DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM FOR STAFF ASSESSMENT
N.I. Ishchenko, G.G. Rekhina
National Research Nuclear University MEPhI (Moscow Engineering Physics Institute), Russian Federation
NIIshchenko@mephi.ru, GGRekhina@mephi.ru
Contents
3.1. Block of monitoring of personnel conditions and reserve training
3.2. Block of analysis and visualization of HR audit results
Annotation
The article covers the experience of using, processing and visualization Assessment center (AC) methodology results and evaluation of candidates’ potential and abilities for key position staff reserve.
Program system «Reserve» provides users amount of data and charts including:
· candidates’ personal information;
· the result evaluation based on AC methodology;
· results of psychophysiological tests.
Keywords: human resources, methodology of Assessment center (AC), psychophysiological testing, results visualization, program system «Reserve».
1. Introduction
In 2015 “Scientific visualization” magazine published an article devoted to the application of the Assessment center-method for evaluation and selection of candidates to substitute the key positions in the organizations of State Corporation “Rosatom”.
At the present time, the AC-method has come into wide application for personnel management practices in domestic organizations. A number of questions and proposals were addressed to the article’s authors. They were related to computer processing of the test procedures data, quantitative and qualitative measures and means of their visualization for analysis and common usage for personnel decision-making support.
The development of the program system for the AC-method support and visualization of the intermediary and conclusive results is in close connection with the method of construction of psychophysiological research test procedures, as well as with the set of formalized models aimed at processing of expert assessments of candidates’ behavior in situations that simulate real management activity.
In this article the authors set forth the experience in development and application of the program system for visualizing tests results conducted as a part of HR audit of candidates selected to the human resources for substitution of key positions in a particular organization of nuclear industry. Evaluation of employees was conducted on the basis of competency models that were designed in compliance with the AC-methods and their psychophysiological examination.
2. Conducting of HR audit to assess candidates to the human resources for key positions of an industrial organization
Work on the evaluation of candidates to the human resources for substitution of key positions in an organization was aimed at the following results:
· comprehensive personnel evaluation based on competency models;
· determination of «development zones» of an employee;
· assessment of skills and abilities to carry out management functions and to adapt to new requirements of their activities;
· assessment of psychophysiological characteristics of candidates, reaction speed, stamina, agility of neural processes, memory and attention characteristics, activity rate of learning the external world;
· planning of employee career and development of opportunities for professional growth in conformity with professional requirements.
For development of competency models it was necessary to:
· define requirements for activity of candidates to the human resources;
· define major conceptual functions of key positions, describe criteria and compare them with the requirements for the activity in a particular organization;
· analyze and select information for development of competency models for different groups of positions;
· conduct computer testing of medical, psychological and psychophysiological characteristics of candidates, make their individual psychological profiles;
· conduct comprehensive assessment of candidates and make recommendations on possibilities and growth directions.
In order to obtain the primary information at the preliminary stage the questionnaires for experts, managers and candidates to the human resources for the purpose of learning their views about management activity were devised. The processing of this information allowed to conduct the content analysis (analysis of information contained in the questionnaires) in order to identify the most significant factors, which were grouped pursuant to their similarity and identity, and in the end to determine diPSrepancies (‘gaps’) in views on management activity [3].
As a result of this work, the grouped criteria descriptions of managers and candidates to the human resources were related with particular functions (requirements to activities), as well as the competency list related to a particular key position (competency profile) was derived.
In keeping with organizational chart and positions for which the reserve will be formed as well as the results of the tests, the group of candidates was divided into three levels.
General characteristics of the level of expertise can be presented as follows:
· first level candidates demonstrate competencies in passive form in response to the established rules; the psychophysiological indicators are low.
· second level candidates fully demonstrate their competencies, they are active and successful n basic business situations; the psychophysiological indicators are average.
· third (the highest) level candidates are candidates with well-defined competencies, and they succeed in the majority of situations; the psychophysiological indicators are rather high.
Thus, the following results were obtained at this stage:
· requirements to the positions and management activity were defined;
· the management and professional activity criteria were described;
· the parameters of management competencies differentiated with respect to the levels of expertise for candidate to the human resources on key positions in an organization were defined.
3. Automated decision support system for evaluation and selection human resources to substitute the key positions in an organization
The program system “Reserve” (PS “Reserve”) was specially designed in conformity with the tasks of HR audit of candidates to the human resources for substitution of key positions in industrial organization management. It enables to perform the task of record and visualization of personnel information and information that was obtained during the audit in an industrial organization. The system consists of two blocks:
· block of monitoring of personnel conditions and reserve training;
· block of analysis and visualization of HR audit results.
3.1. Block of monitoring of personnel conditions and reserve training
The block of monitoring of personnel conditions and reserve training in PS “Reserve” enables to enter and process personnel information of candidates for the human resources for substitution of key positions of an industrial organization. The information contained in this block comprises employees’ personal data that is formally in compliance with conditions to be added to the list of candidates: last, first and middle names, identification code of a candidate, “Report – personal information”, “Personal cards”, education, consistency of the specialty with the job profile, the breadth of special knowledge that the candidate possessed, age, additional training and retraining courses.
The block provides a user with following opportunities:
· input and correction of personal information of an employee that is included in the human resources for key positions;
· input of employee’s assessments conducted on the basis of developed competency models, and also indicators of the psychophysiological examination;
· keeping an archive of employees’ assessments over years;
· preparation of human resource reporting such as “Report – personal information”, “Personal card”, etc. based on the personnel data input into the database of PS “Reserve” with the text output in Word format documents;
· preparation of optional reports and statistics on the whole database using a random-query generator;
· storage and recovery of personnel data on the magnetic media (flash, floppy disk, any folder on a PC) for backup;
· use of PS “Reserve” in the network for several users that enter/correct information simultaneously.
The random-query generator included into this block allows to define conditions for searching groups of candidates to the human resources in conformity with various criteria: age, education, work experience, level of expertise, etc. and also with any competence indicator and psychophysiological factors. Depends on users’ needs, Query results can be output in Word or Excel format tables.
3.2. Block of analysis and visualization of HR audit results
This block of the information system enables to conduct review and analysis of data that was produced as the result of testing of the candidates and to visualize assessments of personnel data (various diagrams) that contain both individual and group data.
A user can apply the following tools:
· generator of diagrams of competency formedness ratio for three levels of the human resources qualification;
· generator of diagrams of psychophysiological factors for three levels of the human resources qualification;
· generator of individual diagrams of competency formedness and psychophysiological factors for particular candidates;
· generator of statistical diagrams of various personnel information statistics and HR audit results of an organization on the basis of the random-query generator.
The results of the listed above tools are visualized in Excel format tables which can be saved and analyzed in a comprehensive way.
Below we provide examples of some diagrams.
The diagram (Figure 1) allows a person, who makes a decision on division of the human resources in compliance with the levels of expertise, visually to see the results of two types of the testing of candidates and assign them to a particular group of expertise.
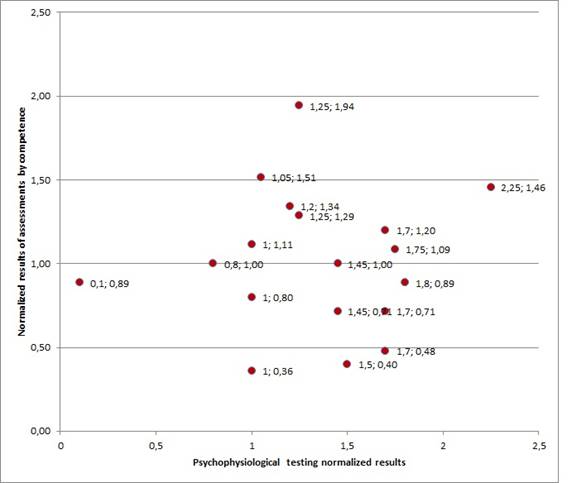
Fig. 1. Diagram that shows the decision-making field on division of the human resources by levels of expertise.
Along the axes of coordinates on the diagram (Figure 1) the scales (from 0 to 2,5) of normalized results of candidate assessments are marked off after passing of two types of tests.
Each point on the decision-making field represents a particular candidate’s normalized assessment’s result by competence as well as his or her normalized result of the psychophysiological testing.
When the cursor is over a particular point of the diagram the data of the probationer (last, first and middle name, position, etc.) in the database of PS “Reserve” appears.
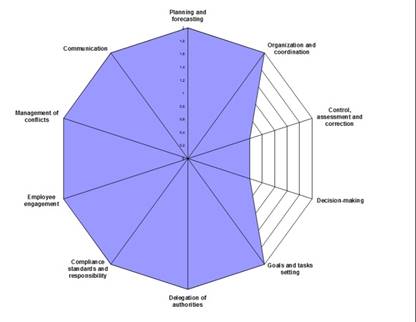
Group characteristics of the development of the candidate’s competence by level of expertise are demonstrated by the radar chart (Figure 2).
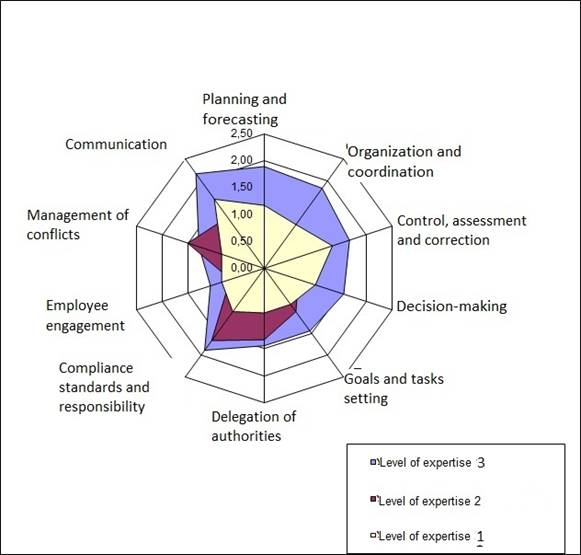
Fig. 2. Diagram of comparative competency development of candidates that belong to different levels of expertise.
Numeric parameters on the diagram correspond to the average value of the candidate’s development assessment of a particular level of expertise, these values are within the interval from 0 to 2,5.
Diagrams of such type in the practice of personnel management are used for training groups and programs development for candidates to the human resources.
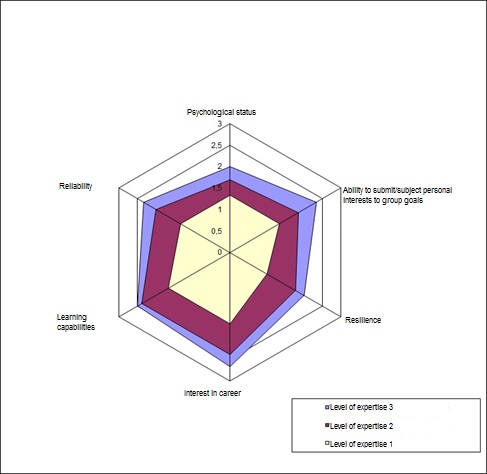
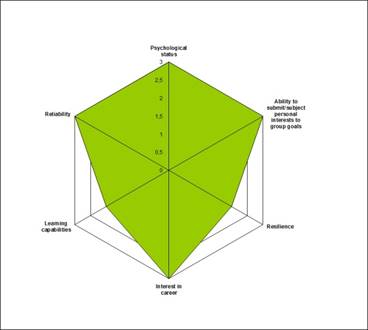
Fig. 3. Diagram of psychophysiological testing results of candidates that belong to different level of expertise of the human resources.
In Figure 3 the comparative radar diagram of psychophysiological testing results of candidates that belong to different levels of the staff management is demonstrated.
Along the axes the average values of psychophysiological indicators of candidates that belong to a particular level of expertise are plotted, these values are within the interval from 0 to 3.
|
|
|
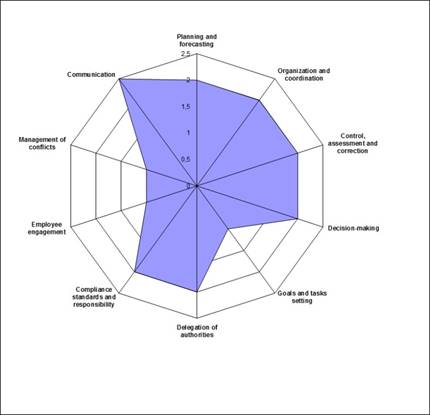
Fig. 4. Example of individual diagrams of candidates that have passed the assessment of the level of development of managerial competencies.
Individual radar diagrams of candidates that have passed assessment of managerial competence development level are demonstrated in Figure 4. Along the axes the values of development level assessments of a candidate pursuant to the AC methodology are marked off.
|
|
|
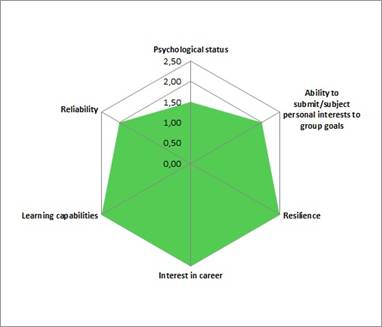
Fig. 5. Diagrams of candidates that have passed psychophysiological examination.
In Figure 5 individual radar diagrams of candidates who have passed psychophysiological examination are demonstrated. Along the axes the psychophysiological testing results of a candidate are marked off.
As shown in Figures 4 and 5 candidates have significantly different indicators for a number of qualities.
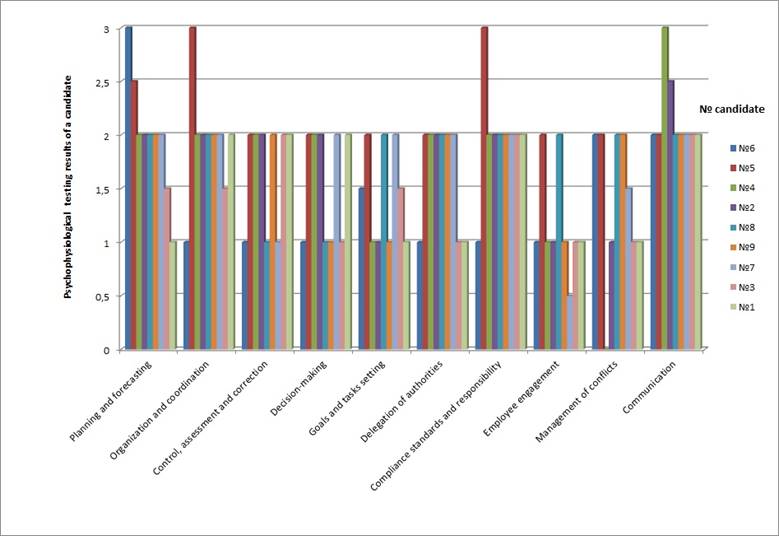
Fig. 6. Diagram of the level of competency development ratio of candidates that belong to the highest level of the human resources.
The diagram (Figure 6) of level of competency development ratio of candidates that belong to the highest level of the human resources expertise allows to reveal the need for development of certain competencies in particular candidates, prepare individual programs for the candidate’s development and devise individual and group training programs that include trainings for the development of poorly resolved competencies.
In the right part of the diagram there are candidates’ identification codes that correspond to a particular employee included in this level of expertise.
As a result of the computer processing of the AC results an organization earns the chance to form training groups for the human resources purposefully, taking into account individual characteristics of candidates.
As an example there is a set of trainings for managerial competencies development:
· planning, arrangement, management, control and coordination, responsibility;
· creation and management of efficient team and resolution of disputes;
· time management;
· communication;
· holding meetings and business talks, and skills of public speech (speech-craft);
· skills of a successful leader;
· project team management;
· decision-making;
· change management;
· leadership;
· delegation of authorities.
Secondary testing with results processing using PS “Reserve” will enable to compare levels of expertise of particular employees included to the human resources before and after conducting one or many series of classes.
4. Conclusion
The use of visualization tools for assessment of professional and psychological traits of a candidate to the human resources and comparative analysis of such assessment with competency models designed especially for a particular position, as experience confirms, allows a decision-maker executive to speed up the decision making process. Moreover, it is necessary to note that the decision becomes more objective and reasonable.
It is connected with the fact that social objects, as a rule, are marked by a large enough amount of characteristics that form multidimensional vectors. The correlational study tasks between components of the vector characteristics assume an essential significance here. Moreover, it is necessary to define these correlations on the basis of a limited number of multivariate observations.
It is worth noting that the software implementation of the human resources evaluation using the methodology of Assessment center and psychophysiological testing significantly increases the application efficiency of these concepts.
PS “Reserve” expands the opportunities of the AC-method and psychophysiological testing that enables to compare their evaluations, obtain various informational ‘assessments’ in the tabular and visualized form.
Diagrams of various types generated by PS “Reserve” allow to study both group and individual employment information.
PS “Reserve” enables to set a number of selection conditions out of the whole informational array and analyze them simultaneously. That increases efficiency and reasonableness of making personnel decisions.
References
1. Ishchenko N.I., Rekhina G.G. Visualization of talant pool evaluation results for key positions promotion. Scientific visualizing. 2015. Vol. 7. No. 1. Pp. 96-107.
2. Ballantyne I., Powa N. Assessment-centr. Polnoe rukovodstvo. [Assessment center. Full guidance] (2nd edition). Moscow: Publisher GIPPO, 2008.
3. Kibanov A., Kashtanova E. Upravlenie delovoj kar'eroj, sluzhebno-professional'nym prodvizheniem i kadrovym rezervom. Uchebno-prakticheskoe posobie [Business career, official and professional promotion and human resources management. Training manual]. State University of Management. Moscow: Publisher Prospect. 2013.
4. Ishchenko N.I. Voprosy organizacii sistemnyh issledovanij kadrovogo potenciala jaderno-jenergeticheskogo kompleksa [Issues on organization of personnel potential system research of nuclear energy complex]. Open education. 2013. No. 1.
5. http://www.buPSon.ru/aboutus/article0060.php
6. http://www.hr-portal.ru/tags/assessment-centr