we divide this task in two different
stages, the simulation stage and visualization stage, the completion of these
two stages allows to the system to generate a plausible urban environment into
the simulation.
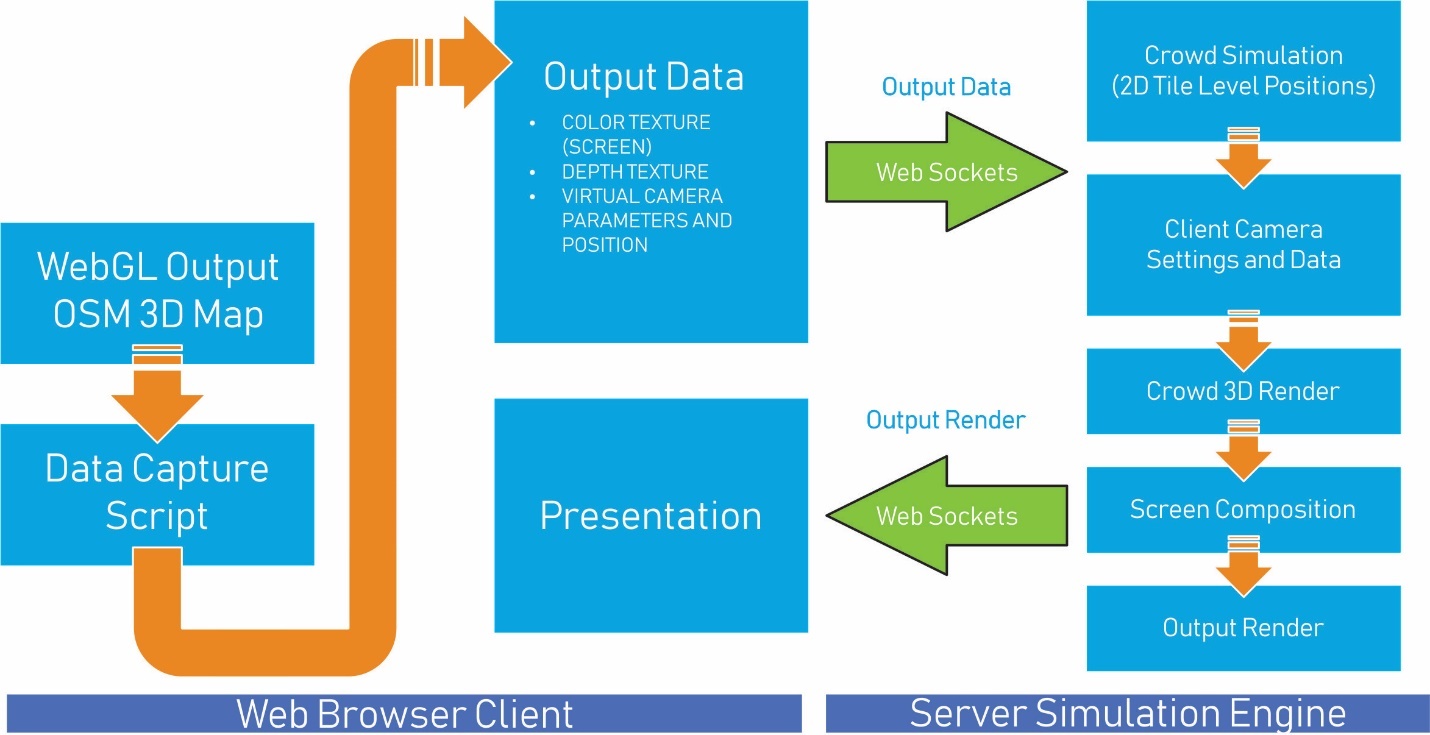
Figure 2. Visualization Engine Architecture.
Figure 2 gives an overview on how
the pipeline is currently working, we make our simulations using a webserver
which allows to communicate within the application to fetch and process
important data. The client initializes local map information to construct the
environment, here we load all the requirements and begin the simulation, for
instance, we fetch the OSM (Open Street Map) 3D map and the output is sent to
the server where data is synchronized and get the final render. Figure 3 shows
an example of the depth buffer also known as Z-buffer, this buffer is generated
by rendering an extruded scene from the urban environment.
Figure 3. Z-buffer generated from OSM data.
Under this conception our client (a
web browser) is used to visualize the urban crowd, therefore our server will be
a dedicated process running the crowd simulation in an urban map scene. The
server process uses web-sockets to establish a communication channel between
the server and the browser, the general idea of communication between server
and client is depicted in figure 2. On the following section we detail the jobs
performed both by the client and the server.
In the client side we have coded a script in a
web page that uses a lightly modified version of open Source Tangram, which is
a visualizer of urban environments in 3D, using Open Street Maps (OSM) geometry
as input. The output is an interactive version of a city using real world
information, which allows the users to navigate freely in the environment, our
main focus in this stage is to synchronize the camera with the information that
is displayed and merge it with our simulation, whenever the user applies any
transformation to the camera, (i.e rotation or translation) we extract the
depth buffer (DBF) of the scene, we also retrieve the scale in pixels per meter
of the current zoom level, the 2D position relative to the current map, and the
RGB of that specific frame. This is used to reconstruct the scene later and
composite it with the crowd.
The server side is the one that performs all
the important data processing, all the process starts when the master process
initializes the simulation and render parameters, the slave processes are also
initialized, and will be running and simulating a predefined Map (in this case
a part of an arbitrary city). The master process will spawn a server process
with the web sockets protocol listening for a client. When the client performs
a connection with the server, the initial simulation parameters are processed
(world map position the most important). After that, the slave processes are
taken from the idle state to a simulation state, the relative camera position
and important data are loaded from the sent client frame buffer and the camera
position is distributed from the master process to the slave process of the camera,
along with other necessary render parameters. This scene is rendered from every
slave process camera’s point of view to a texture. The rendered scenes textures
are sent to the master process, and the image composition is performed by the
master process. Finally, the output render is sent to the client by the server
process, all this will be repeated in an infinite loop until the client close
the current connection or a prudent time without response from the client will
be expired.
Compositing in OpenGL is a straightforward
process and its implementation on the GPU shading language also. To create a
compositing we only need a fragment shader that writes the depth and the output
color of every screen pixel for each composited image in our pipeline; as an
example if we have 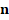 processes rendering a part of a crowd in a
separated Frame Buffer Object (FBO) to a texture along with its depth buffer,
the master process will take each one of the output render textures and will
render
processes rendering a part of a crowd in a
separated Frame Buffer Object (FBO) to a texture along with its depth buffer,
the master process will take each one of the output render textures and will
render 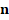 times simply writing the depth value (usually glFragDepth ) and
the texture output color using the GL DEPTH TEST option enabled to allow
the render automatically discard the all the fragments, with exception of the
closest one written by the master process, on figure 4 we have the Join of two
computational jobs to obtain a composite image, the first component corresponds
to the output of four partial rendering processes of the crowd characters and
the second one corresponds to the process that generates the background.
times simply writing the depth value (usually glFragDepth ) and
the texture output color using the GL DEPTH TEST option enabled to allow
the render automatically discard the all the fragments, with exception of the
closest one written by the master process, on figure 4 we have the Join of two
computational jobs to obtain a composite image, the first component corresponds
to the output of four partial rendering processes of the crowd characters and
the second one corresponds to the process that generates the background.
Figure 4. Join of two computational jobs yielding a composite image.
There are several techniques employed to
create complex urban scenarios, some use a detailed model generated from scans
and photographs, some others simply use extrusion to generate buildings of the
appropriate height from the contours in the 2D map and height information. We
chose to use “MapzenTangram”, where as stated in its manual, we can
generate extruded buildings by using a function that applies to polygons and
lines, and returns such features drawn with the polygons draw style into 3D space
along the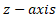 . this function raises elements drawn with the lines draw style
straight up from the ground plane, using the values in the feature’s
. this function raises elements drawn with the lines draw style
straight up from the ground plane, using the values in the feature’s 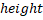 and
and 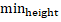 properties. Our web application will call Mapzen Tangram to generate an
appropriate 3D view of the city, using extrusion, whenever the mouse is moved.
from this view, we generate the color and depth buffers by rendering (as
explained in the following). these buffers and the appropriate camera
parameters are used to generate the rendering of the crowd and generate the
final composite image.
properties. Our web application will call Mapzen Tangram to generate an
appropriate 3D view of the city, using extrusion, whenever the mouse is moved.
from this view, we generate the color and depth buffers by rendering (as
explained in the following). these buffers and the appropriate camera
parameters are used to generate the rendering of the crowd and generate the
final composite image.
Finally, to make each pedestrian inside the
virtual environment move realistically, we need a system able to simulate the
subtle variations on the steering behavior of pedestrians without needing large
amounts of data, we extracted from videos the steering movements of pedestrians
and store them as examples to create a knowledge base of learned steering
behaviors. To model social group phenomena, we used group social forces
proposed by Moussaïd [Moussaid2010]. In this manner, we get the
best features of both models.
The first goal of the process is to obtain
from the video a record of each path followed by each pedestrian. Each path is
processed and later use to create a data structure for store these steering
behaviors. We use a video shot looking directly down on the subject, also
called bird’s eye view shot. This view is chosen to avoid occlusions and
artifacts in the tracked paths usually caused by inconsistent mappings between
the real world and the image coordinates. A general plane to plane projective
mapping is given by the equation:
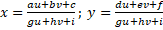
Eq. 1
From the above 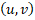 represents world coordinates,
represents world coordinates, 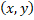 correspond to images coordinates, and
correspond to images coordinates, and 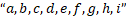 are calibration constants.
Using a top-down shot the equation 1 tends to be closer to:
are calibration constants.
Using a top-down shot the equation 1 tends to be closer to:
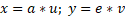
Eq. 2
The scene is split into background and
foreground using the codebook algorithm [Schreiber2009]. Foreground
regions are considered region of interest “ROI”. These ROIs are passed one by
one to an LBP feature extraction module and then are classified as human head
or not. Once a human head is detected, a point is associated with it. Each
detected point is tracked over every frame using the pyramidal version of the
Lucas-Kanade tracker implemented on the OpenCV library (see figure 5), The pipeline
of human tracking starts with top view shots. then the human heads are
segmented and tracked to get the path of every pedestrian in the scene.
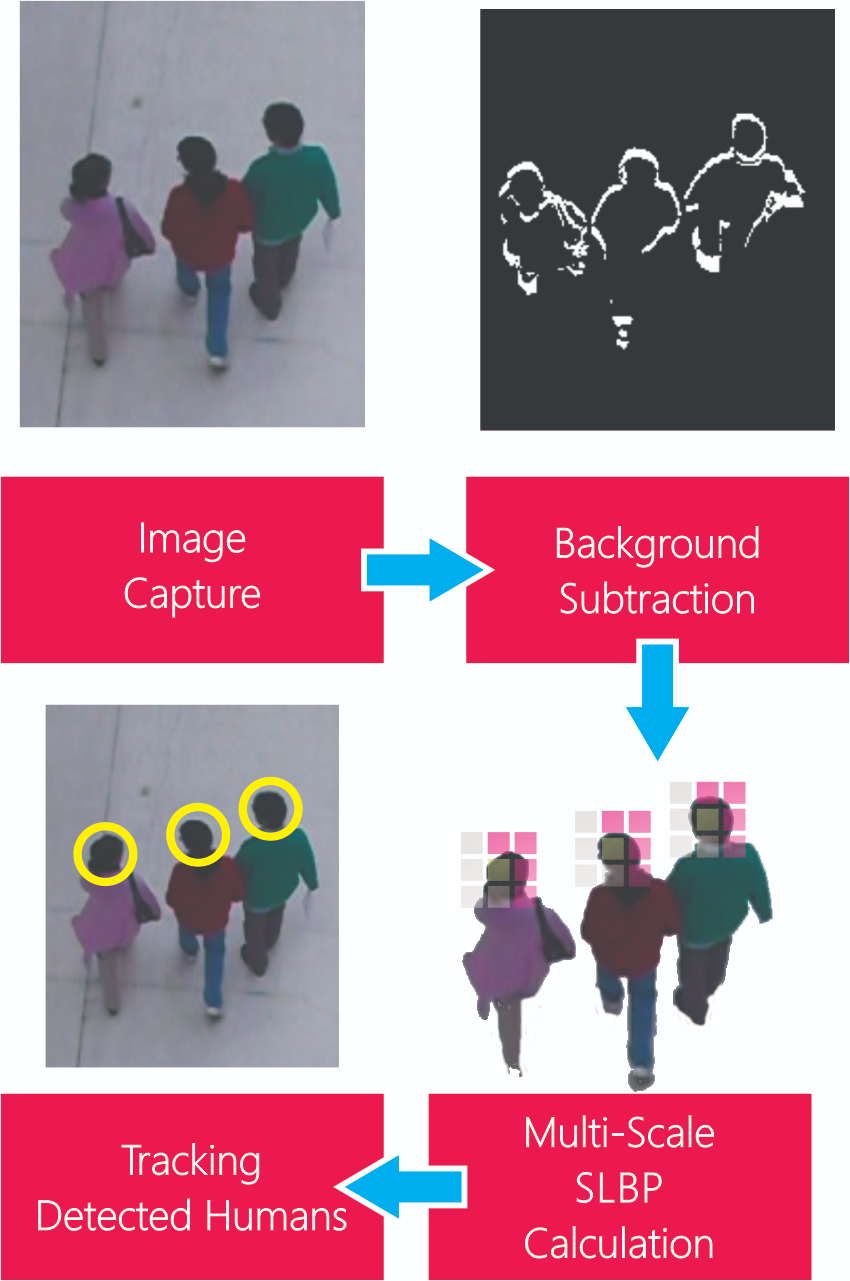
Figure 5.
Human tracking pipeline.
A trajectory of each pedestrian 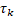 is defined as a set of
is defined as a set of 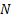 displacements
displacements 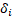 from position
from position 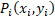 to
to 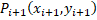 . In consequence each displacement
. In consequence each displacement 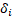 is given by:
is given by:
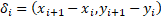
Eq. 3
Therefore 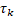 is conformed as:
is conformed as:
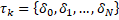
Eq. 4
Once all the trajectories have been collected,
the next step is to extract a tuple of set of features and actions to build the
behavior cores [Lee2007]. We propose a set of 3 features which have
strong influence in the steering decision of a pedestrian: normalized
pedestrian velocity, closeness to goal and obstacle code.
Before explaining how to get the normalized
pedestrian velocity, we need to describe how to get the goal vector,
which is expressed in the following equation:
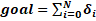
Eq. 5
The data we have collected is made of a wide
range of starting points and destinations of each pedestrians. To better deal
with each agent's decision-making process, is necessary normalizing the vectors
that describe movement. Given the fact that the goal vector is defined
as the sum of the partial displacement of a pedestrian, we decided to transform
the global coordinate system obtained in the tracking visual phase to a local
one, offsetting all displacements to make the goal vector pointing
toward the local “y” axis. Therefore, given a goal vector, we use
a vector 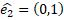 to get a normalization angle, which is the angle needed to align the
goal vector with “y” axis. We call it a normalization angle which is
calculated using the following equation:
to get a normalization angle, which is the angle needed to align the
goal vector with “y” axis. We call it a normalization angle which is
calculated using the following equation:
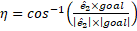 eq. 6
eq. 6
Given a
vector displacement 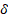 . The normalized
version
. The normalized
version 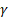 of that vector
according to angle
of that vector
according to angle 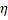 is given by the
following expression:
is given by the
following expression:
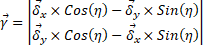
Eq. 6
Therefore,
once we calculate the normalized angle, the goal vector is rotated or
normalized using equation 6. Producing the goalN, notice the new vector
has no “x” component due to normalization. See figure 6.
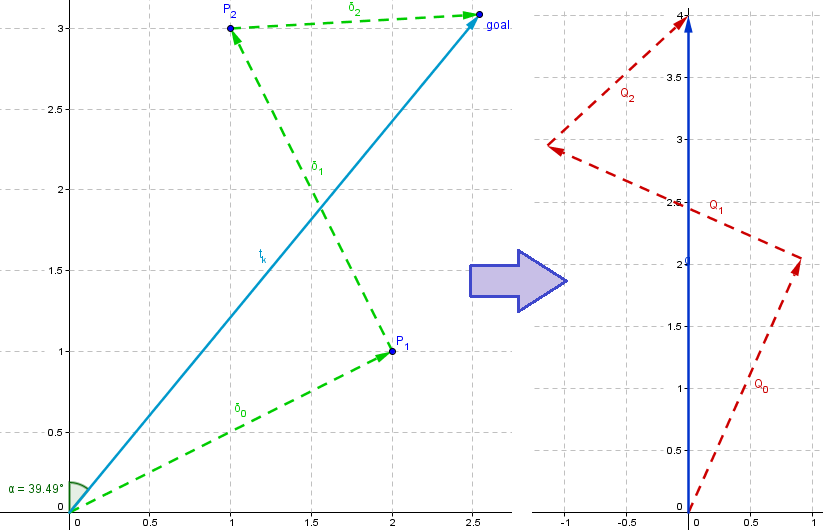
Figure 6.
This figure shows on the left a path obtained from the tracking process, on the
right the normalized version.
The second
feature is the velocity, this factor comprises the rate of change of time, 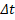 of the displacement of the pedestrian as a function of time. The
velocity given by equation 7 provides part of the component of behaviors that
describe collision avoidance.
of the displacement of the pedestrian as a function of time. The
velocity given by equation 7 provides part of the component of behaviors that
describe collision avoidance.
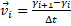
Eq. 7
Once the
velocity has been calculated it is reoriented by the normalization angle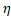 . From here we will call as
. From here we will call as 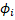 to all the velocity vectors normalized using equation 6.
to all the velocity vectors normalized using equation 6.
The next
feature is the closeness to goal, this feature outlines how close (in
percentage) the pedestrian is from its current position to the destination
observed in the trajectory dataset. The closeness to goal factor is defined by:
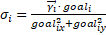
Eq. 8
This
feature is important in our model given the fact that it affects directly the steering
behavior of a pedestrian making able to a virtual pedestrian to react differently
when is close to its goal.
The last
feature that makes up our state vector is the obstacle code.
The obstacle code 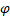 is a factor that is calculated by using eight discrete radial regions.
This kind of subdivision has been frequently used to capture the influence of
the neighborhood in data-driven approaches [Torrens2011]. Perceptual
studies have demonstrated that regions toward the intended direction have a
larger radius of influence on the trajectory of pedestrians [Lerner2007] that
fact lead us to introduce a slight difference consisting on incrementing the
radius of the section pointing toward the direction of pedestrian's motion (see
figure 7). The angle of obstruction
is a factor that is calculated by using eight discrete radial regions.
This kind of subdivision has been frequently used to capture the influence of
the neighborhood in data-driven approaches [Torrens2011]. Perceptual
studies have demonstrated that regions toward the intended direction have a
larger radius of influence on the trajectory of pedestrians [Lerner2007] that
fact lead us to introduce a slight difference consisting on incrementing the
radius of the section pointing toward the direction of pedestrian's motion (see
figure 7). The angle of obstruction 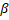 of a pedestrian
of a pedestrian 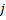 in the neighborhood of a pedestrian
in the neighborhood of a pedestrian 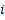 walking at a velocity
walking at a velocity 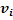 is given by:
is given by:
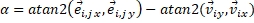
Eq. 9
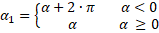
Eq. 10
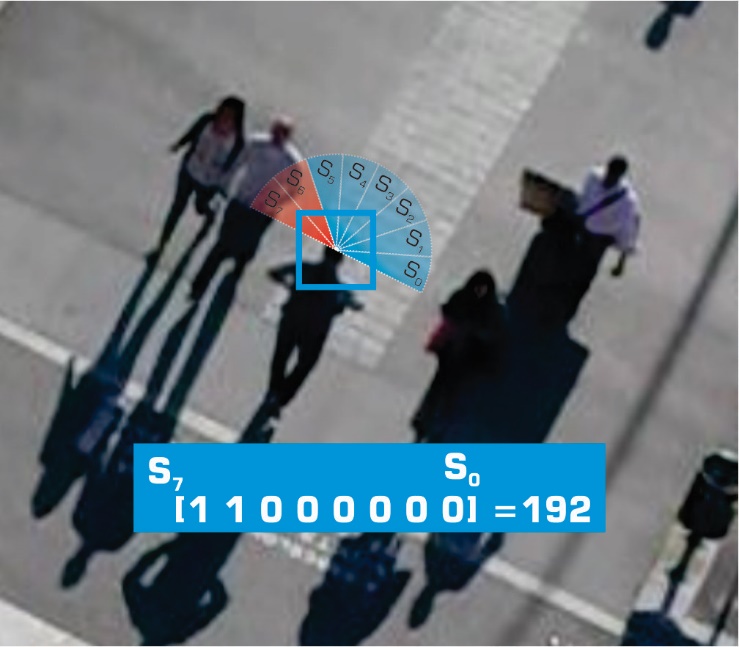
Figure 7.
The space around the agent establish the obstacle code  .
.
From the equation 9, the  vector is pointing from pedestrian
vector is pointing from pedestrian 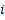 to
to 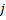 . With the angle of
obstruction
. With the angle of
obstruction 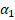 the next quadrant adjustment is performed:
the next quadrant adjustment is performed:
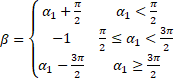
Eq. 11
Finally,
the quadrant obstructed by pedestrian 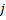 is:
is:
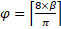
Eq. 12
The set of features 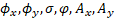 define a state vector
define a state vector 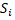 (see Eq. 13). In this case
(see Eq. 13). In this case 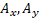 forms a 2D vector which represents the motion performed by the
pedestrian, also known as a pedestrian’s state vector. All the vectors
forms a 2D vector which represents the motion performed by the
pedestrian, also known as a pedestrian’s state vector. All the vectors 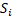 which match the same goal
which match the same goal 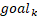 are packed in a look-up table
are packed in a look-up table 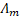 see Eq. 14.
see Eq. 14.
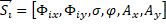
Eq. 13
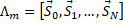
Eq. 14
Therefore
table 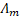 represents our knowledge-base. The input for the knowledge base will
be a state S, the system finds the closest match between the incoming
state vector inside the knowledge-base. Once we have a match, the system
returns the action vector
represents our knowledge-base. The input for the knowledge base will
be a state S, the system finds the closest match between the incoming
state vector inside the knowledge-base. Once we have a match, the system
returns the action vector 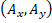 .
.
Finally, the resulting steering vector of a
pedestrian is modeled according to equation 15. The A component of the
steering force is given by the knowledge base as a function of the pedestrian
state presented in the simulation. The rest of the components are given by 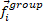 which is the last component of the Moussaïd model of group social
forces [Moussaid2010].
which is the last component of the Moussaïd model of group social
forces [Moussaid2010].
This fact allowed us to avoid demanding more
memory resources to store persistent data related to group formations in the
knowledge base. We chose the group force equation presented by Moussaïd
because reproduces faithfully the group formations in pedestrians.
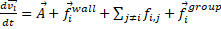
Eq. 15
For our experiments we execute the
simulation and visualization process in a workstation with these
characteristics: Intel Core i7-4820zK CPU @ 3.70GHz 8, 16Gb of RAM, GeForce GTX
TITAN Black, 2880 CUDA Cores and 6Gb of RAM.
Since our simulation engine was
developed previously, it is ready to be executed in a cluster environment.
However, for this paper, and to have a better control of the environment,
avoiding inter-node communication problems, we focus in the integration of the
urban scenarios, and present results obtained by running both client and server
in the same workstation. We execute the simulation with five, ten and seventeen
“mpi” processes. One of them manage the urban environment and do the
composition, the rest are used to simulate and render the agents. All
the client-side interaction and
scripts where developed and tested in Google Chrome for Linux.
The maximum number of agents in the
simulation is restricted to the GPU’s memory, in this workstation the limit was
80000 agents.
Each frame the simulation engine
updates the agents positions to be subsequently rendered as full characters way
by the visualization engine, as shown in Figure 8 and 9. We still have some
work to do in improving the quality of the renders in the client side without
making the latency increase. Our tests have been tried with a better-quality
render in the client’s side, but the latency generated by the texture capture
cycles, affects negatively the client’s user experience and generates a set of
artifacts in the client side because of large render cycles.
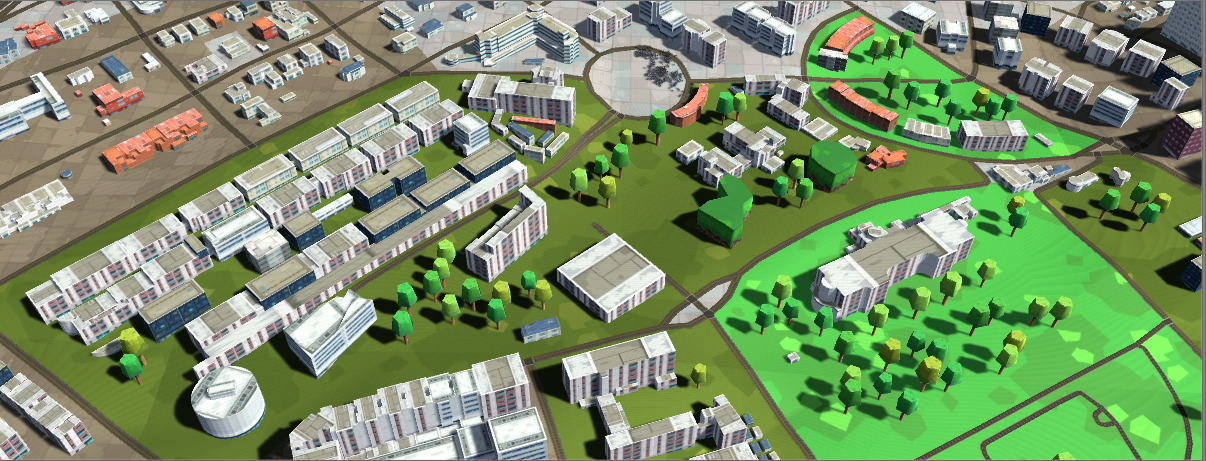
Figure 8. Visualization of the city from an aerial view.
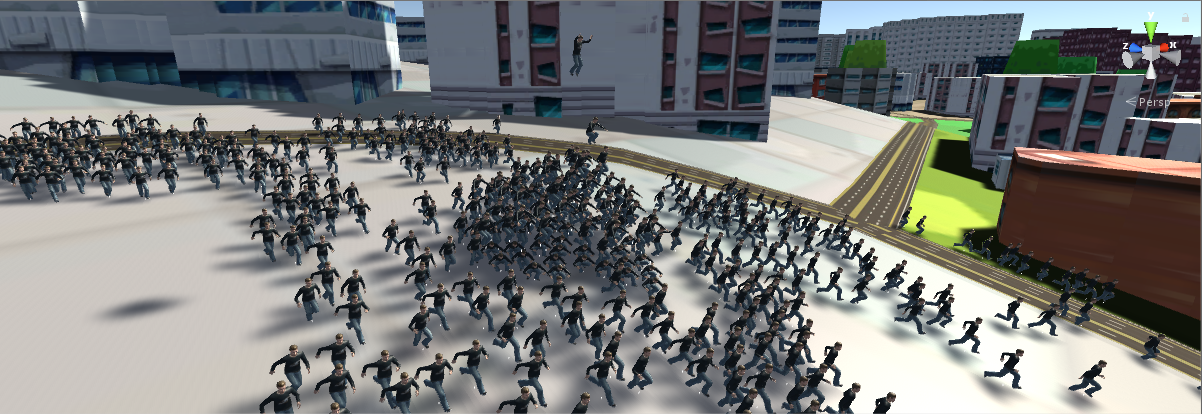

Figure 9. Final render that includes the
city and the pedestrians.
Aiming to evaluate the simulation of the
pedestrian steering motions, we employ a metric based on entropy as a measure
of the size of the predicted error.
In the scientific community, one can find
several proposals for evaluating the quality of a crowd simulation. Some of the
existing work focuses on evaluating crowds based on quantifying the extent to
which people respond realistically to virtual events and situations
[Pelechano2008]. A similar perception-like proposal is presented by Ahn et
al. [Ahn2012] who conducted a test user study in a four-screen CAVE to
compare different crowd simulations. Other proposals such as Kapadia [Kapadia2011]
use a set of metrics based on path smoothness, collisions between virtual
characters and path lengths.
Previous approaches were designed to compare
the results in synthetic environments but are not suitable to be used to
compare the similarity between a simulation and the real behavior of a
pedestrian by the other hand the entropy has proven to be applicable to data
generated with small and large number of pedestrians in sparse and dense scenes
[Guy2012].
The measure of entropy is defined as follows:
Given a state of a real scene 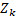 the difference between the action vector
the difference between the action vector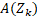 and the next state
and the next state 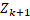 is calculated giving an entropy vector. In this case the total entropy
for a given path is calculated using equation 16. In this case, the smaller the
entropy the better the simulation.
is calculated giving an entropy vector. In this case the total entropy
for a given path is calculated using equation 16. In this case, the smaller the
entropy the better the simulation.
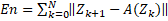 Eq. 16
Eq. 16
We ran a
test measuring the entropy for a single path followed by a pedestrian again
different simulation models: vector based, data-driven based and our hybrid
model (Fuzzy data-driven with group forces “FDDGF”), we called this test “Single
Agent Entropy” the result of this test is presented in figure 10 where the
sample size was of fifty random pedestrians walking alone.
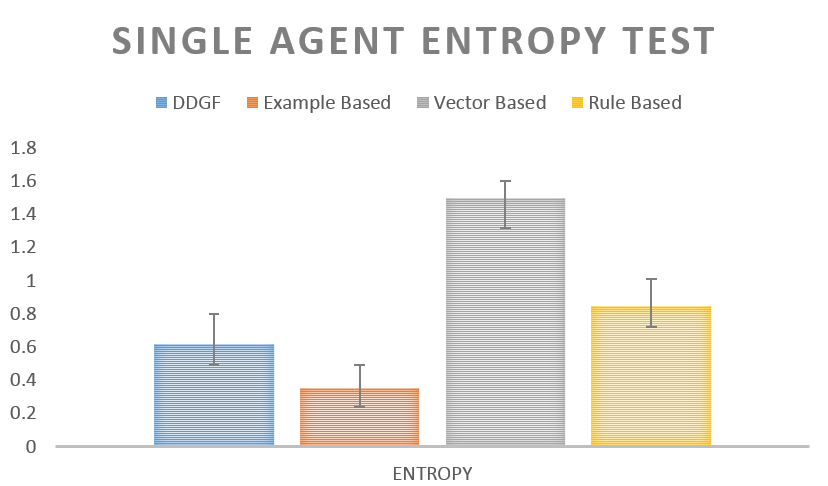
Figure 10.
Single Agent Entropy Test with 50 pedestrians.
Our system ranked in the second place (The
lower the better) just slightly above over pure data driven techniques (example
based). It is a matter of fact that Data-driven methods closely reflect the
behavior of pedestrians in real scenes, but a major drawback in this approach
is that they require large amounts of data and scaling those systems sometimes
becomes unfeasible. On the other hand, vector-based methods and rule-based
methods demand less memory but they need hard fine-tuning parameters that
govern agent behaviors, which can be a very demanding task.
The second test we ran was quite similar to
the first one but instead of having one pedestrian, the scene was composed of
many individual pedestrians not belonging to any group. These results can be
seen in Figure 11.
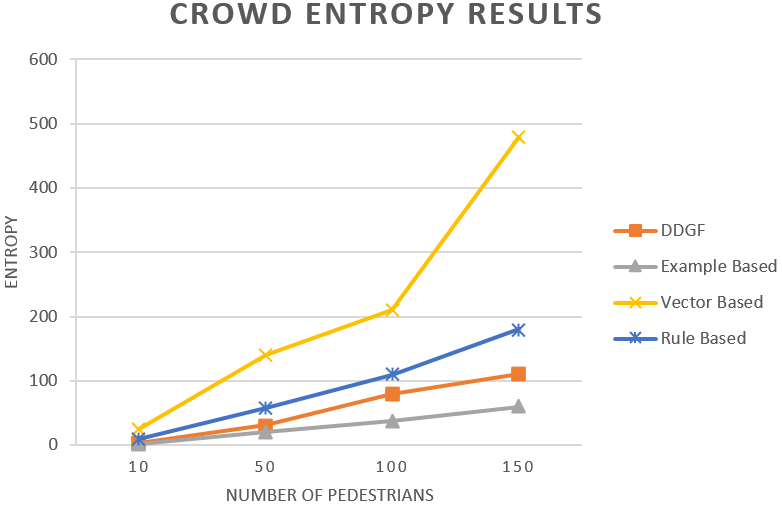
Figure 11.
Crowd Entropy Test.
In this simulation of crowds without social
group formations again the data-driven method achieves the best result
meanwhile our method reaches the second place on the low entropy measures just
slightly below the example-based method which consumes more data.
The last test done was in scenes where social
groups up to 4 people are presented. We called this test “Crowds with social
groups” (Figure 12), on this test our method achieves the best result getting close
to data-driven techniques, but also the data-driven presents the best results.
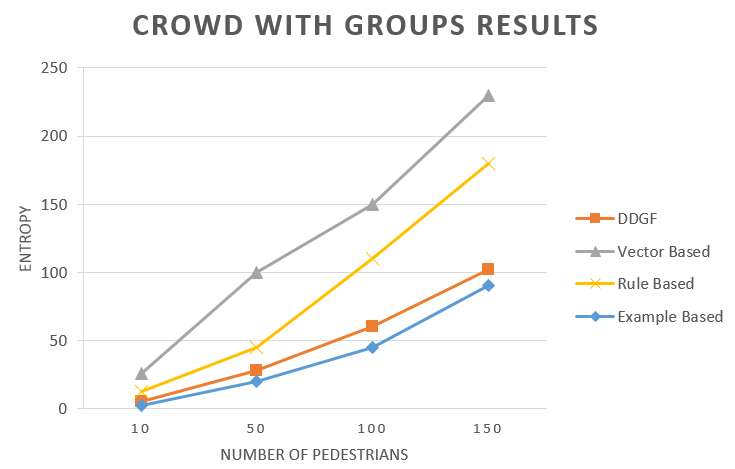
Figure
12. Crowd with Social Groups.
Our experiments show that mixing data-driven
methods with group forces allow us to achieve results comparable to those
obtained with data-driven systems but using less memory and avoiding fine
tuning parameters jobs. Figure 13 shows the comparison of our method again the
above mentioned in terms of number of parameters and memory that make our
system usable even in devices with limited memory and computational power.
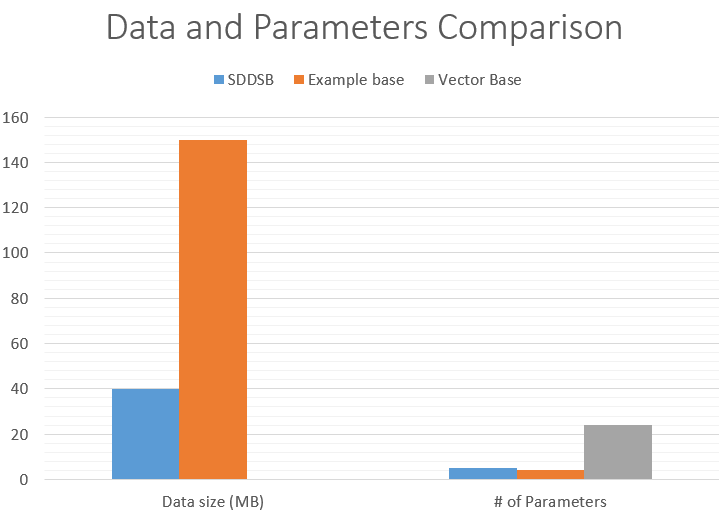
Figure
13. Data Consumption Comparison.
The simulation generated by our
method produces a steering behavior learned from real videos, resulting in
similar trajectories to those observed in real pedestrian steering. Our
Data-Driven technique allow us to get plausible results since the system
captures some of natural movements presented in real scenes
Crowd simulation is a field that is
constantly challenging and testing graphics hardware since most of the times
the available resources are not enough to simulate a crowd without any
optimization technique, such as LOD or compositing. This field demands a lot of
computational power and resources, so an efficient way to assign memory and
processing power is mandatory to achieve the desired results. Applications for
virtual city generation range from research and
educational purposes such as urban
planning and creation of virtual environments for simulation. Movie and game
industries have a high demand for quick creation of complex environments in
their applications, since they are in constant need for more art assets that
form virtual worlds to support interaction, training, evaluation, virtual sets,
and other uses. Security, crisis management and virtual training can take
advantage of this environments as well. In the present work we described a
workflow able to visualize and simulate 80000 agents per frame inside an urban
environment, we incorporate steering behavior to each pedestrian, and GPS
information to manage the flow of people inside the urban environment. The
future steps will consist in add realism to the buildings rendering.
Special thanks to SECTEI in Mexico for
providing part of the founding for the present research, also we must express
our gratitude for all the team that conforms the Barcelona Super Computing
Center for facilitate the equipment and the infrastructure for the project.
[Ahn2012] AHN, J;
WANG, N; THALMANN, D; ANDBOULIC, R. 2012. Within Crowd Immersive Evaluation of
Collision Avoidance Behaviors. Vrcai, 231–238.
[Boatright2013]
Boatright, C.D; Kapadia, M; Shapira, J.M; Badler, N.I.: Context-sensitive data
driven crowd simulation. Proceedings of the 12th ACM SIGGRAPH International
Conference on Virtual-Reality Continuum and Its Applications in Industry -
VRCAI ’13 pp. 51-56 (2013), http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=2534329.2534332
[Charalambous2014] CHARALAMBOUS, P; AND CHRYSANTHOU, Y. 2014. The PAG Crowd: A Graph
Based Approach for Efficient Data Driven Crowd Simulation. Computer Graphics
Forum 33, 0, 95–108.
[Dai2013] DAI, J.,
LI, X; ANDLIU, L. 2013. Simulation of pedestrian counter flow through
bottlenecks by using an agent-based model. Physical A: Statistical Mechanics
and its Applications 392, 9(May), 2202–2211.
[Essen2008] Van
Essen, R.: Maps Get Real: Digital Maps evolving from mathematical line
graphs to virtual reality models, pp. 3-18.
Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg (2008)
[Guy2012] GUY, S.
J; VAN DENBERG, J; LIU, W; LAU, R; LIN, M. C; AND MANOCHA, D.
2012. A statistical similarity measure for aggregate crowd dynamics. ACM
Transactions on Graphics 31,6, 1.
[Helbing1995]
HELBING, D; ANDMOLNÁR, P. 1995. Social force model for pedestrian
dynamics. Physical Review E 51, 5 (May), 4282–4286.
[Kapadia2011] KAPADIA, M; WANG, M; SINGH, S; REINMAN, G; ANDFALOUTSOS, P. 2011.
Scenario Space: Characterizing Coverage, Quality, and Failure of Steering
Algorithms. ACMSIGGRAPH / Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation (SCA) 1,
53–62
[Lakoba2005] LAKOBA, T. I. 2005. Modifications of the
Helbing-Molnar-Farkas-Vicsek Social Force Model for Pedestrian Evolution
Simulation 81, 5 (May), 339–352.
[Lee2007] LEE, K;
CHOI, M; HONG, Q; ANDLEE, J. 2007. Group behavior from video: a data-driven
approach to crowd simulation. In Proceedings of the 2007 ACM, 109–118.
[Lerner2007] LERNER,
A., CHRYSANTHOU, Y, AND LISCHINSKI, D. 2007.Crowds by Example. Computer
Graphics Forum 26, 655–664.
[Loviscach1006]
Loviscach, J.: Deformations: Wrinkling coarse meshes on the GPU 25(3), 467-476
(Sep 2006)
[Moussaid2010] MOUSSAÏD,
M., PEROZO, N; GARNIER, S; HELBING, D; AND THERAULAZ, G. 2010. The walking
behaviour of pedestrian social groups and its impact on crowd dynamics.PloS one
5, 4(Jan.), e10047.
[Navarro2011]
Navarro L., Flacher F., Corruble V.: Dynamic level of detail for large scale
agent-based urban simulations. In The 10th International Conference on
Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems - Volume 2 (Richland, SC, 2011), AAMAS
'11, International Foundation for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, pp.
701-708. URL:
http://0-dl.acm.org.millenium.itesm.mx/citation.cfm?id=2031678.2031717.
[Pelechano2008] PELECHANO,
N., ANDSTOCKER, C. 2008. Being a part of the crowd: towards validating VR
crowds using presence. Proceedings of the 7th international joint conference on
Autonomous agents and multiagent systems, Aamas, 12–16.
[Pettre2009]
PETTRÉ, J; ONDREJ, J; OLIVIER, A.-H; CRETUAL, A; ANDDONIKIAN, S. 2009.
Experiment-based modeling, simulation and validation of interactions between
virtual walkers. Proceedings of the 2009 ACM SIGGRAPH / Eurographics Symposium
on Computer Animation 2009, 189.
[Reynolds1987] REYNOLDS,
C. W. 1987. Flocks, herds and schools: A distributed behavioral model.ACM
SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics 21, 4(Aug.), 25–34.
[Schreiber2009] SCHREIBER,
D; ANDRAUTER, M.2009.GPU-based non-parametric background subtraction for a
practical surveillance system.2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on
Computer Vision Workshops, ICCV Workshops (Sept.), 870–877.
[Shinohara2011] SHINOHARA,
K.; AND GEORGESCU, S. 2011. Modelling Adopter Behavior Based on the Navier
Stokes Equation. ISRN Mathematical Analysis 2011, 1–10.
[Silverira2006] Da
Silveira, L.G., Musse, S.R.: Real-time generation of populated virtual cities.
In: Proceedings of the ACM Symposium on
Virtual Reality Software and Technology.
pp. 155-164.
VRST ’06, ACM, New York, NY, USA (2006), http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/1180495.1180527.
[Sullivan2002]
O’Sullivan C., Cassell J., Vilhjalmsson H., Dingliana J., Dobbyn S., McNamee
B., Peters C., Giang T.: Levels of detail for crowds and groups. Computer
Graphics Forum 21, 4 (2002), 733{741. URL:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1467-8659.00631, doi: 10.1111/1467-8659.00631.
[Sun2011] SUN, L;
ANDQIN, W. 2011. A Data-Driven Approach for Simulating Pedestrian Collision
Avoidance in Crossroads.2011 Workshop on Digital Media and Digital Content
Management (May),83–85.
[Thalmann2009] Thalmann,
D; Grillon, H; Maim, J; Yersin, B.: Challenges in Crowd Simulation. 2009
International Conference on Cyber Worlds pp. 1-12 (2009), http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=5279720
[Thomsen2008]
Thomsen, A., Breunig, M., Butwilowski, E., Broscheit, B.: Modelling and
Managing Topology in 3D Geoinformation Systems, pp. 229{246. Springer Berlin
Heidelberg,
Berlin, Heidelberg (2008)
[Torrens2011] TORRENS,
P; LI, X; AND GRIFFIN, W.A. 2011. Building Agent-Based Walking Models by
Machine-Learning on Diverse Databases of Space-Time Trajectory
Samples.Transactions inGIS 15, 67–94.